Sequencing Neanderthal DNA
advertisement
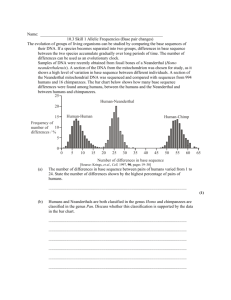
Sequencing Neanderthal DNA Lauren Edelson Road Map • Sequencing ancient DNA: methods & outcomes (Review article) • DNA sequencing to infer Neanderthal ancestry in modern humans (Sankararaman et al) • Examining the Altai Neanderthal population in depth (Prüfer et al) Learning About Human Population History From Ancient And Modern Genomes (Review, 2011) Mark Stoneking and Johannes Krause High-throughput sequencing of ancient DNA Challenges of sequencing ancient DNA • Repairing damaged DNA • Avoiding contaminant DNA Challenges of sequencing ancient DNA (continued) • Post-mortem chemical damage We can use cytosine deamination to test the authenticity of ancient DNA sequences! Okay, so we sequenced some Neanderthal DNA. What now? How much can you actually tell from ancient DNA? • Genetic composition of organisms • Phylogenetic relationships • Divergence times • Population structure • Population hybridization • Population bottlenecks • Phylogeographic patterns Emerging technologies allow for more complex population divergence models Our best models as of 2009 for population divergence SNP data used to compare possible dispersal route scenarios Key Dates • Neanderthal/Denisovan split with humans: 820,000 ya (350,000 ya?) • Neanderthal and Denisovan split: 680,000 ya • Out of Africa: 50,000 ya • Further human population divergence: 3550ya The genomic landscape of Neanderthal ancestry in present-day humans (March 2014) Sriram Sankararaman et al Subjects 1004 modern humans – 176 West African (Yoruba tribe: Ibadan, Nigeria) – 758 Europeans – 572 east-Asians Three features of genetic information 1. Allelic pattern at SNPs 1. High sequence divergence 2. Haplotype length These features are then used to generate a Conditional Random Field (CRF)! Conditional Random Fields (CRFs) • Based on “3 features” • Used to predict likelihood of Neanderthal ancestry in a given DNA sequence • Feature functions 1. Single SNP in Africans vs Europeans vs Test 2. Multiple SNPs used to capture ancestry (divergence) Tiling path from inferred Neanderthal Haplotypes Chromosome 9 in several Europeans Average contig length Maps of Neanderthal Ancestry European East Asian African Neanderthal Ancestry in 1000 modern genomes European East Asian High selection against Neanderthal DNA on X chromosome Male hybrid sterility Male donkey Female horse Mule (infertile) • After crossing two species, offspring are often infertile, keeping the two species distinct • Evidence for this in humans and Neanderthals? Yes! • But it’s not the only factor causing selection against Neanderthal genome B statistic • Background selection (B) value “indicates the expected fraction of neutral diversity that is present at a site” • Ranges from 0-1 Values near 0: Almost all diversity removed by selection Values near 1: little effect of selection • Relatively obscure “Widespread Genomic Signatures of Natural Selection in Hominid Evolution” (McVicker et al, 2009) Functionally important regions are deficient in Neanderthal ancestry Neanderthal GWAS Genome-Wide Association Studies (GWAS) can be used to associate Neanderthal-derived alleles with modern phenotypes Genome-wide estimates of Neanderthal ancestry • Neanderthal ancestry: east-Asian > European • Larger European population: less time for selection to remove deleterious alleles The complete genome sequence of a Neanderthal from the Altai Mountains (January 2014) Kay Prüfer et al Phylogenetic relationships of the Altai Neanderthal Modern humans Neanderthals Homozygosity • Inheriting identical copies of the same gene from each parent • Eg Tay-Sachs (from population bottleneck) • Long runs of homozygosity indicate inbreeding Indications of Inbreeding in Altai Neanderthal individual Heterozygosity estimates by group Inference of population size change over time Possible model of gene flow Remember this guy? Possible model of gene flow Takeaways • Although major challenges exist, it is possible to accurately sequence ancient DNA with modern technology • We can use these methods to compare ancient and modern DNAAll non-African modern day humans have a small genetic presence of Neanderthal ancestry • We can learn much about ancient populations (eg bottlenecks & inbreeding of Altai Neanderthals) by looking solely at one bone fragment! thank you QUESTIONS?