OCR 21st Century Science
Unit B4a Revision
Animal and Plant cells
Respiration and Photosynthesis
Animal and Plant Cells
mitochondria contain enzymes
for the reactions in aerobic
respiration (in animals, plants
and yeast)
cell membrane allows gases
and water to pass in and out
of the cell freely while
presenting a barrier to other
chemicals
nucleus or circular DNA in
bacteria contains DNA which
carries the genetic code for
making enzymes used in the
chemical reactions of
respiration
cytoplasm where enzymes and
proteins are made
chloroplasts contain
chlorophyll and the enzymes
for the reactions in
photosynthesis
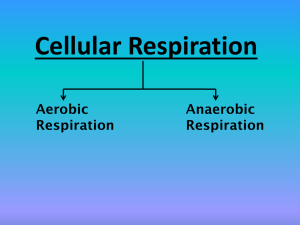
Respiration
Uses for respiration summary
Animals and plants have many uses for the energy they
generate from respiration:
1)To perform the life processes, such as moving, _____ etc
2)To build up body _______
3)To maintain a constant body ___________ (warm-blooded
mammals only)
4)To build up sugars, ________ and other nutrients in plants
5)Active __________
Words – nitrates, tissue, proteins, transport, growing
Synthesis
“Synthesis” means “making large molecules out of small ones”. Two examples:
1) Glucose (sugar) can be used to make long chains of insoluble starch…
Glucose
molecules
Starch
molecule
2) Glucose can be combined with nitrates to make proteins (for growth)…
Glucose
molecules
Proteins
Aerobic Respiration
• all living things depend on
chemical reactions within cells
that require energy released
by respiration
• Respiration is a series of
chemical reactions that
release energy by breaking
down large food molecules in all
living cells
glucose + oxygen
carbon dioxide + water
(+ energy released)
C6H12O6 + 6O2
6CO2 + 6H2O
Aerobic respiration summary
All living organisms have to move, _____, reproduce etc. Each of these
life processes needs ENERGY. ___________ is the process our bodies
use to produce this energy:
Glucose + oxygen
water + carbon dioxide + ENERGY
The glucose we need comes from ______ and the oxygen from
_________. Water and carbon dioxide are breathed out. The MAIN
product of this equation is _________. Respiration happens in
_________ in cells.
Words – breathing, energy, grow, respiration, food, mitochondria
Anaerobic Respiration
anaerobic respiration takes
place in animal, plant and
some microbial cells in
conditions of low oxygen or
absence of oxygen, to
include:
In Animal Cells:
glucose lactic acid (+
energy released)
In Yeast
glucose ethanol +
carbon dioxide (+ energy
released)
Happens in
roots in waterlogged soil
bacteria in puncture wounds
human cells during vigorous exercise
Anaerobic respiration summary
Unlike aerobic respiration, anaerobic respiration is when energy is
provided WITHOUT needing _________:
Glucose
lactic acid + a bit of energy
This happens when the body can’t provide oxygen quick enough for
__________ respiration to take place.
Anaerobic respiration produces energy much _______ than aerobic
respiration but only produces 1/20th as much.
Anaerobic respiration can also take place in other low-oxygen conditions,
such as plant roots in _________ soil or bacteria in ________ wounds.
Words – oxygen, aerobic, quicker, puncture, waterlogged
Respiration in cells
1) Cytoplasm where enzymes are
made
2) Nucleus – carries
genetic info for
making enzymes
3) Cell Membrane –
controls what comes in
and out
4) Mitochondria –
contain enzymes for
respiration reactions
In bacteria cells, this job
is done by circular DNA
OCR 21st Century Science
Unit B4b Revision
Enzymes, Osmosis and Diffusion
Enzymes in respiration and photosynthesis
Enzymes are proteins that speed up chemical uses. Here are two important
natural uses for them:
Cells use glucose to generate energy – this
process is called “respiration”.
Respiration happens in mitochodria and is
catalysed by enzymes.
Photosynthesis is
catalysed by
enzymes in the cells.
Enzymes- The lock and Key
Model
• enzymes are proteins that speed up
chemical reactions
• cells make enzymes according to the
instructions carried in genes
• molecules have to be the correct shape
to fit into the active site of the enzyme
(the lock and key model)
Enzyme
Substrate
Factors affecting enzyme action (Denaturing)
heat
pH
normal
denatured
• The shape of the enzyme is vital to its function.
• The main factors affecting enzyme action are 1.) temperature and 2.) pH
1.) High temperatures can destroy the enzymes ‘special shape’ so it becomes denatured.
2.) Different enzymes work best at different pH values.
