pptx
advertisement

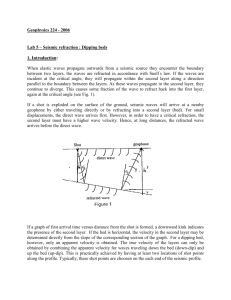
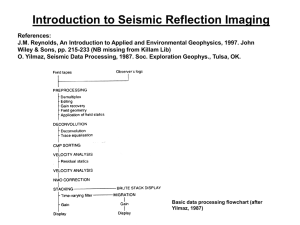
Transmitter/Receiver Vs. Geophones Seismic Reflection • One source • Lots of geophones • Stacking and Velocity performed in one step • Moveout • Peak Power GPR • One source (Transmitter) • One receiver • Both are antennas • Stacking performed by repeating the EM pulse • Moveout • Peak Power GPR Travel Time Equation 𝒉𝟐 + 𝒅= 𝑻= 𝒅 𝒗 𝒂 +𝒙 𝟐 𝟐 𝒅𝒕𝒐𝒕𝒂𝒍 = 𝟐 𝒉𝟐 + 𝒂 𝒙− 𝟐 𝟐 Two Way Travel Time = 𝟐 𝒉𝟐 + 𝒗𝟏 𝒂 𝟐 𝟐 Radar Velocity • In seismic reflection, velocity is found during stacking from the moveout patterns • In GPR, we only have one receiver, so we need a different method • Fixed offset survey (i.e. a normal survey) • Look for point sources (hyperbolas) • Common Midpoint Survey (CMP) • Get reflections off of a horizontal reflector • Increase antenna spacing, repeat • Produces a hyperbola Common Midpoint Surveying GPR Travel Time Equation 𝒉𝟐 + 𝒅= 𝑻= 𝒅 𝒗 𝒂 +𝒙 𝟐 𝟐 𝒅𝒕𝒐𝒕𝒂𝒍 = 𝟐 𝒉𝟐 + 𝒂 𝒙− 𝟐 𝟐 Two Way Travel Time = 𝟐 𝒉𝟐 + 𝒗𝟏 𝒂 𝟐 𝟐 Common Midpoint Surveying Velocity in Fixed Offset Surveys • In a regular, fixed offset survey, radar velocity can be determined only if diffraction hyperbolas are encountered • Typically point sources Velocity in Fixed Offset Surveys 𝑑1 = 𝑑2 = ℎ2 + ℎ2 + 𝑎 +𝑥 2 𝑎 𝑥− 2 2 ℎ2 2 𝑇𝑊𝑇 = + 𝑎 2 +𝑥 2 + 𝑣1 ℎ2 𝑎 + 𝑥− 2 2 Velocity in Fixed Offset Surveys Source Wave Properties Ground-Penetrating Radar (GPR) Electromagnetic Waves Seismic Surveys (Refraction/Reflection) Seismic Waves • Microwaves / Radio Waves • Velocity (in air)≈ 3x105 km/s • P, S, R, L waves • Velocity ≈ 0.4-14 km/s • I.e. the speed of light (0.3 m/ns) • Slower in most geologic materials (0.02 – 0.2 m/ns) • Depends on electromagnetic properties of medium • Frequency ≈ 10-2000 MHz • Depends on antenna • Wavelength ≈ 30-1.5x10-8 m • Depends on mechanical properties of medium (elastic moduli and density) • Frequency = 0.1-100 Hz • Depends on source • Wavelength = 140-4,000 m GPR Frequency Comparison • Higher Frequency • Better detail • Less penetration (penetration also depends on material) Attenuation Comparison Ground-Penetrating Radar (GPR) Electromagnetic Waves Seismic Surveys (Refraction/Reflection) Seismic Waves • Decay Exponentially with distance from source • Decay Exponentially with distance from source • Spherical spreading • Spherical spreading • Can’t penetrate through electrically conductive materials • Can’t penetrate through inelastic layers • Metals/Metallic Ores • Saltwater • Clays/Muds • Fluids • Fault/Fracture Zones • Scatter waves Attenuation What Causes a Reflection? Ground-Penetrating Radar (GPR) Electromagnetic Waves Seismic Surveys (Refraction/Reflection) Seismic Waves • Change in relative permittivity • Change in acoustic impedance 𝒗𝒓𝒂𝒅𝒂𝒓 = 𝒄 ℇ𝒓 c = speed of light εr = Relative Permittivity Acoustic Impedance = ρv R a refl a incid Relative Permittivity: a measure of the ability of a material to store a charge when an electric field is applied 𝒂𝒓𝒆𝒇𝒍 Reflection Coefficient: 𝑹 = 𝑮𝑷𝑹 = 𝒂𝒊𝒏𝒄𝒊𝒅 ℇ𝟐 − ℇ𝟏 𝒗𝟐 − 𝒗𝟏 = ℇ𝟐 + ℇ𝟏 𝒗𝟐 + 𝒗𝟏 2 v 2 1v1 2 v 2 1v1 Visualization of Data • Identical to seismic reflection • Wiggle traces • Variable Area • Variable Density