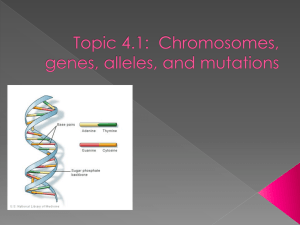
Mendelian Inheritance
Part 2
BIO 2215
Oklahoma City Community
College
Dennis Anderson
Multiple Alleles
• More than two forms of an allele exist in a
population
• An individual only has two of the alleles
Multiple Blood Alleles
A allele for making the A antigen on red
blood cells
B allele for making the B antigen on red
blood cells
O allele for NOT making the A or B antigen
on red blood cells
Three alleles give four blood types
AA or AO = Type A blood
BB or BO = Type B blood
AB = Type AB blood
OO = Type O blood
California Court Case
• 1946 the California supreme court ruled
that Charlie Chaplin was the biological
father of a child he claimed was not his.
• His defense was that the baby had type B
blood. He had type A and the woman who
sued him had type O (These may not be the actual
blood types, but it illustrates the point)
• Was the court correct?
AA, AO = Type A
BB, BO = Type B
AB = Type AB
O
O
A
AO
AO
O
OO
OO
OO = Type O
The judge should take a course in zoology!
Mutation
• Change in a gene
– nucleotide sequence is often altered
– Produce abnormal protein
• Cause a disease (sickle cell anemia)
• Resistance to a disease (AIDS)
Levels of Mutation
• Molecular level
– Deletion of nucleotides
– Addition of nucleotides
– Substitution of nucleotides
• Chromosomal level
– Change in structure
– Change in number of chromosomes
Mutant
• Unusual phenotype
• Mutations cause mutants
Normal
Mutant
Has different phenotype because of a
change in his DNA
Hemoglobin
• Protein molecule made
of 4 globin chains
– 2 alpha chains with 141
amino acids
– 2 beta chains with 146
amino acids
Sickle Cell Anemia
• Gene for making
hemoglobin is
changed from normal
Normal Hemoglobin Beta Chain
First six amino acids
Valine
Histidine
Leucine
Thre. Proline
.
Glutamic acid
CTC
Hemoglobin S Beta Chain
First six amino acids
Valine
Histidine
Leucine
Thre. Proline
.
One nucleotide has changed
Valine
CAC
Hemoglobin S
• Forms long rod like molecules that stretch
RBC into a sickle shape
• Sickled cells obstruct circulation of blood
• Allele for hemoglobin S is recessive
• SS = Normal
• Ss = Carrier
• ss = Sickle cell anemia
Why is the s allele more
common in Blacks than Whites?
• Ancestors of Blacks lived in areas where
malaria was present
• Malaria parasite cannot survive on
hemoglobin S
– Even Ss are immune to malaria
• The s allele is beneficial in an environment
where malaria is present
Beta Globin Mutations
• Over 300 different mutations!
Causes of Mutations
• Spontaneous
– Random
– About 1/100,000 chance of a gene mutating
• Induced
– Caused by mutagens
•
•
•
•
X-rays…break DNA
UV radiation….Thymine dimers
LSD…Break chromosomes
Cigarette smoke…damages tumor suppressor
genes
Spontaneous Mutation
• Two people of normal height have a child
with dwarfism
• Bacteria become resistant to antibiotics
• Cold virus mutates every year
– Immunity for this years cold will not protect
you from next years cold
• AIDS virus mutates too fast to make a
conventional vaccine
Ultraviolet Light
Causes adjacent Thymines to bond together
A C
A
A C
A
T
T G
T C
T T G
T C
Excision Repair Enzyme
Removes small section of DNA
A C
A
T T G
T C
Excision Repair
Removes small section of DNA
A C
T C
DNA Polymerase fills in missing nucleotides
A C
A
T
T G
T C
Xeroderma Pigmentosum
• Skin blisters from sun
exposure
• Develop skin cancer
as children
• Recessive gene does
not produce DNA
repair enzyme
Sunlight Exposure Increases
the Risk of Skin Cancer
• DNA repair enzymes do not always fix
the damage that sunlight inflicts on DNA
of skin cells.
• The more a person is exposed to
sunlight, the greater the risk of skin
cancer
Homologous chromosomes line up
in a double file in metaphase I of
meiosis
Homologous Pairs
Separate
Four Gametes With Single
Chromosomes
Fertilization
Nondisjunction
One pair of chromosomes fails to
separate during meiosis
Trisomy
Zygote ends up with 3
chromosomes instead of
2 for a given
chromosome pair.
Karyotype
• Picture of
chromosomes
• Often arranged with
autosomes in
descending order
and sex
chromosomes
separate
Normal
Male
Normal
Female
Trisomy 21
Down Syndrome
Down Syndrome
• Large tongue
• Flat face
• Single crease across
palm
• Slanted eyes
• Mental retardation
– Some are not
Maternal Age & Down
Syndrome
Trisomy 18
Edward Syndrome
Edward Syndrome
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Heart defects
Displaced liver
Abnormal hands
Low-set ears
Severe retardation
98% abort
Lifespan < 1 year
Trisomy 13
Patau Syndrome
Patau Syndrome
• Cleft lip and palate
• Extra fingers & toes
– polydactylism
• Defects
– Heart
– Brain
– Kidney
• Most abort
• Live span < 1 month
Klinefelter Syndrome
Klinefelter Syndrome
•
•
•
•
Breast development
Small testes
Sterile
Low intelligence
– Not retarded
Klinefelter Website
Turner Syndrome
Turner Syndrome
• Short
• Not go through
pruberty
• Produce little
estrogen
• Sterile
• Extra skin on neck
Abnormal Chromosome
Numbers
• Aneuploidy
– Missing or extra
chromosome
• Polyploidy
– Extra set of
chromosomes
– Usually lethal
– Common in cancer
– Common in plants
Fetal testing can determine
abnormal karyotypes
The End