Lab Exercise #17

Bio 112 Genetics Lab
Exercise 17
Dihybrid Cross in Corn
There are four grain phenotypes in the above ear of corn: Purple & Starchy(A),
Purple & Sweet(B), Yellow & Starchy(C) and Yellow & Sweet(D).
These four grain phenotypes are produced by the following two pairs of heterozygous genes (R & r and SU & su) located on two pairs of homologous chromosomes (each gene on a separate chromosome):
Dominant alleles
R = Purple
SU = Starchy
Recessive alleles r = Yellow su = Shrunken
The cross which produced the corn ear above was:
Rr SUsu X Rr SUsu
DNA Extraction from Bacteria
Transformation of Bacteria
(pGLO)
We will introduce a gene into E. coli that will produce a protein (green fluorescent protein-GFP) that will cause the colonies to glow green when exposed to ultraviolet light
What is Transformation?
Uptake of DNA (in this case a plasmid pGLO) from the surrounding environment of the cell.
What is Green Fluorescent Protein-
GFP)?
GFP was discovered in the bioluminescent jelly Aequorea
victoria. The gene that makes this protein is used extensively in research…and also for fun?
Transformation Procedure … in a nutshell.
•
•
•
•
•
•
Suspend bacterial colonies in Transformation Solution,
CaCl
2
Add pGLO plasmid
DNA to +DNA tube
Place tubes on ice
Heat shock at
42 o C and place on ice
Incubate with
LB broth
Streak plates
Expected Results
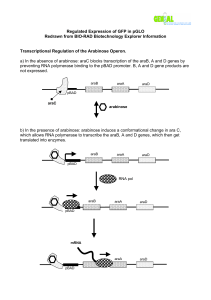
Our genes of interest: amp…araC…GFP ori bla pGLO araC
GFP
amp – this gene will give our transgenic bacteria resistance to the antibiotic ampicillin
araC – this gene will produce a protein which in the presence of the sugar arabinose will allow the bacteria to turn on the GFP gene
GFP – in the presence of arabinose, this gene will
“turn on” and cause the transformed (transgenic) bacteria to glow green
The Role of Arabinose
• The bacterial genes that make the digestive enzymes needed to break down arabinose for food are not expressed (made) when arabinose is absent.
• When arabinose is present the genes are turned
“on”. When it is absent the genes remain “off”.
• Arabinose initiates transcription of the genes by promoting the binding of RNA polymerase to the promoter.
ori bla pGLO araC
GFP
Expected Results