Genetic Traits
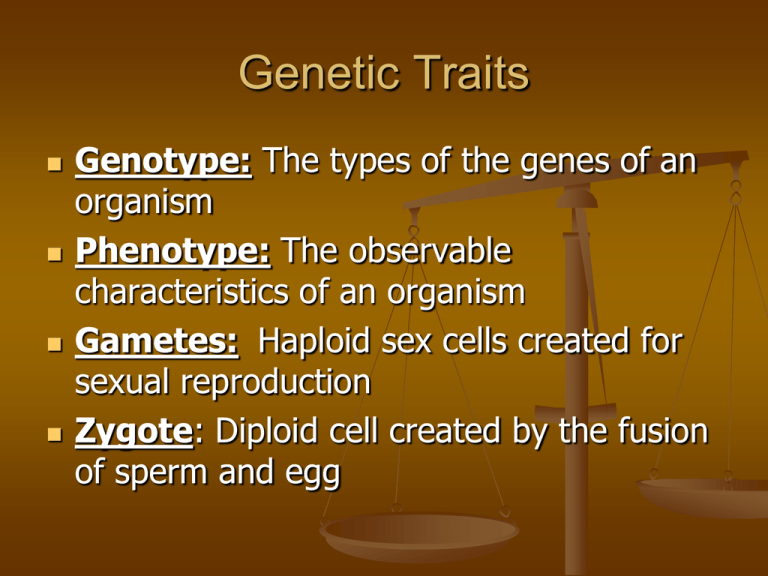
Genotype: The types of the genes of an
organism
Phenotype: The observable
characteristics of an organism
Gametes: Haploid sex cells created for
sexual reproduction
Zygote: Diploid cell created by the fusion
of sperm and egg
Genetic Traits and Vocab
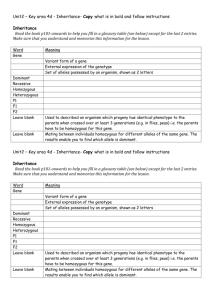
Dominant Gene: A gene that can be
expressed in the homozygous (2 copies)
or heterozygous condition (1 copy of
each).
Recessive Gene: A gene that is only
expressed in the homozygous (two copies)
condition. This gene can be masked by
the dominant gene.
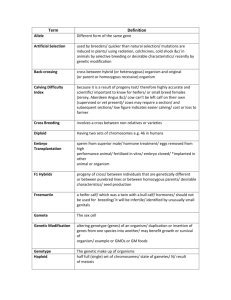
Allele: Version of a gene (may be dominant or
recessive)
Homozygous: The state of having two identical
alleles of a particular gene (eg AA, aa).
Hybrid/Heterozygous: The state of having
two different alleles of a particular gene (eg Aa)
Mendelian Genetics:
Gregor Johann Mendel (1822-1884)
Augustinian monk, Czech Republic.
Foundation of modern genetics.
Studied segregation of traits in the garden
pea (Pisum sativum) beginning in 1854.
Published his theory of inheritance in 1865.
Mendel was “rediscovered” in 1902.
Some basic terminology:
Generations:
P = parental generation
F1 = 1st filial generation, progeny (offspring) of the P
generation
F2 = 2nd filial generation, progeny of the F1 generation (F3 and
so on)
Crosses:
Monohybrid cross = cross of two different true-breeding strains
(homozygotes) that differ in a single trait.
*Genetics etiquette - female conventionally is written first
Simple Dominance Examples:
Fig. 10.4, Mendel’s 7 garden pea characters.
(W)Widows Peak vs. Straight (w)
(E)Wet ear wax vs. Dry ear wax (e)
(F)Free Earlobe vs. Attached (f)
Six-digits (F)
Cleft chin (C)
Tongue Roll (T)
Hitchhiker’s Thumb (H)
Hand and Arm Crossing
Left hand clasped over right is dominant
Right arm folded over left is dominant
PTC
People who have the ability to taste PTC
are dominant to people who cannot
What is the benefit for having certain
taste?
About 40 percent of people cannot taste/smell
cyanide.