Detector systems

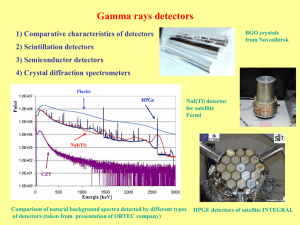
Detector systems
1) Anti-Compton spectrometers
2) Pair spectrometers
3) Crystal spheres, walls, complex set-ups of semiconductor and scintillation detectors
4) PET chambers
Photon spectrometer TAPS
PET chamber at „Cyclotron
BioMedical de Caen“
WWW pages of this device
Progress of gamma ray measurement:
Comparison of measurements by one
NaI(Tl) at 1963 and by set-up
EUROGAM II (1994), taken from N. Poenaru, N. Greiner:
Experimental Techniques in Nuclear
Physics
Anticompton spectrometer
HPGe detector surrounded by scintillation detector (NaI(Tl), BGO)
HPGe
– high energy resolution
Scintillation detector – high detection efficiency of Compton scattered photons
Strong suppression of Compton background and escape peaks up to one order
Photons after scattering → lower energies → higher probability of photo effect
Asymmetrical position of HPGe detector inside NaI(Tl) or BGO detector is advantage
Monte Carlo simulation
Distance in which given fraction of scattered photons is absorbed at BGO
HPGe detector with anticompton BGO shielding ( N. Poenaru, N. Greiner: Experimental Techniques in Nuclear Physics
Pair spectrometer
HPGe surrounded by scintillator (NaI(Tl), BGO)
Coincidence of HPGe and 2 × 511 keV at scintillator
Suppression of all, exclude double escape peaks
Strong background suppression, possible only for lines with high enough energy → high enough probability of pair production
Simple, anticompton and pair spectrum of anticompton spectrometer at NPI ASCR
Summation spectrometer
Again combination of more detectors – often HPGe and scintillation detectors
Sum makes possible to increase intensity of full absorption peak without marked downgrade of energy resolution
Spectrometer consisted of HPGe surrounded by scintillation detector can work at anticompton, pair and summation modes
Usage of inside geometry of source placement for cascade studies
Crystal spheres for nuclear structure studies
Studies of very rare phenomena, high energies of nuclear excitation, high angular momenta, long cascades, superdeformed states, giant resonances, exotic nuclei
First generation ( eighties) :
6 -21 HPGE detectors with anticompton shielding, BGO set-ups, combination of semiconductor and scintillation detectors
TESSA3 (UK), Chateau de Cristal (France), OSIRIS (SRN), NORDBALL (Denmark)
Superdeformed band discovery I < 0,01, cascades up to 20 transitions
Second generation (nineties):
Way to modular, flexible nomad set-ups, work on more accelerators
Efficiency ε
F
, Peak/Compton, resolution ΔE/E influence of Doppler shift – dominates at ΔE/E
Usage of semiconductor (HPGE) with BGO shielding
(efficiency up to ε
F
= 10 %)
( tenths, hundreds of detectors) Detector set-up EUROGAM II
USA –LBNL, ANL, from 1995 - GAMMASPHERE - 70 -110 HPGe detectors with BGO shielding, 4π geometry
Some photos of
Set-up
GAMMASPHERE real and also presentation at film Hulk
WWW pages of experiment
Europa – Daresbury, Heidelberg, Darmstadt, ... from 1992 - EUROGAM I, II, EUROBALL III, IV - 2002
Some photos of set-up EUROGAM and EUROBALL
WWW pages of experiments
Scintillation „walls“ for high energy physics
Detection of electromagnetic showers – identification of high energy photons
Heidelberg/Darmstadt – 162 NaI(Tl) ,
SLAC-DESY
– 672 NaI(Tl) elmg calorimeters
CLEO II 8000 CsI(Tl) detectors – usage of silicon photo diods -Cornell Electron-positron Storage Ring (CESR)
1991 TAPS 384 BaF
2 detectors
Crystal length 250 mm, diameter 59 mm
Crystals of CsI(Tl) spectrometer CLEO II
1) Thin plastic detector – identification of charged particles
2) Time of flight – separation of fast particles
3) Pulse shape analysis (BaF
2 has two components of light emission)
Detection of photons from hundreds keV up to tenth GeV produced directly or by decay of particles (π 0 , η, ω, φ)
TAPS worked at GSI Darmstadt,
KVI Groningen, GANIL Caen, CERN,
MAMI Mainz, Bon
Block ofBaF2 crystals - spectrometer TAPS
Photon spectrometer TAPS at GSI Darmstadt and at KVI Groningen
Electromagnetic calorimeter of LHC experiment ALICE: photon spectrometer PHOS
Crystals of PbWO
4
: 15X
0
→ 14 cm, R
0
~ 2 cm sizes: l = 18 cm S = 2,2×2,2 cm 2
Whole area: ~ 8 m 2
Optimized for E
γ
~ 0,5 GeV – 10 GeV
Crystals of PbWO
4 are ready for PHOS
PET chambers for lékařskou diagnostiku
Positron emission tomography (PET) makes possible to obtain 3D pictures of patient tissues
Detectors record coincidences of annihilation quantum pairs 511 keV
Positron + electron – annihilation in the rest → two annihilation quanta with energy 511 keV flight in opposite directions
Two coordinates – position of photon detection
Third coordinate – determination from detection time difference for photon pair
From hundreds up to thousands pair detectors
γ
1
(511 keV)
Annihilation
γ
2
(511 keV)
Example: Standard chamber of HR+Siemens at „Cyclotron BioMedical de Caen:
576 crystals, space resolution 4,5 a 3,6 mm