Optimum conditions
Enzymes work best in certain conditions:
Enzymes are
denatured
beyond 40OC
Enzyme
activity
400C
Temp
Could be
protease (found
in the stomach)
pH
Could be amylase
(found in the
intestine)
pH
Enzymes are used in industry to bring about reactions at normal temperatures
and pressures that would otherwise be expensive. However, most enzymes
are denatured at high temperatures and can be costly to produce.
Diffusion and concentration gradients
high
low
concentration
concentration
• Diffusion is the spreading of the particles of a gas, or of any
substance in solution.
• This results in a net movement from a region where they are of
a higher concentration to a region of lower concentration
•The greater the difference in concentration, the faster the
rate of diffusion.
Diffusion Summary
Diffusion is when particles spread from an area of high
concentration to an area of ___ concentration. The
particles move along a “concentration _____” and this
process takes no _____ (it’s a “passive” process”). Diffusion
can be accelerated by increasing the _______ of the
particles, which makes them move _______.
Words – faster, low, gradient, temperature, energy
Osmosis
Osmosis
Osmosis summary
Osmosis is a “special kind of ___________”. It’s when water diffuses
from a __________ area to a less concentrated area through a partially
permeable _________ (i.e. one that allows water to move through but not
anything else):
In this example the water molecules will move from left to right (along
the concentration ______) and gradually _____ the sugar solution. Plants
use osmosis to take in water through their roots.
Words – membrane, concentrated, dilute,
diffusion, gradient
Water
Potato cells
Which way does movement take
place?
Strong sugar
solution
Medium
sugar
solution
Weak sugar
solution
Active transport
Active transport summary
Outside cell
Inside cell
Cell membrane
In diffusion substances moved along a
concentration gradient. In active transport,
substances move against this gradient:
This process takes ______ and this comes
from ___________. It enables cells to take
in substances even though there are in very
small __________. Root hair cells take in
______ using active transport.
Words – concentration, energy, respiration,
nutrients
OCR 21st Century Science
Unit B5a Revision
Animal & Plant cells and Stem cells
Specialisation of animal cells
During the
development of a
multi-celled organism
cells differentiate to
form specialised cells:
Ciliated
epithelial cell
White blood cell
Nerve cell
(neurone)
Egg cell (ovum)
1. Guard cell – can open
and close to control exchange
of gases
and water loss
4. Egg cell
(ovum) – large
– maximum
exposure for
sperm, has a
large food
store
7. Neurone –
long like wires
to carry
messages
around the
body
2. Sperm cell – long tail
providing movement s it can
swim to and fertilise egg.
Nucleus contains genetic
material
3. Red blood cell –
concave disc shape increases area to carry
more oxygen
6. White blood
cell – can change
shape to digest
microbes
5. Root hair cell – large surface area to absorb water and
minerals. Thin cell wall so minerals can pass through easily.
Positioned close to xylem tissue.
Cells, tissues and organs
Basically, all living things are
made up of cells…
A group of CELLS makes up a
TISSUE
A group of TISSUES makes up
an ORGAN
A group of ORGANS makes up a
SYSTEM
A group of SYSTEMS make up an
ORGANISM
Adult stem cells
It is also possible to have
adult stem cells – these are
unspecialised cells that can
become specialised later
(but they can’t form ALL
types of cell)
Adult stem cells can be
found in places like bone
marrow.
Ciliated epithelial
cell
White blood cell
Nerve cell
(neurone)
Egg cell (ovum)
Adult stem Cells
Cells inside an organism contain the same genes. So how can
cells specialise if they have the same genes and make the same
proteins?
The reason is that many of the
genes in the nucleus are
“switched off” so that the cell
only produces the proteins it
needs.
It is possible to “switch on” different genes to make the cell
produce different proteins – this is the basis of stem cell
research.
Adult Stem cells
As well as adult stem cells from bone marrow, stem cells can also come
from...
These stem cells have the
potential to develop into any
kind of cell. The rest of the
embryo is destroyed. Most of
these embryos come from
unused IVF treatments.
Embryo
Egg and
sperm
Cloned
embryos
The ethical issue:
Should these embryos be treated as humans?
Meristems
Plant growth occurs in areas called meristems. These
meristems are “mitotically active”:
This meristem causes the plant
to grow upwards.
This meristem causes the plant
to grow in width.
Cells from the meristem behave like
stem cells – they can develop into
any kind of cell. Cloned plants can
be produced from these cells.
Phototropism
………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………
Plant hormones
The growth of roots and shoots is controlled by hormones:
In the shoots the hormone
auxin is “destroyed” by
light, so the shoot will bend
towards the light as the
cells on the shaded side
grow quickest.
In the roots hormones slow
down growth of the cells in
the lower region, which
makes the root bend down.
Shoots grow
towards light
(positive
phototropism)
and against
gravity
(negative
geotropism).
Roots grow
away from light
(negative
phototropism)
and in the
direction of
gravity
(positive
geotropism).
