Flow Measuring Devices
advertisement

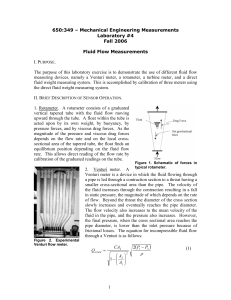
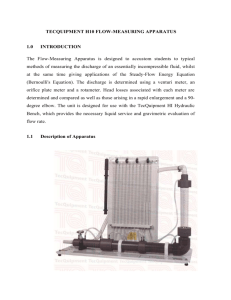
Flow Measuring Devices ENTC-303 Dr. Alvarado 1 Flowmeters • Devices used to measure flow rate: – Venturi (based on pressure difference) – Orifice Plate (based on pressure difference) – Rotameter (based on drag forces) – Coriolis (measure mass flow rate) – Magnetic (magnetic field is used to measure flow rate) – Ultrasonic (ultrasonic waves are used to measure flow rate) ENTC-303 Dr. Alvarado 2 Manometers The height of a liquid column or difference of height of two columns is used to measured the pressure: p po gh ENTC 303 PROF. ALVARADO 3 Venturi Effect • The Venturi effect is the reduction in fluid pressure that results when a fluid flows through a constricted section of pipe. - The Venturi effect is a jet effect; as with an (air) funnel, or a thumb on a garden hose, the velocity of the fluid increases as the cross sectional area decreases, with the static pressure correspondingly decreasing. ENTC-303 Dr. Alvarado 4 Venturi Meter From Bernoulli Equation: 2 2 æ æ AB ö ö PA - PB v B,t ç1- ç ÷ ÷ = =h ç ÷ 2g è è AA ø ø rg in theoretical velocity: vB,act = Cv v B,t C v takes into account reduction Flow mass is given by: m = Cv r AB vB,t Substituting with know values we have: m = 0.962 Cv h1/2 ENTC-303 Dr. Alvarado 5 Orifice Plate • An orifice plate is a device used for measuring the volumetric flow rate. It uses the same principle as a Venturi nozzle, namely Bernoulli’s principle which states that there is a relationship between the pressure of the fluid and the velocity of the fluid. When the velocity increases, the pressure decreases and vice versa. ENTC-303 Dr. Alvarado 6 Orifice Meter From Bernoulli Equation: 2 2 æ æ AF ö ö PE - PF v F,t ç1- ç ÷ ÷ = =h ç ÷ 2g è è AE ø ø rg in theoretical velocity: vF,act = Cv vF,t Flow mass is given by: m = CC Cv r AF v F,t CC takes into account the area contraction: AF AE C D takes into account reduction CD = CC Cv CC = Substituting with know values we have: m = 1.398 CD h1/2 ENTC-303 Dr. Alvarado 7 Rotameter -Pressure difference is constant in the rotameter -Peripheral velocity is constant -To maintain a constant velocity, the cross sectional area must vary -This variation of cross sectional area occurs as the float moves up and down the rotameter. ENTC-303 Dr. Alvarado 8 Rotameter Time to Mass A (mm) B (mm) C (mm) E (mm) F (mm) (cm) Fill (s) Flow(kg/s) Cv Cd 18 16 14 12 10 Average: Calculated Rotameter (cm) Venturi m (kg/s) 18 16 14 12 10 Calculated Orifice m (kg/s) Error Venturi Error Orifice HL Venturi (mm) HL Orifice (mm) References • • • • en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Venturi_effect en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Orifice_plate www.orificeplates.com www.omega.com ENTC-303 Dr. Alvarado 10