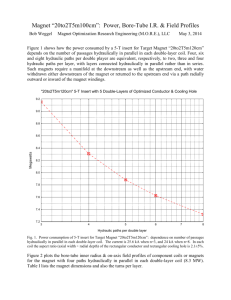
Asymmetries in Maxwell`s Electrodynamics

Asymmetries in Maxwell’s
Electrodynamics
W. J. Wilson
Department of Engineering & Physics
University of Central Oklahoma
Edmond, OK 73034
Web: www.physics.uco.edu/wwilson
Email: wwilson@uco.edu
ON THE ELECTRODYNAMICS OF MOVING BODIES
By A. EINSTEIN
“It is known that Maxwell's electrodynamics - as usually understood at the present time - when applied to moving bodies, leads to asymmetries which do not appear to be inherent in the phenomena.
Take, for example, the reciprocal electrodynamic action of a magnet and a conductor. The observable phenomenon here depends only on the relative motion of the conductor and the magnet, whereas the customary view draws a sharp distinction between the two cases in which either the one or the other of these bodies is in motion. For if the magnet is in motion and the conductor at rest, there arises in the neighborhood of the magnet an electric field with a certain definite energy, producing a current at the places where parts of the conductor are situated. But if the magnet is stationary and the conductor in motion, no electric field arises in the neighborhood of the magnet. In the conductor, however, we find an electromotive force, to which in itself there is no corresponding energy, but which gives rise - assuming equality of relative motion in the two cases discussed - to electric currents of the same path and intensity as those produced by the electric forces in the former case.”
Engineering & Physics 2/12
Motionless Magnet/Galvanometer
When there is no relative motion, there is no current indicated by the galvanometer:
B = Const.
∂B/∂t = 0 E = 0.
Engineering & Physics 3/12
Moving Magnet
Moving bar magnet generates time change of magnetic field.
B
t
0
Variable magnetic field, in turn, generates induced electric field according to the Maxwell's equation:
B
t inside the coil that moves free electrons of the coil producing induced current through the galvanometer, whose needle is moving left and right.
Engineering & Physics 4/12
This is obviously inconsistent being that the two last cases are equivalent and they
should be described by same fundamental equations.
Engineering & Physics
Moving Coil
When bar magnet stands still, there is no time variation of magnetic field and there is no induced electric field, according to Maxwell's equations:
B = Const.
∂B/∂t = 0 E = 0
However, the galvanometer needle is equally moving left and right. This phenomenon is now explained by the
Lorentz's force:
F = q v x B that acts on free electrons of the coil.
5/12
Scientists were aware of this asymmetry of Maxwell's equations at the beginning of the 20th century. Hertz proposed a variant of
Maxwell's equations (H.R. Hertz, Electric Waves), that differed slightly from Maxwell's original form (partial derivatives were substituted by total ones), and that did not "lead to asymmetries" as mentioned by
Einstein and are invariant to Galilean transformations.
4
4
0
1
B
4
c
t
J
c
1
E c
t
0
1 d B
4
c dt
J
c
1 d E c dt
Maxwell Electrodynamics
Engineering & Physics
Hertz Electrodynamics
6/12
Moving Frames
Let's now append a truck to the previous experiment. Let's take into consideration that part of the case when bar magnet
SN moves toward the coil, say by the velocity v
1
O
1
= 3m/s. For the blue observer on the illustration, the galvanometer needle turns due to induced electric field that pushes electrons in the coil.
Let's now take that this observer with all his gadgets is inside a truck that moves by the opposite velocity v
2
= -v
1
= -3m/s.
For another observer O
2 outside the truck, the bar magnet is standing still, while the coil is moving toward the bar.
For that observer, there is no electric field and the galvanometer needle turns due to Lorentz force.
In other words, the same physical event is described by two different equations, i.e. by two different physical laws.
Namely, in the first case by the low of electromagnetic induction, and in the second case by the low of Lorentz force.
Thus, it is violated one of the fundamental postulate of physics:
The laws of physics are the same in all inertial frames!
Engineering & Physics 7/12
Moving Truck and Special Relativity
Using Special Relativity, we'll start with green observer O
2
, since E
2
= 0 in the coil for him Now get the electric field in the coil inside the reference frame of the blue observer O
1
.
Applying relativity transformations on
E
2
, we get:
E
1
= E
2
+ v
2
× B/c,
Since: E
2
E
1
= v
= 0, we get, finally:
2
× B/c.
Engineering & Physics 8/12
From these results we can deduce the conclusions
Expressions for relativistic transformation of electric and magnetic field:
E
1
= E
2
* + v
2
× B/c, B
1
= B
2
* − v
2
× E/c, it may be seen that they comprise just those parts missing from Maxwell's equations that are included in Hertzian equations:
E d B dt
B t
v
B
B t
v B
B
0
J
1 d E
2 c dt
0
J
c
1
2
E t
v
E
0
J
c
1
2
E t
c
1
2
If the bar magnet moved by a non-uniform velocity, it
v E
would be inappropriate to use special relativity for it is valid just for uniform transformations.
Engineering & Physics 9/12
Faraday Homopolar Generator Asymmetry
d
Faraday noticed that only the rotation of the
Copper Disk
copper disk above the magnet influences the generated potential.
Permanent Magnet
M
Engineering & Physics
The rotation of the permanent magnet does not affect the magnitude of generated potential at all!
10/12
Action-Reaction Asymmetry
F
12
q
1 v
1 c
B
2
, B
2
F
12
1 q v
2 2
c R
2 q q
1 2 v
1
v
2
2 2 c R
F
21
q
2 v
2 c
B
1
, B
1
1 q v
1 1 c R
2
F
21
q q
2 1
2 2 c R v
2
v
1
v
1
1
R 2
F
21
F
21 v
2
Engineering & Physics 11/12
References
H.R. Hertz, Electric Waves: Being researches on the Propagation
of Electric Action with Finite Velocity through Space, Cornell
University Press (1893) ISBN: 1429740361
Petrovic Branko, “Lorentz's Force”, http://www.angelfire.com/sc3/elmag/files/MaxLor.html
H. Aspden, “Electromagnetic Reaction Paradox” , Lettere Al
Nuovo Cimento 39, 247 (1984).
Engineering & Physics 12/12
References
H.R. Hertz, Electric Waves: Being researches on the Propagation
of Electric Action with Finite Velocity through Space, Cornell
University Press (1893) ISBN: 1429740361
Petrovic Branko, “Lorentz's Force”, http://www.angelfire.com/sc3/elmag/files/MaxLor.html
H. Aspden, “Electromagnetic Reaction Paradox” , Lettere Al
Nuovo Cimento 39, 247 (1984).
Engineering & Physics 13