PowerPoint - UCSF Immunology Program
advertisement
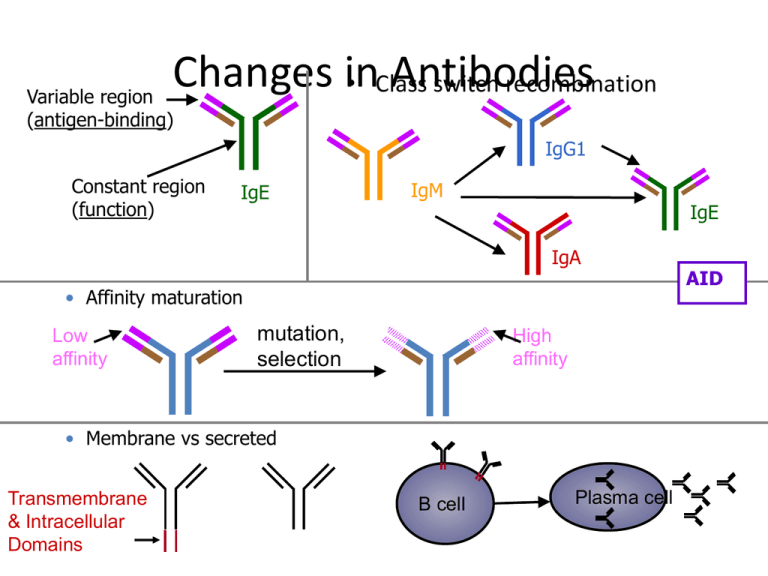
Changes in Antibodies • Class switch recombination Variable region (antigen-binding) IgG1 Constant region (function) IgE IgM IgE IgA • Affinity maturation Low affinity mutation, selection High affinity • Membrane vs secreted Transmembrane & Intracellular Domains B cell Plasma cell AID B Cell Differentiation Pathways Short-Lived Plasma Cell Memory B Cell Germinal Center Long-Lived Plasma Cell Activated B Cell Affinity Maturation Hypermutation, Selection Normal Functions of Antibodies Neutralization viruses Parasitic worm toxins IgG1 inflammation IgA Mast cell IgE Opsonization bacteria Macrophage Antibody-dependent cytotoxicity Foreign/ infected cell Toxic granules Complement activation bacteria IgM Questions • Why do IgE and IgG1 differ in abundance? • How do IgE vs IgG1 B cells behave in germinal centers? • What are possible models leading to the loss of IgE germinal center B cells? Questions • Why do IgE and IgG1 differ in abundance? • How do IgE vs IgG1 B cells behave in germinal centers? • What are possible models leading to the loss of IgE germinal center B cells? Helminth parasite model: Nippostrongylus brasiliensis infection Infection N. brasiliensis Serum IgG1 vs IgE Erazo A. et al. Immunity 2007, 26:191-203. L3 larvae Cheng L.E. et al. J Immunol 2010, 185:5040-5047. Questions • Why do IgE and IgG1 differ in abundance? • How do IgE vs IgG1 B cells behave in germinal centers? • What are possible models leading to the loss of IgE germinal center B cells? IgE vs IgG1 B cells IgG1 TNP-OVA Alum adjuvant NP-KLH Alum adjuvant GFP (IgE) Talay O. et al. Nat Immunol 2012, 13:396-404. N. brasiliensis infection GFP (IgE) Yang Z. et al. Immunity 2012, 36:857-872. N. brasiliensis infection Kinetics of IgE vs IgG1 B cells in GCs Yang Z. et al. Immunity 2012, 36:857-872. Talay O. et al. Nat Immunol 2012, 13:396-404. He J.S. et al. J Exp Med 2013, 210:2755-2771. Questions • Why do IgE and IgG1 differ in abundance? • How do IgE vs IgG1 B cells behave in germinal centers? • What are possible models leading to the loss of IgE germinal center B cells? – BCR signaling BCR expression in IgE vs IgG1 Germinal Center B Cells HA-specific B cells He J.S. et al. J Exp Med 2013, 210:2755-2771. Questions • Why do IgE and IgG1 differ in abundance? • How do IgE vs IgG1 B cells behave in germinal centers? • What are possible models leading to the loss of IgE germinal center B cells? – BCR signaling – Plasma cell differentiation IgE+ B cells are Biased Toward Plasma Cell Differentiation NP-KLH Alum adjuvant subQ 8 days Draining LNs (FACS) in vivo Yang Z. et al. Immunity 2012, 36:857-872. spleen Naïve + Anti-CD40 B cells & IL-4 4 days in vitro Cell-Intrinsic Increase in IgE+ GC B Cells Caused by Blimp-1 Deficiency Yang Z. et al. Immunity 2012, 36:857-872. Blimp-1 is a transcription factor needed for plasma cell differentiation CD45.2 GC B / CD45.1 GC B CD45.2 naive B / CD45.1 naive B Shorter Lifespan Reduced Affinity Yang Z. et al. Immunity 2012, 36:857-872. Why IgE B cell lifespan and affinity may be limited Neutralization viruses Parasitic worm toxins inflammation Mast cell IgE Systemic IgE activation IgG1 IgA IgA Background • IgA is secreted in mucosal tissue and is transported across mucosal epithelial barriers by the poly-Ig receptor • In the gut, class switch to IgA occurs in Peyer’s patches and Isolated Lymphoid Follicles • IgA plasma cells traffic via the blood back to mucosal sites • IgA deficiency is very common (~1 in 500) but is asymptomatic in a majority of individuals IgA: Questions 1. What about gut bacteria induces an IgA response? 2. Are IgA-secreting plasma cells long-lived or short-lived? 3. Do IgA responses exhibit immunological memory? 