LS HAT review
advertisement

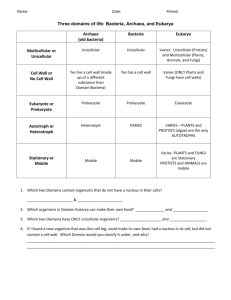
Ebonie J. LS HAT REVIEW LS.2 CELL THEORY KEY TERMS Cell membrane: the outside layer that determines what goes in and what goes out of the cell Cell wall: mostly in plant cells, covers the outside of the cell and acts as protection Cytoplasm: the jelly-like substance floating in the cell Vacuole: acts as a storage tank for food, wastes, and water Mitochondrion: acts as the powerhouse of the cell Endoplasmic Reticulum: transports things around the cell Nucleus: the control center or brain of the cell Chloroplast: contains chlorophyll Similarities between plant and animal cells Plant and animal cells both have membranes, cytoplasm, vacuoles, mitochondrion, and an endoplasmic reticulum, but animal cells don’t have cell walls or chloroplasts. LABELS OF ANIMAL AND PLANT CELLS Cell wall Cytoplasm Cell Membrane Cell membrane Cytoplasm Vacuole Nucleus Nucleolus Nucleus Nucleolus Nuclear Membrane Nuclear Membrane Golgi Bodies Vacuole Mitochondrion ER Mitochondrion Golgi Bodies ER CELL THEORY 1. 2. 3. All living things are composed of cells Cells are the basic unit of function and structure of living things All cells come from other cells Scientist Robert Hooke Anton van Leeuwenhoek Matthias Schleiden Rudolf Vischow Cell Theory Discovery Looked at cork; noticed boxes like 1 and 2 cells Viewed animalcules; first to see 1 and 2 bacteria Concluded all plant parts are made 1 and 2 up of cells Cells come from existing cells 3 TYPES OF CELL DIVISION/ MITOSIS What is the difference between passive and active transport? Passive is when the molecules travel from a higher concentrated area to lower one through different pressures, but active is the same without the pressures. Mitosis Interphase Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Mitosis is asexual, but meiosis is sexual. LS.3 CELL ORGANIZATION KEY TERMS Unicellular: single-celled, one cell Multicellular: more than one cell Respiration: the process of breathing Digestion: breaking down food Excretion: waste Growth: how an organism develops into a adult Reproduction: to produce more of oneself Active Transport: molecules going from higher to lower concentration Passive Transport: molecules going from higher to lower concentration with different pressures LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Cells Tissues Organs Organ System Organism TYPES OF TRANSPORT Define osmosis: Osmosis is when a big molecule travels from high concentration to low concentration. Describe what is happening in the picture above: The solute is passing through the barrier and going into a lower concentrated area Define diffusion: Diffusion is when molecules spread or dissolve from a high concentrated area to a lower one. Describe what is happening in the picture above: The red molecules are spreading or dissolving from a high concentrated area to a lower one. LS.13 GENETICS KEY TERMS DNA – contains your genetic make-up Gene – a specific trait Allele – pairs of genes Homozygous – pure genotype Heterozygous – different genotype Chromosome – made up of DNA Phenotype – your genes appearance Genotype – the letters of your genes Dominant – the capital letter in a genotype Recessive – the lower-case letter in a genotype Hybrid – different genotype (heterozygous) ROLE OF DNA DNA is coded instruction that store and pass genetic information from one generation to the next. DNA rungs are made of four sets of nitrogen bases and a backbone of phosphate and sugar. Nitrogen Bases Adenine - Thymine Thymine - Adenine Cytosine - Guanine Guanine – Cytosine ROLE OF DNA (CONTINUED) Mendel – father of genetics Watson & Crick – created the 1st model of DNA; won the Nobel prize Wilkins & Franklin – took pictures of DNA PUNNET SQUARES 2 possible phenotypes – yellow and green 3 possible genotypes – YY Yy yy Yy – heterozygous YY, yy – homozygous YY, Yy – dominant/ yy – recessive Green Yellow 2:4 50% ½ 2:4 50% ½ YY 0% 0 0 Yy 2:4 50% ½ yy 2:4 50% ½ LS.5 CLASSIFICATION KEY TERMS Taxonomic key: statements that describe the physical characteristics of an organism Dichotomous key: a key that categorizes species Phototroprism: an organism’s response to light Eutrophication: rich nutrients in a lake Succession: predictable changes in a community Dormancy: a state of quiet Hibernation: a state of greatly reduced body activity in the winter LEVELS OF CLASSIFICATION Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species King Phillip Came Over For Good Spaghetti BINOMIAL NOMENCLATURE Pisum sativam Rana hexadactyla Mangifera indica Felis domestica Ficus bengalensis Canis familiaris Glycine max Naja naja The genus is in yellow and the species is underlined ANIMAL PHYLA Animal Phylum Snail Mollusk Fish Chordate Earthworm Annelids Anemone Cnidarians Frog Chordate Jellyfish Cnidarians Starfish Echinoderms Alligator Chordate Crayfish Chordate Ant Arthopods Elephant Chordate Coral Cnidarian PLANT PHYLA 1. 