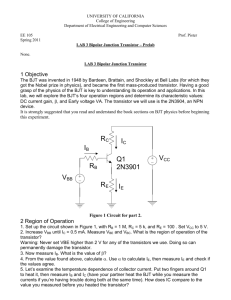
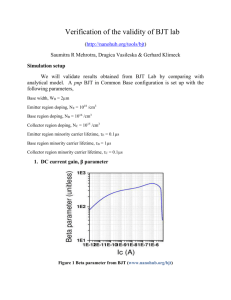
Transistors
advertisement

ME 4447/6405 Student Lecture Justin Chow Jacob Huang Daniel Soledad Overview History Properties Types BJT JFET MOSFET Applications Daniel Soledad Introduction Transistor History “Transistor” is combination of “transconductance” and “variable resistor” How Transistors Are Made ▪ Vacuum tubes ▪ Inefficient, fragile, bulky, generated a lot of heat ▪ First Transistors ▪ Semiconductors – Bell Labs 1947 Introduction Packaging Surface Mount or Through Hole Usually 3 or 4 terminal device ▪ Can be packaged into ICs General Applications Amplification/Regulation Switches Current Controlled i.e: BJT The output current is proportional to input current Voltage Controlled i.e.: JFET, MOSFET The output current is proportional to input voltage BJT Transistor Bipolar Junction Transistor 3 semiconductor layers sandwiched together Comes in two flavors NPN BJT PNP BJT Justin Chow BJT Transistor Diodes Forward Biased Reverse Biased current flows when VPN > .6-.7V no current flows BJT Transistor BJT Basics (NPN) BE Forward Biased BC Reversed Biased β=IB / Ic ≈ 100 IE = IB + IC Electron Flow emitter base collector BJT Transistor Things to remember PNP, biasing opposite Conventional current vs electron flow A small input current controls a much larger output current. BJT Transistor Operating Regions Operating Region Parameters Cut Off VBE <0.7 V IB = IC = 0 Linear VBE >0.7 V IC = β*IB Saturated IB > 0, IC > 0 VBE >0.7 V, VCE 0.2 V BJT Transistor Operating Regions From 3rd Exercise Turns on/off coils digitally BJT Transistor Common Emitter Amplifier β=100 BJT Transistor Common Emitter Amplifier IB = (Vin − VB) / 10000Ω = (Vin − 0.7) / 10000Ω IC = β(Vin − 0.7) / 10000Ω Vout=10000*(Vin-0.7)/1000 When VCE = 0.2V IC = 9.8 / 1000Ω = 9.8mA IB = IC / β = 0.098mA Vin − 0.7 = (0.098mA)(10000Ω) Vin = 1.68V or greater. BJT Transistor Power Dissipation PBJT = VCE * iCE Should be below the rated transistor power Important for heat dissipation as well Increased Gain β = β1 * β2 VBE = VBE1 + VBE2 Slower Switching 2N6282 Analogous to BJT Transistors Output is controlled by input voltage rather than by current 4 Pins vs. 3 BJT FET Collector Drain Base Gate Emitter Source N/A Body FET (Field Effect Transistors) MOSFET (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor) JFET (Junction Field-Effect Transistor) MESFET HEMT MODFET Most common are the n-channel MOSFET or JFET Jacob Huang MOSFET In practice the body and source leads are almost always connected Most packages have these leads already connected D D B G G S B S JFET D G S Metal-Oxide Semiconductor F.E.T. A.K.A. Insulated-Gate FET (IGFET) 2 Modes: Enhancement/Depletion N-Channel + Vgs -> More electrons -> More Current - Vgs -> Less electrons -> Less current P-Channel – Reversed Different from BJT Current flow D G B S N-Channel VGS > Vth -> Turns on device VGS < VTH -> No Current P-Channel Reversed Only E-type used now Region Criteria Effect on Current Cut-off VGS < Vth IDS=0 Linear Saturation VGS > Vth Transistor acts like a variable resistor, And VDS <VGS-Vth controlled by Vgs VGS > Vth Essentially constant current And VDS >VGS-Vth Current flow D G B S Current flow D G B S Used in high-power applications Heat Sink Vertical layout Not Planar like other transistors Reverse Bias VGS => Reduces channel size => Reduced Current Defaults “on” Vgs = 0 “on” |Vgs|> |Vp| “off” Vp = Pinch-off or Cut-off Voltage Internal Capacitance Bi-directional Cut-off voltage is varying for each JFET 0.3V – 10V N-Channel – Negative VGS P-Channel – Positive VGS Do not Forward Bias JFET – burn out Property BJT MOSFET JFET Gm Best Worst Medium Speed High Medium Low Noise Moderate Worst Best Good No Switch High-Z Gate No Yes Yes Yes Yes ESD Sensitivity More Less Less Complementary MOS Used in Logic Gates P-channel (PMOS) to high N-channel (NMOS) to low HIGH usually +5 V LOW usually ground Q is high when A = 0, Q is low when A = 1 References Spring 2007/2008 Slides http://www.made-in-china.com/image/2f0j00ZhaTKREnIQkfM/IC-Transistor.jpg http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/JFET http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MOSFET http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bipolar_junction_transistor http://www.allaboutcircuits.com/vol_3/chpt_2/8.html http://www.mcmanis.com/chuck/robotics/tutorial/h-bridge/images/basicbjt.gif&imgrefurl=http://www.mcmanis.com/chuck/robotics/tutorial/hbridge/bjt_theory.html http://www.allaboutcircuits.com/vol_3/chpt_2/6.html http://web.engr.oregonstate.edu/~traylor/ece112/lectures/bjt_reg_of_op.pdf http://hades.mech.northwestern.edu/wiki/index.php/Diodes_and_Transistors#Com mon_Emitter_Amplifier_Circuit http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Darlington_transistor http://www.allaboutcircuits.com/vol_3/chpt_6/2.html http://www.allaboutcircuits.com/vol_3/chpt_4/2.html http://www.designers-guide.org/Forum/YaBB.pl?num=1162476437/4 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CMOS