David E. Karas MD
Connecticut Pediatric Otolaryngology
Yale New Haven Children’s Hospital
Yale School of Medicine
Speaker’s Bureau for Alcon
Major
Significant functional or cosmetic impact
Heart defect, abnormal brain formation, cleft lip/palate
Minor
No major functional or cosmetic impact
Environmental (Teratogenic)
Alcohol exposure
Chromosomal
Single gene
Multiple gene
Sequence
Syndrome
Multiple defects from a single malformation
Pierre Robin
All components are pathologically related
Trisomy 21 or Fetal Alcohol
Association
Occur together more frequently
VATER/VACTERL
CHARGE
Branchial cleft sinuses
Hearing Loss
Renal Dysplasia (12-20%)
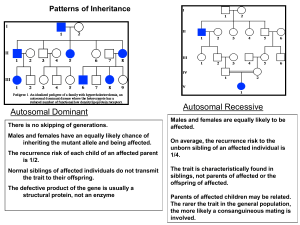
Autosomal Dominant
Sensorineural but may be mixed
1 in 40,000 Births
Variable penetrance
Associatied with 8q
Facial Palsy/Lacrimal duct
Autosomal Dominant
1 in 50,000 births
5q
Abnormal structures of 1st and 2nd Branchial
arches, grooves and pouch.
Small, absent, or low set ears
Micrognathia
Cleft Palate (35%)
Normal Intelligence
Malar Hypoplasia
Down-slanting palpebral fissures
Absence of lower eyelashes
Atretic External Auditory Canals
Conductive Hearing Loss
Normal cognition and development
Localization to 9q
Limb abnormalities, particularly
absent thumbs
High Arched/Cleft palate
Broad nasal root
Cognitive impairment
Cardiac anomalies
Velopharyngeal Insufficiency (VPI)
Immunologic deficiencies
22q11 deficiency, Autosomal Dominant
Feeding difficulties
Hypocalcemia
Trisomy 21
Stenotic ear canals/Low set ears
COME/Eustachian tube dysfunction
Middle ear anomalies
Delayed Speech
Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Macroglossia
Narrowed subglottis/trachea
Cardiac defects
Lysosomal Storage Disease
7 distinct types
Hurlers, Hunters, Sanfillipo
Morquio, Maroteaux-Lamy
Coarse facial features
AIRWAY ISSUES!!!!!
Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Enzyme Replacement for
types I,II, and VI
Coloboma
Heart Anomalies
Atresiae Chonae
Retardation
Genital Anomalies
Ear Anomalies
~60% defect of CHD7 gene(chromosome 8)
Vertebral Anomalies
Anal
Cardiac defects
Tracheo-esophageal Fistula
Renal/Radial anomalies
Limb defects
No specific genetic pattern or inheritance
Incidence 16/100,000
Midface Hypoplasia
Cleft palate (Pierre Robin)
Depressed Nasal Bridge
Hearing Loss (15%)
Dental Anomalies
Mitral Valve Prolapse
Genetic Sequencing is available
Joint dysplasia/
hyperextensibilty
Immotile Cilia
Situs Inversus
Sinusitis
Bronchitis/bronchiectasis
Otitis Media
Autosomal Recessive
Genetically heterogenous
Crouzon’s
Apert’s
Bicoronal synostosis, midface hypoplasia, orbital
hypertelorism, polydactyly
Saethre-Chotzen
Midface hypoplasia, coronal suture synostosis
Bilateral coronal synostosis , variable midface
hypoplasia, low set hairline , cleft palate
Pfeiffer
Multiple types with synostosis
and most with limb abnormalities
More prevalent than you think
Look for abnormalities minor malformations
may indicate that major ones may also exist
More than one family member may be affected
Identification should not be underestimated
Better care
Better counseling
Better Surveillance