2. 3. 4. Mosses – club moss Ferns – Silver fern Conifer – pine tree Flowering plants - tulips THE SIX KINGDOMS Archaebacteria Eubacteria Protista Fungi Plant Animal Unicellular/multicellular Prokaryote/eukaryote Heterotroph/autotroph Asexual/sexual Aquatic/terrestrial/air Motile/non-motile Unicellular/multicellular Prokaryote/eukaryote Heterotroph/autotroph Asexual/sexual Aquatic/terrestrial/air Motile/non-motile Unicellular/multicellular Prokaryote/eukaryote Heterotroph/autotroph Asexual/sexual Aquatic/terrestrial/air Motile/non-motile Unicellular/multicellular Prokaryote/eukaryote Heterotroph/autotroph Asexual/sexual Aquatic/terrestrial/air Motile/non-motile Unicellular/multicellular Prokaryote/eukaryote Heterotroph/autotroph Asexual/sexual Aquatic/terrestrial/air Motile/non-motile Unicellular/multicellular Prokaryote/eukaryote Heterotroph/autotroph Asexual/sexual Aquatic/terrestrial/air Motile/non-motile LS.6 PHOTOSYNTHESIS Photosynthesis is the foundation of all food webs. Equation for photosynthesis Reactants: carbon dioxide, water Products: carbohydrates, oxygen LS.7 ENERGY FLOW KEY TERMS Producer: an organism that makes it’s own food Consumer: an organism that doesn’t make it’s own food Decomposer: an organism that breaks down dead organisms Heterotroph: an organism that eats other things Autotroph: an organism that makes it’s food THE WATER CYCLE Sun Condensation Evaporation Ocean Evaporation: when the water turns into water vapor and starts floating upward Condensation: when the vapor Condensation turns into clouds Precipitation: the water falls from Precipitation the clouds THE CARBON CYCLE In this cycle, the regular carbon is being turned into alternative fuel by grounding corn. THE NITROGEN CYCLE FOOD CHAIN AND WEB PRACTICE Producer: grass 1st consumer: ant 2nd consumer: spider What is the difference between a food chain and a food web? A food chain only maps 1 path, but a food web shows more than 1 path. ENERGY PYRAMID Owl Snake Mouse Grass ENERGY FLOW MATCHING 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. A. B. C. D. E. F. B Herbivore E Carnivore C Decomposer D Omnivore A Producer F Consumers an organism that can use sunlight in order to produce its own food (autotroph) an organism that only eats producers an organism that breaks down dead or decaying organisms an organism that will eat producers and consumers an organism that will only eat other consumers an organism that eats in order to obtain energy (heterotroph) COMMUNITIES KEY TERMS Competition: struggle for limited resources Cooperation: working together Social hierarchy: the chain of importance within a species Territorial imperative: to claim or defend a territory Niche: an organism’s role in an ecosystem Predator: a carnivore that hunts animals for food Prey: the animal that the predator hunts Parasite: an organism that lives on and harms the host Host: a organism that provides a source of energy for a virus SYMBIOTIC RELATIONSHIPS A. Commensalism – one animal benefits and the other is not helped or harmed B. Mutualism – both partners benefit from living together C. Parasitism – one organism live on another harming the other B 1. Plover bird gets food by acting as a toothpick for a crocodile. A 2. The cattle egret eats the insects that are escaping as cattle graze in the field. C 3. A tick sucks the blood from a deer. C 4. A tapeworm in a dog gains energy from the dog but the dog loses nutrition due to the tapeworm. B 5. Ostriches and zebras move together to warn each other of impending danger because the ostrich sees well and the zebra hears well. ADAPTION AND CHANGE KEY TERMS Eutrophication: buildup over time of nutrients *phototropism: organism’s response to light *community: all the different populations in one area *population: all the members of one species in one area *biome: a group of ecosystems with similar climates and organisms *ecosystem: all the living and nonliving things that interact in an area *adaptation: a characteristic that helps an organism survive *permafrost: soil that is frozen all year *taiga: a swampy coniferous forest *canopy: a leafy roof formed by tall trees *deciduous: a tree that sheds it’s leaves annually *nocturnal: active at night ABIOTIC AND BIOTIC FACTORS Whale B Clouds A Finger nails B Clock A Corpse B Pipe A Water A Snail B Cotton fabric A Fish B Steak A Wool A Paper A Pork chops A Gold A Glass A Salad A Plastic A Aluminum A Bread A Grapes B