T cells
advertisement

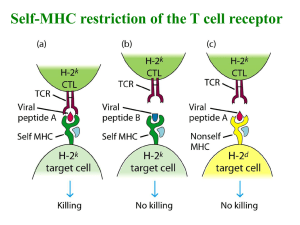
Chapter 8 B/T cell development B T Innate immunity Pattern recognition B/T cells BCR/TCR: epitope recognition Gene rearrangement of AgR Adaptive immunity Gene rearranged receptors BCR/TCR: Ag recognition Extracellular Ag Epitope MHC-restriction Intracellular Ag Structure Techniques One cell one Ag-specific receptor Clone Fate 細胞差異 T/B: Rearranged AgR T: MHC restriction Adaptive immunity Four characteristics 1. Antigen specificity 2. Diversity 3. Immunological memory 4. Self tolerance Foreign (non-self) Ag Self Ag (encoded by the host’s genome) Aim of development Production of AgR 1. Productive rearranged AgR 2. Functional Ag recognition 3. Self tolerance Self Ag? MHC-restricted? 2 Hematopoiesis Central lymphoid organs Microenvironment Commitment Productive rearrangement? Cell survival & death B-cell development T-cell development Positive & negative selection Fate Self antigen Before or after gene rearrangement of AgR ? Development of B cells Microenvironment Stromal cells Adhesion molecules Chemokines & R Cytokines & R The dependence on bone marrow stromal cells Cell-cell interaction Early stages B cell commitment SDF-1 Constitutive production Migration Gene rearrangement Gene rearrangement Loop Ig gene rearrangement & B cell stages Proliferation Antibody structure Protein-regulated gene rearrangement Cell survival or death One cell one Ag-specific receptor Allelic exclusion Self-reactivity Fate The presence of autoreactive lymphocytes in periphery Low frequency of Ag-specific B cells B-cell development T B cell commitment BCR rearrangement Cell survival & death (BCR, self tolerance) Stromal cell-dependent (Spatial regulation) Temporal regulation of protein expression Proteins: receptors, cytokines, TS factors, recombinase, .. Protein-regulated gene rearrangement One cell one AgR Cell survival & death T cell development Self MHC restriction Self tolerance Cells Microenvironment T cell development Thymus Epithelial cell network: thymic stroma gdTCR ab TCR genes abTCR or gdTCR ? b Developmental control of gd T cells Ordered sequence Repeated rearrangements can rescue nonproductive VaJa joins a gene rearrangement induces d gene deletion T cell commitment R: Notch 1 T cell development Gene rearrangement Cortex Medulla Positive selection : MHC restriction Negative selection : Self tolerance 33 Self MHC restriction T cell development MHC Positive selection : MHC restriction Negative selection : Self tolerance MHC Gene locus H-2k 37 H-2k 親代來源 基因 38 Analyze all the possible types of MHC class I and II restriction for CD4 T and CD8 T cells developed in an MHCbxk F1 hybrid mouse. 39 Ch6 section 6-12 MHC: co-dominant d/k 40 ? 41 TCR: MHC restriction MHC haplotype Ch6 section 6-12 MHC polymorphism 個體獨特性 MHC polymorphism Alleles / locus Formula: 100(DPa) X 100(DPb) X 100(DQa) X 100(DQb) X 100(DRa) X 100(DRb) X 100(A) X 100(B) X 100(C) =1018 Variability of MHC alleles MHC I Peptide presented on MHC I/II MHC II MHC-binding ability of peptides Multiple epitopes 46 MHC-restricted presentation of antigenic peptides d/k 47 Positive selection : MHC restriction H-2k Self MHC restriction 3 2 48 d/k Self MHC restriction 3 6 2 8 49 MHC and immune responsiveness Flow cytometry: immunostaining 51 T cell subsets in central and peripheral organs Normal Flow cytometry: immunostaining 52 Hybridoma Low frequency of Ag-specific T cells High frequency TCR transgenic mice TCR transgene T cell clone 53 Flow 54 Positive selection : MHC restriction MHCI-CD8 T Cortex MHCII-CD4 T Techniques 基因剔除鼠 Knock-out mice 56 Knock-out mice 57 黑 白 Knock-out mice Knock-in mice 58 Application of Tg & KO mice system ? Positive selection MHC II restriction: Interaction of CD4 with MHCII KO Host KI KI 59 KO Lethal effect Inducible knock-out mice Tissue specificity Cre/lox system Enzyme (recombinase) in other tissues 60 Immunodeficient mice Defective gene repairing system Severe combined immunodeficiency Genetic defect of a gene coding for transcription factor Wnt required for terminal differentiation of cortical epithelial cells What do SCID & nude mice lack (T/B cells) ? 61 Cells & microenvironment Adoptive transfer Flow cytometry 62 T cells : thymus MHC restriction Positive selection 63 MHCa MHCaxb Hematopoiesis MHCb APC MHCa MHCb MHCaxb 64 Bone marrow chimera Thymic non-lymphoid stroma Bone marrow-derived APC ? 65 Positive selection : MHC restriction 66 T cell development Gene rearrangement Cortex Medulla Positive selection : MHC restriction Negative selection : Self tolerance 67 Negative selection: self tolerance AIRE (Autoimmune regulator) Transcription factor AIRE regulates the expression of ubiquitous self antigens & a wide variety of tissue-restricted self Ag (e.g. pancreas, brain) at low levels in the thymus APC CD8T DC 69 Natural regulatory T cells (Treg) Negative ? selection Negative selection: self tolerance Bone marrow-derived Negative selection : clonal deletion & Treg Ann Rev Immunol 30: 531, 2012 T cell development AIRE medulary cells Natural Treg The presence of autoreactive lymphocytes in periphery T cell development T cell subpopulations T cells ab TCR CD4T CD8T gd TCR 1. Antigen specificity 2. Diversity MHCII MHCI 3. Immunological memory 4. Self tolerance AgR Innate immunity Pattern recognition Germline-encoded receptors Epitope recognition Gene rearranged receptors: TCR/BCR Adaptive immunity B/T cells