4. What effect does IgA have on bacteria in the gut? Question 1: What about gut bacteria induces an IgA response? Question 1: What about gut bacteria induces an IgA response? Approach 1: Controlled antigen delivery to the mucosal immune system HA107 is an E coli auxotroph for m-diaminopimelic acid (DAP) and for D-alanine (required for peptidoglycan biosynthesis and not made by host) Reversible microbial colonization of germ-free mice Hapfelmeier et al. Science 328: 1705-9, 2010 Most IgA plasma cells in gut are dependent on gut bacteria Hapfelmeier et al. Science 328: 1705-9, 2010 HA107 gavaged 6 times over 14 days; IgA plasma cells (green) evaluated after 4 weeks total (blue: DAPI staining of nuclei) (ASF: altered Schaedler flora, a mixture of 8 mouse gut bacteria that creates a relatively stable community) Threshold for IgA response to E coli K-12 Hapfelmeier et al. Science 328: 1705-9, 2010 Question 1: What about gut bacteria induces an IgA response? Hapfelmeier et al. Science 328: 1705-9, 2010 Live bugs induce IgA >10X better than heat-killed bugs Question 2: Are IgA-secreting plasma cells short-lived or long-lived? Question 2: Are IgA-secreting plasma cells short-lived or long-lived? Hapfelmeier et al. Science 328: 1705-9, 2010 What does this result imply for the longevity of IgA plasma cells? Question 2: Are IgA-secreting plasma cells short-lived or long-lived? Hapfelmeier et al. Science 328: 1705-9, 2010 What does this result imply for the longevity of IgA plasma cells? Question 3: Do IgA responses exhibit immunological memory? Approach 2: Deep sequencing of gut IgA+ plasma cells Deep sequencing of gut IgA+ plasma cells Lindner et al. J Exp Med 209: 365-77, 2012 -Gut IgA plasma cells are highly polyclonal with a subset of highly expanded clones -The frequency of somatic mutations goes up with age Question 3: Do IgA responses exhibit immunological memory? What can be done to look at a memory response in this system? Question 3: Do IgA responses exhibit immunological memory? Lindner et al. J Exp Med 209: 365-77, 2012 Lindner et al. J Exp Med 209: 365-77, 2012 Plasma cells are killed off with Bortezomib, a proteasome inhibitor (used in multiple myeloma patients) Question 3: Do IgA responses exhibit immunological memory? Lindner et al. J Exp Med 209: 365-77, 2012 Lindner et al. J Exp Med 209: 365-77, 2012 Gut IgA plasma cells show considerable clonal overlap before and after killing plasma cells with Bortezomib Question 4: What effect does IgA have on bacteria in the gut? Approach 3: Genetic defect in the IgA response (Activation-induced cytidine deaminase, AID, is required for somatic mutation AND class switch) AID-/- mice exhibit a dramatic expansion of Peyer’s patches and ILFs AID+/- AID-/- 3 wks of age 20 wks of age Fagarasan et al. Science 298: 1424-1427, 2002. AID-/- mice exhibit a dramatic expansion of Peyer’s patches and ILFs AID+/- AID-/- 3 wks of age 20 wks of age Fagarasan et al. Science 298: 1424-1427, 2002. Why is there a large expansion of germinal centers in the mucosal lymphoid tissues? Changes in representation of different gut bacteria in AID-/- mice Fagarasan et al. Science 298: 1424-1427, 2002. Somatically mutated IgA restricts the numbers of bacteria in the gut Wei et al. Nature Immunology, 2011 AID G23S: 9-15x lower somatic mutation; equivalent fraction of plasma cells that are IgA IgA restricts the numbers of Segmented Filamentous Bacteria in the small intestine Upper Small Intestine Lower Small Intestine Suzuki et al. PNAS 101: 1981-1986, 2004 Question 1: What about gut bacteria induces an IgA response? Segmented filamentous bacterium Ivanov et al. Cell 139: 485-498, 2009 Question 1: What about gut bacteria induces an IgA response? Different components of the gut microbiome may differ greatly in their localization within gut, invasiveness, ability to induce inflammation, etc. (“pathobionts”) Question 1: What about gut bacteria induces an IgA response? Approach 4: Separate bacteria that are coated with IgA from those that are not by flow cytometry Sorting IgA-coated bacteria MICE Palm et al. Cell 158: 1000-10, 2014 Sorting IgA-coated bacteria ICI: relative abundance IgA+/ relative abundance IgA- Palm et al. Cell 158: 1000-10, 2014 Sorting IgA-coated bacteria from people with Inflammatory Bowel Disease Palm et al. Cell 158: 1000-10, 2014 Consortia of IgA+ vs. IgA- microbes Palm et al. Cell 158: 1000-10, 2014 Consortia of IgA+ vs. IgA- microbes: stable short-term colonization of mice Palm et al. Cell 158: 1000-10, 2014 Consortia of IgA+ vs. IgA- microbes: different degrees of IgA induction Palm et al. Cell 158: 1000-10, 2014 Consortia of IgA+ vs. IgA- microbes: invasion of the mucus layer by the IgA+ bugs Palm et al. Cell 158: 1000-10, 2014 Consortia of IgA+ vs. IgA- microbes: inflammatory action Palm et al. Cell 158: 1000-10, 2014 Somatically mutated IgA limits number of pathogenic bacteria that reach MLN Wei et al. Nature Immunology, 2011 Yersinia enterocolitica numbers detected in mesenteric LN