Phototropism summary
Cuttings
………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………
OCR 21st Century Science
Unit B5b Revision
DNA and Mitosis & Meiois
Inside the nucleus
the genetic code is in the cell nucleus of animal and plant cells
but proteins are produced in the cell cytoplasm
DNA
• DNA has a double helix
structure
• both strands of the DNA
molecule are made up of
four different bases which
always
• pair up in the same way: A
with T, and C with G
• the order of bases in a
gene is the genetic code
for the production of a
protein
DNA and coding for proteins
• the order of bases in a
gene is the code for
building up amino acids in
the correct order to make
a particular protein
Building proteins
1) DNA “unravels” and a copy of one strand is
made
2) The strand copy is made to produce RNA
3) The copy (with its code) then moves towards
the ribosome
4) The ribosome “decodes” the code which tells
the ribosome how to make the protein
In other words, genes do NOT leave the nucleus but a copy of the gene (the mRNA)
carries the genetic code to the cytoplasm.
Building proteins
……………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………
DNA summary
Some facts:
- DNA has a “double ______” structure
- This contains instructions on what a cell does, how the organism
should work etc
- The instructions are in the form of a ______
- The code is made up from the four ____ that hold the strands
together with hydrogen bonds; A always pairs with T and C with G
- The bases represent the order in which _____ acids are assembled to
make specific ________
Words – helix, amino, code, bases, proteins
Chromosomes in body cells
•
In body cells the chromosomes are in
•
Body cells have two sets of
chromosomes;
Sex cells (gametes) have only one set.
Sex cells (gametes) are made by meiosis
•
•
pairs
Asexual and sexual reproduction
Mitosis
parent
cell
mitosis
daughter cells
• cell division by mitosis produces two new cells that are
genetically identical to each other and to the parent cell
• a fertilised egg cell (zygote) divides by mitosis to form an
embryo
Mitosis
The chromosomes are
copied…
Each daughter cell has
the same number of
chromosomes and genetic
information as the parent
– it’s a “clone”.
The nucleus
divides…
The
chromosomes
separate…
Mitosis summary
Meiosis
• meiosis is a type of cell division that produces gametes
• in meiosis, it is important that the cells produced only contain
half the chromosome number of the parent cell
• a zygote contains a set of chromosomes from each parent.
Meiosis
Each daughter cell has half
the number of chromosomes
of the parent.
Meiosis summary
Mitosis Vs Meiosis
Mitosis:
Meiosis:
1. Used for growth and
repair of cells
1. Used to produce haploid
gametes for sexual
reproduction
2. Used in asexual
reproduction
3. Cells with identical
number of chromosomes
and genetic information
are produced (“clones”)
2. Each daughter cell has
half the number of
chromosomes of the
parent
OCR 21st Century Science
Unit B6a Revision
Nervous system and Reflex actions
The nerve cell
The CENTRAL
NERVOUS
SYSTEM (CNS)
enables us to
react to
changes in our
surroundings
(“stimuli”). It
consists mainly
of the brain,
the spinal
chord, nerve
cells
(“neurones”) and
receptors.
Receptor cells
Types of receptor:
1) Light receptors in
the eyes
2) Sound receptors
in the ears
3) Taste receptors
on the tongue
4) Smell receptors in
the nose
5) Touch, pressure
and temperature
receptors in the
skin
6) Changes of
position receptors
in the ears
(balance)
The nerve cell
Nerve cells (neurons) are elongated with branched endings to
connect to many muscles fibres and aid the transmission of
electrical impulses:
Nucleus
Axon – a long extension
of cytoplasm surrounded
by a membrane
Muscle strands
(effector)
Fatty sheath to increase the speed of
transmission and to insulate the
neuron from surrounding cells
CNS and PNS
The Central Nervous System (CNS) is the
spinal cord and brain:
The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) is the
collection of neurones connected to the CNS:
There are two types of neurone we need to
consider:
1) Sensory neurone
Impulse
These carry impulses
from the receptors to
the CNS
2) Motor neurone
Impulse
These carry impulses
from the CNS to
effectors
Synapse summary
Neurones never ____ each other – there is a small gap between them
called a _____. A signal is sent from one _______ to the next by a
_______ transmitter across the synapse (called a “neurotransmitter”).
These transmitters are then ________ back into the sensory neurone to
be used again. This process only reacts with specific chemicals that bind
to the receptor molecules.
Words – chemical, synapse, neurone, touch, reabsorbed
A Conscious action
A conscious action is one where the brain makes a considered response.
