Dynamo
advertisement
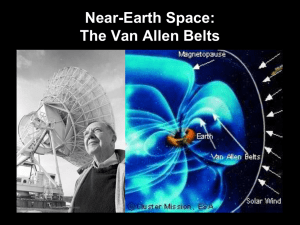
Dynamo Fausto Cattaneo ANL - University of Chicago Stewart Prager University of Wisconsin Madison 2006 Dynamos Sustained mechanism to convert kinetic energy into magnetic energy within the bulk of an electrically conducting fluid. Invoked to explain the origin of magnetic fields in the universe. The Madison Dynamo Experiment • Abstract dynamo theory – Conditions for dynamo action – Structure of resulting fields • Laboratory dynamos – Dynamo events in RFP – Liquid metal experiments • Astrophysical dynamos – – – – – – Planets Stars Galaxies ICM Magnetars Etc. Madison 2006 Active research areas • Role of turbulence in dynamo action • Large scale field generation in laboratory and astrophysics • Flux redistribution in accretion flows and jets Madison 2006 Dynamos and turbulence Conditions for dynamo action in a turbulent fluid. Turbulence consists of velocity fluctuations on different spatial and temporal scales (self similar range) plus coherent structures (long lived). Pseudo-vorticity B field Madison 2006 Turbulent dynamo action If < dynamo must operate in the inertial range of the turbulence. Reconnection is mediated by a strongly fluctuating (rough) velocity. Linear: Can dynamo operate for arbitrarily small ? Nonlinear: Does field amplitude decrease indefinitely with decreasing Pm=/ ? Rm =550, Re=1100 Rm =550, Re=550 • • Pm = 1/8 Madison 2006 Large scale generation Equipartition mean fields are often observed in astrophysics. What are the mechanisms to generate strong, large-scale fields? Traditionally discussed within framework of Mean Field Theory (introduce averaging). MFT correct for kinematic fields and small Rm. Neither satisfied in astrophysical situations. Exact sol. MFT solve filter solve MHD filter ??? • • • Does this diagram commute? What happens to (mean induction) in the nonlinear regime? If turbulent induction is suppressed, how are large scale fields generated? Madison 2006 Large scale generation Finite helicity Kinematic • • Nonlinear Non rotating Rotating x MFT Under suitable conditions it is possible to transform dynamo problem into QM System has both extended modes (MFT) and bound states (fastest growing) Unstable extended modes Unstable localized modes • • • At high Rm fluctuations dominate. Either -effect is collisional. Or -effect is turbulent but strongly nonlinearly suppressed. Madison 2006 Non MF dynamos What generates strong, large-scale fields? • • Turbulent -effect is rescued by – Boundary effect (magnetic helicity injection) – Strong spatial inhomogeneities Non MF effect – Large scale motions – Magnetically induced instabilities (essentially nonlinear). By - By + Madison 2006 Dynamo action in the laboratory Toroidal flux (Wb) MST Dynamo event Time (ms) E Energy source j instability B v˜ , B˜ dynamo and magnetic field fluctuations. Tearing mode instabilities generate velocity interactions (-effect) regenerate toroidal field. Fluctuation-fluctuation • • Madison 2006 Dynamo action in the laboratory • • • Evidence for strong mean induction effects Evidence for non MHD effects at some locations ˜ j E v˜ B Volts/m • What non MHD physics is important? – Hall effect – Diamagnetic Incorporate two fluid effects in simulation codes (Nimrod). Time (ms) • Why is the -effect strong in the RFP and weak in numerical simulations? • Turbulence not strong in RFP. Similarities to buoyancy driven dynamo. jB Hall ne pe Diamagneti c ne Madison 2006 Accretion flows-jets Radio galaxies show coherent magnetic structures with Kpc scales. Magnetic field (probably) generated by dynamo action in accretion disk around compact central object. Evidence for moderately strong fields in the ICM. • • • • • • What is the role of magnetic fields in jet dynamics ? What is the role of rotation and external pressure in the formation of coherent magnetic structures ? Are there analogies between laboratory and astrophysical magnetic structures? Both super Alfvénic injection and magnetic pinch help to collimate. Finite external pressure (possibly ram pressure as well) can lead to containment of magnetic structure. Similarities between spheromaks and disk arcades; kink instability (flux conversion) in jets and reversed field pinch experiments. Poloidal Toroidal Madison 2006 • Abstract dynamo theory – Mechanisms for large scale generation • Shear • Flux pumping • Essentially nonlinear Sim. By N. Brummell Future directions • Laboratory dynamos – Introduce PIC and two-fluid codes to study dynamo processes • Astrophysical dynamos – Magnetized/relativistic jets (Pluto) – Accretion flows • Jet launching • Accretion disk dynamos – Stellar dynamo models Madison 2006 THE END Madison 2006