Non-Mendelian Genetics
advertisement

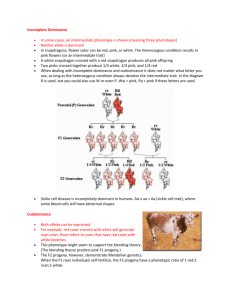
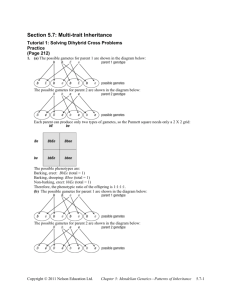
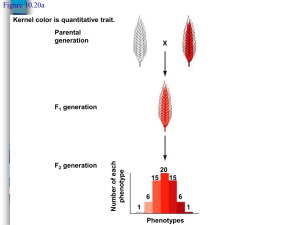
Non-Mendelian Genetics • i.e. exceptions to Mendel’s Rules Recall Incomplete Dominance •pattern of gene expression in which the phenotype of a heterozygous individual is intermediate between those of the parents. Codominance • the condition in which both alleles in a heterozygous organism are expressed. • Ex. Roan horses or cows Multiple Alleles • genes with three or more alleles • Ex. Blood types- there is an A, B, and O allele (IA, IB, i) • (More on this when we discuss blood type genetics) Polygenic Trait• when several genes influence one trait. • Ex. Eye color, height, hair, and skin color Height is a polygenic trait Skin color is a polygenic trait. The greater the total number of dominant alleles, the darker skin color an individual will have. For this example, assume 3 genes control this trait as shown in the chart: 6 dominant (ex. AABBCC) – extremely dark skin 5 dominant (ex. AABBCc)– very dark skin 4 dominant (ex. AaBBCc)- dark skin 3 dominant (ex. AaBbCc) - olive skin 2 dominant (ex. aaBbCc) - light skin 1 dominant (ex. aaBbcc)- very light skin 0 dominant (ex. aabbcc) – extremely pale skin If a father with the genotype AABbcc has a child with a mother whose genotype is aabbCc, what are the chances their child will have the genotype AaBbCc? What would the phenotype of this child be? Pleiotropy • one gene that affects more than one seemingly unrelated phenotypes Anemia, infections, weakness, impaired growth, liver and spleen failure, death. Traits (phenotypes) associated with the sickle cell allele. Epistasis • one gene masks the expression of a different gene for a different trait • Ex. The gene for albinism masks the effects of genes for skin, hair, and eye color. Influence of Environment • phenotype depends on conditions in the environment. • Ex. Arctic fox, Siamese cats, height, and skin color Temperature sensitive – The cold extremities (ears, nose, tail, and feet) express pigmentation while the warm body does not) Practice Problems INCOMPLETE DOMINANCE: • Yellow coat color in guinea pigs is produced by the homozygous genotype YY • Cream color by the heterozygous genotype Yy • White by the homozygous genotype yy. What genotypic and phenotypic ratios are matings between cream-colored individuals likely to produce? 1:2:1 yellow: cream: white CO-DOMINANCE: • In cattle, reddish coat color is not completely dominant to white coat color. Heterozygous individuals have coats that are roan colored (ie. reddish, but with spots of white hairs). • What would be the results of the following crosses: a. red x roan: b. white x roan: c. red x white: d. roan x roan: Genotype 1:1 RR:Rr 1:1 Rr:rr All Rr 1:2:1 RR:Rr:rr phenotype 1:1 Red: Roan 1:1 Roan:White all Roan 1:2:1 Red:Roan:White • Outline a breeding procedure whereby a pure breeding strain of red cattle could be established from a roan bull and a white cow: – First cross a roan bull with a white cow; next cross two roan progeny and 25% should be red. Height in humans is polygenic. Each upper case letter adds 3”. Males (aabbcc) are 5’ and females (aabbcc) are 4’ 7”. How tall would a male with the genotype AaBbCc be? 5’9” A female? 5’4” Probability that mating with this male & female result in a child that is homozygous recessive for all three traits? (1/4)3 = 1/64 How tall would that child be if it were a girl? 4’7” Epistasis • In Labs, black is dominant to chocolate (B or b). Yellow is recessive epistatic (when present, it blocks the expression of the black and chocolate alleles) E or e. • Determine the number of chocolate labs produced from a black female and a yellow male (BbEe x bbee) Phenotype Possible Genotypes BBEE BbEE BBEe BbEe bbEE bbEe BBee Bbee bbee BbEe x bbee BE Be bE be be BbEe Bbee bbEe bbee Color Black Yellow Brown Yellow Pea Plants • In sweet peas, purple flower color (P) is dominant over white (p), but there is also a control gene such that if the plant has a “C”, the purple has “permission” to express itself. – If the plant is “cc”, the purple does not “have permission” to express itself and the flower will be white anyway. – If a plant with homozygous purple, controlled flowers(CC) is crossed with a plant with white, non-controlled(cc) flowers, diagram the Punnett square for the F1 and F2 generations and calculate the phenotype ratios. • First, what are the genotypes of the parents in the first generation? PPCC and ppcc • What are the genotypes of their offspring? PpCc • What is always the phenotypic ratio for a dihybrid cross: 9: Dominant for both traits 3: Dominant for first trait and recessive for second 3: Recessive for first train and dominant for second 1: Recessive for both traits P-CP-cc ppCPpcc What are the phenotypes? purple white white white genotype P-CP-cc ppCppcc