Basic 504- for New Principals
advertisement

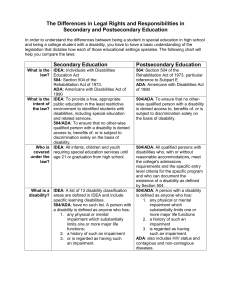
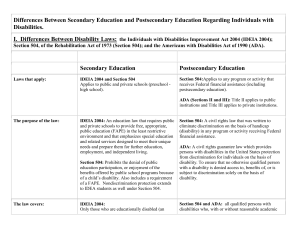
Basic 504/ADAfor Site Administrators Based on the final regulations to the ADA 5/24/11 Co-Presented by: Mary Samples, Assistant Superintendent and Fran Arner-Costello, Director of Programs and Services, Ventura County SELPA www.venturacountyselpa.com Why 504/ADA? • New requirements- ADA Amendments went into effect January 2009. • Conformity between 504 and ADA • Address discrimination • Keeps some kids out of Special Education 504 and ADA are Civil Rights Acts • Guarantee non discrimination for “unalterable characteristics” • Guarantee “equal and meaningful access” • “No otherwise qualified person shall be excluded solely on the basis of the disability.” • Office for Civil Rights is the oversight agency Isn’t this just a “cop out”? • Disabilities are real • This process documents the disability • Students should get the accommodations that they need for their disability But What About Special Ed? • 504 is simpler, less time-consuming • 504 generally provides supports and accommodations vs. services What About Cost? • 504 generally has less financial impact • Special Education is funded on TOTAL ADA • No fiscal incentive for IEP School District Level of Responsibility for 504 • “Presence of” Disability- Provide services and supports • “Record of”- may not exclude or discriminate • “Regarded as”- may not exclude or discriminate How is a Referral Made? • “Child Find” (pp.6-7) • Parent request for 504 Plan evaluation • SST/IPT/PLC is concerned about the presence of a disability or suspected disability • Site administrator for 504 should proceed with a Consent for Evaluation or (p.38) Notice to Parents (pp.50-51) The Steps 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Student evaluated Team meets Eligibility Determined (If eligible) Plan written Plan implemented and monitored Special steps for discipline Reevaluation if substantial changes 1. Evaluation A. Presence of the Disability B. Impact of disability on school-related activity C. Level of impact 1A. Presence of Disability • Physical Impairment- Impairments such as disfigurement, anatomical loss, neuromuscular, respiratory, sense organs, speech organs, cardiovascular, skin, etc. • Mental or psychological disorder- Such as intellectual disabilities, organic brain syndrome, emotional or learning disabilities Presence of Disability cont’d. • Limit to major bodily functions such as immune system cell growth, digestive, neurological, respiratory. * If a person has a substantial limitation, they don't also need to be limited in a school activity. Presence of Disability cont’d. • “Virtually always”- Deafness, blindness, intellectual disabilities, missing limb, use of wheelchair, autism, cancer, cerebral palsy, diabetes, epilepsy, HIV, multiple sclerosis, muscular dystrophy, depression, bipolar, PTSD, OCD, and schizophrenia. More Details about Disability • May be eligible even if episodic or in remission • Short term disabilities (such as broken limbs) are usually not considered if less than six months in nature – unless substantial impact • Exclusions: Illegal drugs, gambling, addiction Aren’t these kids all on IEPs? • Not necessarily • For an IEP, the student needs to have the disability and also require Special Education and related services • IEPs are limited to 13 specific handicapping conditions, 504 is much broader 1B. How is the presence of the disability determined? • If parents have a diagnosis, district can review it and accept it (unless they want to refute it) • If no diagnosis, the district needs to assist in establishing presence of disability • If there are qualified school staff, they may assess • If not, district may need to pay for a medical diagnosis What about ADHD? • Student has diagnosis from doctor • We pay for a medical diagnosis • Education staff conducts behavioral evaluation (pp. 67-69) Types of Evaluations • Medical reports (with parent permission) (p.39-40) • Parent/family member interviews • Review of school records • School observations • Teacher interviews • Social/emotional checklists • Academic assessments • Formal tools not required 1C. Impact on One or More School Related Activities Caring for self Manual tasks Seeing Hearing Eating Sleeping Walking Standing Working Sitting Reaching Lifting Bending Speaking Breathing Learning Reading Concentrating Thinking Communicating Interacting w/others Impact of Disability • Without effect of mitigating measures such as medication, prosthetics, hearing aids, mobility devices, assistive technology, learned behavioral modifications • Does not include eyeglasses or contact lenses • For episodic or in remission, consider effects when active • Compare to most other students Timeline for Evaluation • There is no timeline- the law refers to “reasonable” • No more than 60 days is a good rule of thumb 2. Team Meets • No required members- must include at least parents and school administrator • If determining eligibility, must be people who: – Know the student – Know evaluation data – Know accommodations/supports options • Meeting Notice – (p.41) 3. Eligibility Determined • Eligibility Summary Form (p. 45) • Rubric available if needed to determine level of impact (p. 46) 4. Service Plan Developed • Consider area in which there is impact • “Allows student to participate in and benefit from public education programs and activities” • Physical, instructional, social/emotional/behavioral accommodations • May include regular or Special Education and related aids and services Service Plans • • • • No required elements like an IEP Goals not required Must include a plan for periodic review Should appoint a “Contact Person” to monitor the plan and communicate with family • Method to document staff is informed LRE Under 504 • General education environments unless demonstrated that such education cannot be achieved satisfactorily with supplemental aids and services • Students with disabilities must participate with students without disabilities to the “maximum extent appropriate to the needs of the students with disabilities.” More About Service Plans • Brainstorm with student and parents • See the SELPA website www.venturacountyselpa.com for the “A+ Brochure” and “99 Ways to Help a Child with ADHD” brochure • Use existing staff if possible • Least intrusive as possible • Plan (pp. 42-48) Even More About Service Plans • May have to pay for extra services- aide support, therapy, etc. • May have to make environmental changes • Provide access to extracurricular activities • May not exclude from enrollment in challenging academic programs. Consideration for Special Education • If a 504 student is requiring intensive services, therapies, or even alternate placement, consider eligibility for Special Education. 5. Plan Implemented and Monitored • Site administrator should ensure that all people involved with the student have a copy • Communicate with Contact Person on a periodic basis about implementation and progress • Failure to implement a 504 plan can have serious legal consequences- people can be held personally liable Review • No required frequency of review, but it must be “periodic” • The plan should specify how often and by whom it will be reviewed • Make sure required reviews occur • Annual review is recommended. 6. Special Steps for Discipline • Same protections for suspension and expulsion as Special Education students • If pattern, Manifestation Determination within 10 days (pp. 48 & 49) • If currently using illegal drugs or alcohol, they lose their right to Manifestation Determination • 45 days IAES for weapons, illegal drugs or serious bodily injury 7. Re-evaluation • The student should be re-evaluated if major changes to the plan are being considered Disagreement with Parents • Parents should be given their rights at the beginning, and sign that they received them – (pp.14-21 and p.34) • If parents disagree with what district is proposing regarding assessment, eligibility, or plan, use the Prior Written Notice form • Approval not needed for change of placement • Parents can appeal to the Office for Civil Rights • No “stay put” as in IDEA (p. 17, #13) Thanks for coming today. With proper information and procedures, your school can avoid legal liability and we can ensure that students have the access and supports that they need!