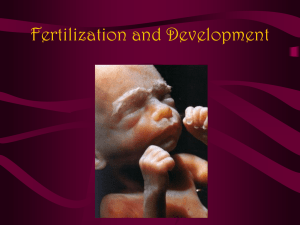
Notes on trimesters
advertisement

Start Strong, Finish Strong Pick up: New DSQ paper Mon, Sept 2, 2014 Please make sure your phones are in your bags up front. Today you will: 1.Receive clicker number 2.Learn what happens during each trimester 3.Review with clickers if time Homework/Planner: Quiz on Topic 3-Fetal Development Tomorrow! Daily Science Question Look in your book: What is the purpose of the amniotic sac/fluid? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QSN5gfb zgwc TriMesters ISN pg 31 TB pg 800-801 3 distinct periods of GROWTH & DEVELOPMENT 1st TriMester 1. Dramatic changes 2. Embryo Blasto Gastrulation 2nd TriMester 1. SKELETON begins to form 3. AMNIOTIC SAC: sac 2. Soft hair (lanugo) in which fetus develop develops over skin 4. PLACENTA: organ connecting fetus to the 3. FIRST uterine wall- allow nutrient uptake, waste MOVEMENTS elimination, gas exchange via the 4. Fetus wakes & mother's blood supply sleeps 5. ALL ORGAN SYSTEMS HAVE BEGUN TO FORM: 1. 2. 3. Brain Heart – heartbeat after 5wks Kidneys 3rd TriMester 1. FETUS RESPONDS TO LIGHT, MUSIC 2. NERVES FORM IN LARGE NUMBERS 3. FAT DEPOSITS under skin DEVELOP, so it can maintain body temp AND survive when born 14 week old fetus Amniotic Sac Umbilical Cord Placenta 5 mm 14 weeks What Your is a very Belly Button??? first scar. http://www.blogthings.com /whatdoesyourbellybutton ayaboutyouquiz/ 1. Scar tissue left over from where umbilical cord joined you to your mother's placenta when you were in her womb. 2. Nourishment going to the baby & all wastes coming out passed through belly button, via the umbilical cord. 3. Once delivered, umbilical cord was usually clamped or tied, and then cut stump withers & falls off after a few days, leaving behind the scar we call the belly button. Organ The Placenta created during pregnancy to nourish fetus, remove its waste & prod. hormones to sustain pregnancy. Attached to wall of uterus by blood vessels that supply fetus with oxygen & nutrition & remove waste from fetus & transfer it to mother. Fetus attached to placenta by umbilical cord. Through this, the fetus receives nourishment & oxygen & expels waste. On one side of the placenta, the mother's blood circulates, and on the other side, fetal blood circulates. http://pregnancy.about. com/cs/placentas/a/pla http://pregnancy.about.c om/cs/rhfactor/a/aa0506 Colored Villi scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of in placenta at the time of childbirth. Villi projections of fetal tissue into maternal part of the placenta Packed with blood vessels, allowing the fetus' blood supply to come very close to the mother's blood. This allows the exchange of gases, nutrients & waste with mother's blood, as the fetus cannot breathe, feed or excrete while in the womb Speaking of the Amniotic Sac, Placenta… the Afterbirth http://video.an placentas-hel 516946810 Many people of the world have known the secret power of the placenta as a medicinal supplement. http://www.birthtoearth.com/FAQs/Placenta +Traditions.html For many the placenta represents the “giver of life” – they will plant the placenta under a tree Among the Chinese and Vietnamese, it is a customary practice to prepare the placenta for consumption by the mother. The placenta is thought to be rich in nutrients that the mother needs to recover more readily from childbirth. In Italy, women have been known to eat parts of the placenta to help with lactation. Hungarian women bite the placenta to expedite the completion of labor. And knowledgeable midwives in this country have their birth mothers take bites of raw placenta to help stop hemorrhaging, due to its beneficial oxytocin content. there is no medical reason to eat the placenta; "Animals eat their placenta to get nutrition - but when people are already well-nourished, there is no benefit, there is no reason to do it."[6] On the other hand, American Medical anthropologists at the University of South Florida and UNLV, surveyed new mothers, and found that about 3/4 had positive experiences from eating their own placenta, citing "improved mood", "increased energy", and "improved lactation".[7] [8] Human placenta has also been an ingredient in some traditional Chinese medicines,[9] including using dried human placenta, known as "Ziheche" (simplified Chinese: 紫河车; traditional Chinese: 紫河車; pinyin: Zǐhéchē), to treat wasting diseases, infertility, impotence and other conditions.[10] Practice Questions for this unit… 1.Which of the following is true of a zygote? A. It forms into a blastocyst B. It is an unfertilized egg C. It produces haploid male gametophytes D. It is made up of only one cell In which of the following structures of the female human reproductive system is the blastocyst implanted during normal human development? A. ovary B. uterus C. vagina 1.What of the following is the correct order of development? A. Zygote – blastocyst – morula – embryo – fetus - baby B. Morula – blastocyst – embryo – fetus – baby C. Zygote – morula – blastocyst –embryo – fetus - baby Below is a diagram of the male reproductive system. A. 1.Which structure is represented by the letter A? A. Scrotum B. Testes C. Epididymis 1.Sperm are created through meiosis in an area of the testes called the seminiferous tubules. Through which structure do the sperm travel to exit the testes? A. vas deferens. B. seminiferous tubules C. epididymis 1.Abnormalities present in the cells that line the uterus may prevent the production of offspring by directly interfering with which process? A. the secretion of estrogen by the ovary B. the production and release of egg cells C. the development of the embryo 1.The drinking of alcoholic beverages by a pregnant woman is harmful to the development of her fetus. This is most damaging early in a pregnancy during this time because… A. the lungs of the fetus become functional. B. many of the essential organs of the fetus are forming. C. the fetus cannot excrete wastes. 1.The human mother’s body nourishes the growing embryo during pregnancy. Which structure nourishes the embryo and removes wastes through a network of blood vessels? A. ovary B. placenta C. uterus 1. The point at which the umbilical cord attaches to the fetus becomes the belly button after birth. What is the function of the umbilical cord for mother and fetus during fetal development? A. Liquids consumed by the mother flow through the umbilical cord and into the stomach of the fetus. B. Nutrients from the mom pass from her blood and waste products produced by the fetus travel through the umbilical cord and out through the mother’s kidneys. C. Nutrients from foods digested by the mother pass from her blood to the fetus through blood vessels in the umbilical cord.