Identification of candidate target proteins of type III effectors
advertisement

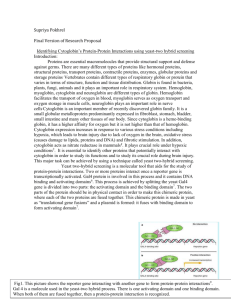
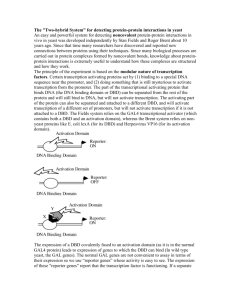
IDENTIFICATION OF CANDIDATE TARGET PROTEINS OF TYPE III EFFECTORS Andres Alvarez Dr. Jeff Chang Plants are susceptible to pathogens Bacterial speck disease: Pseudomonas syringae Bacterial soft rot: Erwinia carotovora Pictures courtesy of www.apsnet.org/education/IntroPlantPath Why should we care about plants’ health? • Agriculture is essential for food production • In the U.S. 10-20% of crops are lost to disease annually • Billions of dollars each year • Threat to food availability How do plants defend themselves? •Two branches of immunity •First branch: PAMP – Triggered Immunity (PTI) •PAMP = Pathogen Associated Molecular Pattern •Pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) detect PAMPs on bacteria •PTI response: e.g., strengthen cell wall How are bacteria able to infect a plant? • Many host-assoc., Gramnegative bacteria use a type III secretion system (TTSS) • Molecular syringe • Injected proteins are known as type III effectors (TTE) • Effectors target defenseassoc. proteins inside the host cell Marlovits et al My project •Use a yeast two-hybrid screen to identify candidate targets of TTEs. •Hypothesize targets are involved in host defense. Yeast two-hybrid overview Bait & Prey • cDNA library derived from a plant that was infected – BAIT • Target proteins are produced while plant is infected • Effectors (HopW and HopAY) – PREY • Proteins that could potentially interact with a protein within the cDNA library Confirmation of transformed yeast WT • DNA transformation into yeast M1 M2 C 1 2 3 C 1 2 3 C 1 2 3 • Confirmation via PCR • Prey: control protein (Krev1) • Baits: control protein interactors (WT, M1, M2) Krev1 clones C 1 2 3 1 2 3 Protein-protein interaction in yeast -Trp YEP -Leu -Trp -Leu Day 1: plate both strains on selection Day 2: replica plate to mate yeast strains, plate on non selective media Day 3: replica plate on to selective media, let grow 1 day Protein-protein interaction in selective media • Takes about 4 days to get to this. Now ready for phenotype screening -leu –trp selection Confirmation of protein-protein interaction Immediately replica clean Culture is replica plated from –leu, -trp plate to a –leu, -trp, -his + 3AT plate Grow one day then replica plate Protein- protein interaction results Expected Conclusions: • Krev1 + WT = Strong • Krev1 + M1 = Weak • Krev1 + M2 = None Experimental Conclusions • Krev1 + WT = Interaction • Krev1 + M1 = Interaction • Krev1 + M2 = None -trp –leu – ura plate Confirmation of transformed yeast w/ effectors genes • PCR screen of transformed Gal4 BD yeast cells with effector genes Future Work •Mate yeast cells containing cDNA library and yeast cells with effectors •Confirm mating results through 3 reporter genes •PCR screen and sequence positive interactions to determine candidate plant protein sequence. Acknowledgements • Howard Hughes Medical Institute • URISC program • Cripps funds • Dr. Jeff Chang and lab members especially Cait Thireault and Allison Creason • Dr. Kevin Ahern