Disability Services Presentation
advertisement

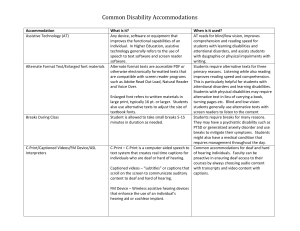
Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA), Section 504 (of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973), Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) , and Americans with Disabilities Act Amendments Act of 2008 (ADAAA) 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 Special Ed Gen Ed IDEA Section 504 Education Law (Federal Statute) Civil Rights Law Purpose is to provide for FAPE for children with disabilities. Purpose is to provide individuals with disabilities an opportunity to participate to the greatest extent possible. Protected are all students with disabilities that impact academic success Protected all students with disabilities who are ‘otherwise qualified’ Qualified students have a disability that meets the criteria in one or more of the 13 identified categories. Qualifications are having a physical or mental impairment that limits one or more of the major life activities Major life activities include, but are not limited to: Caring for oneself, performing manual tasks, seeing, hearing, eating, sleeping, walking, standing, sitting, reaching, lifting, bending, speaking, breathing, learning, reading, concentrating, thinking, communicating, interacting with others, and working; and The operation of a major bodily function, including functions of the immune system, special sense organs and skin; normal cell growth; and digestive, genitourinary, bowel, bladder, neurological, brain, respiratory, circulatory, cardiovascular, endocrine, hemic, lymphatic, musculoskeletal, and reproductive functions. The operation of a major bodily function includes the operation of an individual organ within a body system. IDEA (PK -12) 504 (Post-Secondary) Plan IEP; specific information and components required in the IEP A formalized plan is not required in a postsecondary setting. How services are determined Student is referred; school conducts evaluation; special programs, accommodations and related services are provided by school Student provides current documentation of a disability; student requests accommodations using procedures outlined by the institution; Services The LEA provides a FAPE in the LRE. Classroom teachers provide the IEP accommodations as needed. Student success is monitored by school. Student requests accommodation as needed. Personal devices and personal aides are not provided. Success is the responsibility of the student. Student Obligations Under ADA College Obligations Under ADA Self-identify to office of disability or Ensure that qualified applicants and accessibility services that she/he has a students have access to the college's disability (following the specific college's programs. stated policies and procedures) Provide appropriate documentation of disability Request desired accommodation(s) Follow the agreed-upon procedures for using accommodations Provide reasonable accommodations for the student's documented disabilities Demonstrate a good faith effort to provide the student with meaningful access IDEA is education legislation and ends with graduation from high school; 504 protection does not end. Process may be different ◦ Formal 504 Plans are required in Pk-12 education; accessibility is required at the post secondary level. FAPE is required in PK-12; Accessibility is required in post-secondary institutions. Equal housing accessibility is required if housing is available to other students. Disclosure is not required The determination of when or whether to disclose during the admissions process should be considered on a case-by-case basis. Students may want wait on the admissions decision before disclosing information. ◦ An appeal to the admissions committee may be appropriate if the student is not admitted. Visit with the office of disability or accessibility services. Submit documentation after being accepted. Make an appointment with the disability services office and discuss appropriate accommodations or adjustments. Students are required to submit documentation ONLY if they want to use the services of disability services. Current documentation is required. ◦ Current may be defined differently depending on the condition and the setting. Specific standards are not uniform. ◦ Post-secondary institutions should provide the student with the guidelines for required documentation. ◦ Documentation must be from a qualified professional. The student must follow the process guidelines established by the institution. The requests must be in a timely manner. The student must be “otherwise qualified” ◦ a person with a disability who meets the essential requirements but needs a reasonable accommodation to meet those requirements is otherwise qualified. The available, appropriate accommodation will depend on the student’s documentation and the situation. Typical academic accommodations: ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Using note takers Using recording devices Extended time for tests Quieter area for tests Interpreters for students with hearing impairments Enlarged print or Braille copies as needed Course substitutions (typically not course waivers) Some variation at different institutions ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Meet with the service provider Provide documentation Request the accommodation in a timely manner Meet the instruction Carry out the plan The student is responsible for providing the documentation. The institution may be able to help connect the student with agencies or evaluators. If the student is 18 or older, the student typically must give permission for the parent to have access or information. Encourage students to use needed accommodations The number of students using support services continues to increase, and many of the students are highly successful. Often students keep the disabilities services provider informed even for issues not directly related to the disability. If he/she cannot resolve an issue, the provider can often help the student consider solutions and can make referrals.