JJ Thomson
advertisement

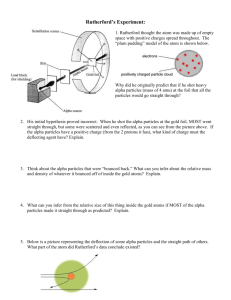
JJ Thomson kamilanowak@yahoo.com By: Anthony, Carly, Amanda, Melissa, and Kamila Background Info • English physicist • Born:1856 • Died:1940 • Attended Cambridge University, then transferred to Owens College in 1870. Became a lecturer after transferring to third school, Trinity College. Perceived structure • JJ Thomson believed that atoms were neutral and had no electric charge. • He thought that electrons had a negative charge. • He thought that the atom is a spherical object that has electrons inside a homogeneous jellylike material. Thompson’s perceived structure of atom Perceived Structure Cont. • He thought that it had a massive positive charge distribution cancels out the electrons. • Thomson's model is sometimes called a plum pudding model. Thomson’s perceived structure of atom. Postulate of the theory • Thomson had theory that the ‘rays’ emitted from a electron gun were inseparable from the latent charge. • Thomson had another theory that the rays carried a negative charge. Thomson's third theory was to try to work out the nature of the particles. They were too small to have their mass or charge calculated directly, but he attempted to conclude this from how much the particles were bent by electrical currents, of varying strengths. Experimental Design • First Experiment: • His first experiment was to build a cathode ray tube with a metal cylinder on the end. This cylinder had two slits in it, leading to electrometers, which could measure small electric charges. He found that when applying a magnetic field across the tube, there was no activity made by the electrometers and so the charge had been bent away by the magnet. This proved that the negative charge and the ray were inseparable and intertwined. First experiment Cathode Ray Experimental Design Cont. • Experiment two: • For this, he made a slightly different cathode ray tube, with a fluorescent coating at one end and a near perfect vacuum. Halfway down the tube were two electric plates, producing a positive and a negative charge, which he hoped would deflect the rays. • As he expected, the rays were deflected by the electric charge, proving that the rays were made up of charged particles carrying a negative charge. Second experiment Cathode Ray Experimental Design Cont. • Experiment three: • Thomson decided to try to work out the nature of the particles. • He found out that the mass to charge ratio was so high that the particles either carried a huge charge, or were extremely small. He came up with the idea that the cathode rays were made of particles that came from the atoms themselves. Third experiment Cathode Ray http://www.experimentresources.com/cathode-ray.html http://www.aip.org/history/electron/jjthoms on.htm http://nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/physics/l aureates/1906/thomson-bio.html