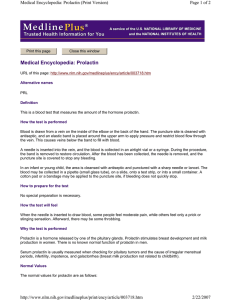
Prolactin - kristashunkwiler
advertisement

PROLACTIN IN MAMMALS By: Megan the epic M, Erica the fried squid pickel, Abby, Alyssa, Katie, Hiba GLAND • Prolactin is produced in the pituitary gland in response to pregnancy and nursing. BASE • Peptide-based • It is a pituitary polypeptide • Alpha helix folded PATHWAY/MECHANISM • Peptide hormone binds to a receptor on the outside of the cell membrane which activates the Jak2 kinase. Stat5, a transcription factor, is activated by Jak2. Stat5 then goes into the nucleus and hooks onto the DNA triggering a cellular response. PROLACTIN’S CELLULAR RESPONSE • Differentiation of the mammary gland which causes the production of the milk proteins. • WAP- encodes for milk proteins • BLG- encodes for milk proteins • Casein- encodes for milk proteins NEGATIVE FEEDBACK LOOP • Suckling is the major stimulus of prolactin production • Thyrotropin-releasing factor stimulated by hypothalamus. • TRH is sent to pituitary gland • Pituitary gland releases prolactin • Prolactin stimulates milk production in breasts beginning in late pregnancy and sustained after birth. • When the mother no longer needs to produce milk, dopamine inhibits prolactin by signaling the hypothalamus to stop. ALTERING PATHWAY • In malignant tissues prolactin fails to trigger, differentiation, and instead enhances breast epithelial survival and motility. • Prolactin, when over-expressed, inhibits apoptosis in cervical cancer cells