Wooden ruler A Plant B Air A Sand A Hair A ADAPTATIONS Shape of bird beaks: physical Type of arms or legs: structural Color of fur or feathers: structural Shape of facial features (nose, eyes, ears): physical Physical, Behavioral, and Structural WATER ECOSYSTEMS Freshwater Rivers and Streams Marine Shorelines black mussels, barnacles, algae, moss trout, catfish, carp, algae Ponds and Lakes Temperate oceans plankton, whales, salmon, hagfish algae, clams, snails, dragon flies Wetlands pond lilies, cattails, shrimp, shellfish, ducks Tropical oceans Clown fish, blue marlin, green turtle, hammerhead DESCRIPTIONS OF BIOMES Tundra Coniferous Forest Deciduous Forest Rainforest Grasslands or Savannah Desert Temperature: ice cold Rainfall: 10 in. per year Plants: cotton grass, lichen Animals: polar bear, penguin Terms: permafrost Movie: Happy Feet Temperature: below 0 ½ of the yr. Rainfall: 30 in. per year Plants: pine tree, needles Animals: beaver, moose, rabbit Terms: conifer, taiga Movie: Brother Bear Temperature: seasons Rainfall: falls throughout the year Plants: willow tree Animals: raccoon, turkey, bear Terms: deciduous Movie: Pocahontas Temperature: mild, humid Rainfall: lots of rain Plants: vines, mangroves Animals: gorilla, vine snake Terms: canopy Movie: Tarzan Temperature: hot summers Rainfall: 10-30 in. per year Plants: blazingstar, coneflower Animals: lions, elephants Terms: Movie: Lion King Temperature: hot Rainfall: 10 in. per year Plants: cactus, dragon tree Animals: rats, bats, vultures Terms: nocturnal Movie: Aladdin LS.14 EVOLUTION KEY TERMS *mutation: a change in a gene or chromosome *adaptation: a characteristic that helps an organism survive *natural selection : The process by which individuals that are better adapted to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce *extinction: a disappeared species from earth *fossil record: fossils scientists have collected *variation: difference between organisms of a different species *dormancy: as if in a deep sleep *hibernation: greatly reduced body activity during winter STIMULUS AND RESPONSE 1. You flinch when a dodge ball is thrown towards you. 2. A doctor hits your knee and you kick your leg. 3. Your mom wakes you up by turning on the lights in your room. 4. You whistle at your dogs and they run towards you. 5. You are hyper because you drank a soda at lunch. NEEDS OF LIVING THINGS T- Temperature, all organisms need to be at a proper temperature O- Oxygen, animals need oxygen to go through respiration W- Water, needed to dissolve and transport substances E- Energy, all organisms need energy L- Living space, provides amount of water, food, and energy CHARACTERISTICS OF LIVING THINGS Digestion: breaking down food for energy Respiration: gas exchange Nutrition: intake of food for energy Excretion: elimination of wastes Reproduction: producing more of oneself Develop: change over time LS.1 EXPERIMENT KEY TERMS *prediction: an educated guess based on what you know *inference: guess about why you think an observation happens *experiment: a test to answer a question *hypothesis: a prediction of what will happen in an experiment *independent variable: the thing that effects the dependent *dependent variable: what happens after an experiment *variable: anything that can change during an experiment *control: the thing that is important *constant: the thing that stays the same *repeated trials: an experiment tested repeatedly *mean: the average *median: the middle number *mode: the most numbers in a number sequence SCIENTIFIC METHOD 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. State the Problem Research Hypothesis Experiment Collect Data Analyze Data Conclusion Share/Publish SCALE MODELS 5 cm 32 cm 53.7 cm 1) How big is a horsefly if 1 cm = 1m? 5 m 2) How big is the ghost if 1 cm = 20 cm? 640 cm 3) How big is the kitty if 1 cm = 10 cm? 537 TYPES OF GRAPHS Type: Bar Graph Use: to display information Type: Histogram Use: to display # information Type: Line Graph Use: to display progress Type: Pie Graph Use: to show percent DENSITY EQUATIONS 1. If an object has a mass of 25 grams and a volume of 5 mL, what is its density? 5 2. What is the volume of a 2 cm cube? 8 cm METRIC CONVERSIONS 1) 50 kg = (50,000,000) mg 2) 200 g = (20,000) cg 3) 72 L = (72,000) mL 4) 11.90 daK = () dK 5) 60 s = (60,000) ms SCIENTIFIC NOTATION 1) 9.87 x 105 = 987, 000 2) 2.09 x 10-8 = .0000000209 3) 9,243,000 = 9.243 x 10(6) 4) .00004945 = 4.945x10(-5) EQUIPMENT Name: Thermometer Measures: temperature Units: F, C Name: Graduated Cylinder Measures: Volume Units: Liters, mililiters Name: Triple beam balance Measures: Mass Units: Grams Name: Ruler Measures: Length Units: Inches, cm