Here’s what happens:
4) The brain
3) Here another sensory neurone
decides to move
carries the signal to the brain
away the hand
5) This impulse is
sent by MOTOR
NEURONES to the
hand muscles (the
effectors) via the
spinal chord…
2) The impulse is carried
by SENSORY NEURONES
to the spinal chord
1) Receptors in
your skin detect
a stimulus
Stimulus
6) Which then
moves the hand
away
Receptor
Motor Neurone
Sensory Neurone
Effector
Coordinator
Response
A conscious nervous pathway
………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………
Copy and complete
3 types of neurons
The reflex arc
………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………
Simple reflexes
Babies can demonstrate simple reflexes:
1)Stepping reflex (legs step back if you hold the baby up)
2)Startle (or moro) reflex (when a baby hears a loud noise
it spreads its arms and legs out)
3)Grasping reflex (gripping your finger with their hands)
4)Rooting reflex
5)Sucking reflex (for breast feeding)
Summary
OCR 21st Century Science
Unit B6b Revision
Learning and memory
Drugs and the nervous system
Drugs are classed as “a substance that affects the central
nervous system, causing changes in psychological behaviour and
possibly addiction”. They do this by affecting the
transmission of impulses. Consider Ecstasy for example:
Ecstasy (MDMA) blocks the
sites in the brain’s synapses
where the transmitter
substance serotonin is removed.
Beta blockers
and Prozac can also
affect the transmission of impulses.
Drugs and the nervous system summary
Some drugs stop the impulse from passing across the ………………………
Drugs such as strychnine cause all the muscles in the body to go into a
continuous spasm of contraction. This also stops the person from
……………………….
Serotonin is a chemical released in the brain that gives feelings of
pleasure. Lack of this chemical can lead to feelings of ……………………….
Prozac is an ……………………… ……………drug that causes serotonin
concentration to build up in synapses.
The Prozac molecule blocks the re-uptake of serotonin from a synapse.
Beta blockers are drugs that can help people who suffer from angina
(chest pain due to a ……………………… condition). They work by blocking the
receptor sites on heart muscle cells so impulses from nerves which would
speed up the heart are ……………………… from passing to the heart.
WORDS: synapse. Breathing depression
prevented
anti-depressant heart
The cerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex is the part of our brain most concerned
with intelligence, memory and consciousness. By studying the
effects (e.g. memory/sight loss) when different parts of the
brain are damaged scientists have been able to identify which
parts of the brain control which functions.
EEG and MRI
1) An electroencephalogram (EEG) is a
visual record of the electrical activity
generated by neurons in the brain. It
works by amplifying and detecting the
electrical signals from the brain.
2) Magnetic resonance imaging
(MRI) scanning is a new
technique that produces images
of different cross sections of
the brain and uses colours to
represent activity.
Conditioning- Pavlov’s dogs
I won the Nobel Prize in 1904 and am most famous for
investigating “conditioned responses”:
Ivan Pavlov, 18491936
1) Steak + dog = saliva
2) Steak + bell + dog = saliva
3) Bell + dog = saliva
Notice that the final response (saliva) has no direct relation to the stimulus (the
bell). Conditioned reflexes can increase an animal’s chance of survival!
Bird finds a black caterpillar
Bird finds a black and orange
and tastes it. It tastes good so caterpillar and tastes it. It is
poisonous and tastes bad so it
it is eaten
is not eaten
Bird finds a black and orange
caterpillar and tastes it. It is
poisonous and tastes bad so it
is not eaten
Bird finds a black and orange
caterpillar but avoids it
because it is poisonous
Underline the primary stimulus
Circle the secondary stimulus
Put a box round the
conditioned response
Bird finds a hairy black and
orange caterpillar, this one is
harmless but the bird still
avoids it.
Extension:
Answer the following questions in your exercise
book:
1. Which organisms benefit? For each one explain
how.
2. Which caterpillar would you expect to find in
the highest numbers? Explain your answer.
Complex behaviour
PET scan
showing areas
“activated” by
doing algebra.
When the brain is asked to do certain tasks different areas are
“activated”. New experiences cause new neuron pathways to develop, while
pathways that are not used are eventually destroyed. This is why we
become better at certain tasks when we practice them more often.
Memory
Our memory is divided into two types: short term and long
term.
Short-term memory lasts for about 30 seconds. This is why,
when you look up a new telephone number, by the time the call
has ended you have forgotten the number. If more information
arrives than can be held in the short-term memory then some
is lost (forgotten).
Long-term memory may last the whole of your life. When you
sing the words of a favourite song, you are using your longterm memory. Although we often complain about how hard it is
to learn new things, there is no limit to how much information
you can store in your long-term memory.
Ways of improving
short term memory,
e.g. a phone number
Ways of improving
long term memory
e.g. exam revision
Multistore model
Scientists have produced models to help explain how memory
works. So far, none of these models has provided an exact
explanation.
The multistore memory model can be used to help explain some
steps involved in long-term and short-term memory.