cardiac hypertrophy
advertisement

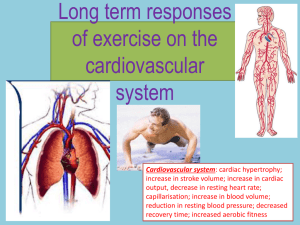
GROUP 4 Introduction The myocardium comprises many different cells. Cardiac myocytes (cardiocytes), The largest of these cells, occupy 75%. 25% include 1) Endothelial cells 2) Vascular smooth muscle cells 3) Cardiac fibroblasts 4) Macrophages and mast cells 2 2 Introduction Blood pressure / volume overload Adaptation - Size of cardiomyocyte - Cardiac muscle mass CARDIAC HYPERTROPHY 3 3 Introduction CARDIAC HYPERTROPHY Physiological hypertrophy (Athlete’s Heart) Pathological hypertrophy (Cardiovascular disease) Increased heart mass Normal or Enhanced cardiac function Reversible Increased heart mass Reduced cardiac function Irreversible Cell death and fibrosis Increased mortality Finding animal study Identified key signaling mechanisms To diagnosis, New Therapeutic 4 4 What induced hypertrophy? Responses to hemodynamic overload Volume overload Pressure overload Systolic wall stress Diastolic wall stress Mechanical transducers Extracellular and intracellular signals Ventricular hypertrophy Concentric hypertrophy 5 5 Eccentric hypertrophy Cardiac Hypertrophy in the Athlete’s Heart Exercise Endurance training Eccentric 6 6 Combination training Eccentric+Concentric Resistance training Concentric Cardiac Hypertrophy in the Athlete’s Heart ENDURANCE TRAINING Endurance training 7 7 Sedentary Resistance training Cardiac Hypertrophy in the Athlete’s Heart Endurance training Eccentric hypertrophy • Increase blood flow • Increase preload • Increasing LV internal diameter • LV wall thickness • Increase cardiac output (HR SV ) 8 8 Resistance training Concentric hypertrophy • Increase blood pressure • Increased afterload • Slightly increase LV internal diameter • LV wall thickness • Increase cardiac output (HR SV ) Cardiac Hypertrophy in the Athlete’s Heart » Physiological Changes with Exercise 9 9 Signaling pathway in Physiological Cardiac Hypertrophy IGF-1 Cell membrane Pathological pathway Angiogenesis Contractility 10 10 IGF-1 Receptor Cell membrane PI3K (p110α) Akt1 Heart growth Anti-fibrosis Anti-apoptosis Signaling pathway in Physiological Cardiac Hypertrophy » Regulation of protein synthesis and cell size Akt1 mTOR Protein synthesis Protein degradation Cell size • mTOR dependent pathway • mTOR independent pathway 11 11 Signaling pathway in Physiological Cardiac Hypertrophy » Improve contractile function L-Type Ca2+ channel Cell membrane Cell membrane Ca2+ Ca2+ Ca2+ SERCA2 Control Ca2+ cycling by increase the density of : • L-type Ca2+ channel Ca2+ Ca2+ • SERCA2 protein Ca2+ SR » Angiogenesis Stimulate cardiomyocytes to secrete 2 growth factors : • Vascular Endothelial growth factor (VEGF) 12 12 • Angiopoietin-2 Signaling pathway in Physiological Cardiac Hypertrophy Cardioprotection » Anti-apoptosis » Anti-fibrosis Stimulated by Aortic banding (pressure overload) Akt1 Cytochrome c releasing Program cell death 13 13 PI3K activity (dnPI3K) PI3K activity (caPI3K) Control Cardiac Hypertrophy in the Failing Heart Eccentric Concentric Etiology: Volume overload Etiology: Pressure overload - Valvular heart disease - Myocarditis - Myocardial infarction - Hypertension - Aortic stenosis - Chronic renal failure chronic chronic Etiology: Mutation - MYBP3 mutation gene effect - Sarcomere act as chronic “calcium trapping” - Sudden cardiac death Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) 14 14 Pressure/volume overload 15 Concentric Diastolic wall stress /Eccentric chronic HT CO ↓ Sympathetic activation chronic 15 Systolic / Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone system (RAAS) Cardiac remodeling Irreversible Decompensated Compensated Cardiac Hypertrophy in the Failing Heart Cardiac Hypertrophy in the Failing Heart Decompensatory stage Cardiac remodleing CO ↓ Sympathetic activation - Peripheral Vasoconstriction - Heart rate ↑ - Contractility ↑ Early 16 16 RAAS ↑ Ang II production ↑ ADH Cardiac filling pressure ↑ ↑ Aldosterone Chronic Cardiac Hypertrophy in the Failing Heart Dilated cardiomyopathy Sarcomere dysfunction Enlarged left atrium Cardiomyocyte death Fibrosis Weakened Muscle wall Thin cardiac wall Enlarged left ventricle Chamber dilatation Heart failure 17 17 Signaling pathway in Pathological Cardiac Hypertrophy G protein couple receptor pathway (GPCR pathway) Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway (MAPKs pathway) AngII, ET-1 Stress 18 18 Signaling pathway in Pathological Cardiac Hypertrophy » Excessive Ang II, ET-1 GPCR Cell membrane Gαq Cell membrane Gβγ PLC MAPKs (ERK, p38, JNK) IP3 DAG Transcriptional factors 19 19 PI3K (p110γ) - Fetal genes expression - Apoptosis - Hypertrophy Akt* Signaling pathway in Pathological Cardiac Hypertrophy Stress (e.g. ischmia, overload) Cell membrane Cell membrane MAPK pathway ERK Transcriptional factors Anti-apoptosis 20 20 JNK, P38 Transcriptional factors - Fetal genes expression - Apoptosis - Hypertrophy Signaling pathway in Pathological Cardiac Hypertrophy Outcomes from these pathways? • Fetal gene expression } - MHC isoform shift (α → β) - SERCA2 protein ↓ - L-type Ca2+ channel ↓ • Cardiomyocyte death → Contractility ↓ Fibrosis • Pathological cardiac hypertrophy 21 21 Endurance exercise Resistance exercise Combination exercise Volume overload Hypertension 23 22 Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) Distinct characteristics of physiological and pathological cardiac hypertrophy IGF-1 GPCR Cell membrane IGF-1 Receptor Gαq PI3K (p110α) Gβγ New therapeutic strategy PLC PI3K activate reguletors of(p110γ) PI3KDAG(p110α) pathway, IP Akt* i.e. ‘PI3K–regulated microRNAs’ 3 Akt1 MAPKs (ERK, p38, JNK) 23 Thank you for your kind attention. Any questions are welcome. 24 24