MathCAD is a versatile teaching tool
advertisement

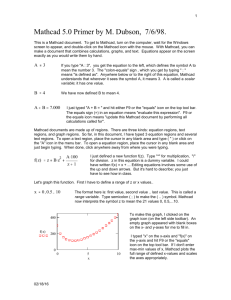
Using MathCAD SCC Spring-08 Electronic Technology Wang Ng x-2638 ngw@scc.losrios.edu Overview • • • • • • • • About MathCAD Using MathCAD as an interactive calculator Using MathCAD with formulas Equation solver Convenient features Advanced features Example : AC calculations Conclusion General features • MathCAD – – – – WYSIWYG K to 4-year College level. Simple, easy to use. Not intended for heavy-duty number crunching. • MatLab – – – – Programming style. Up to M.S. level Extensive training required. Suitable for heavy-duty number crunching. Calculator Mode • The Calculator Tool Bar • The “=“ key (It is the output command) • Examples: 1+1=2 sin(1)=0.841 1mi=1931m 1/3=0.333 sin(1deg)=0.017 1mi=6336ft Interactive: just edit the numbers sin(45deg)=0.707 Complex Calculations • Use i or j for the imaginary part (5+3j)+(2-4j)= (5+3j)*(2-4j)= (5+3j)^2= (5+3j)-(2-4j)= (5+3j)/(2-4j)= 53j = • Polar/Rectangular conversion: |5+3j|= arg(5+3j)= 2e^45j*deg= (type deg) • “j” can be placed in front by typing: 1j*45deg Formulas • You need to provide data: use the “:” key as the input command (it will look like :=). • Then you need to enter the formula. • Use the “=“ key to obtain the result. • Example: Enter the followings E:3V R:2 I:E/R I= Equation solver Find(x,y,...) Solves a system of equations. Minerr(x,y,...) Approximate solution to a system of equations. root(f(x),x,a,b) Solves one equation in one unknown. lsolve(M,v) Solves a system of linear equations. polyroots(v) Solves for the roots of the polynomial whose coefficients are in v. T his QuickSheet can be used to find a solution equation to the built-in the root f ( x) 0 for a function f(x) you specify, using function. Example: Using the “root” command Enter a function f(x): 3 x f ( x) x e Enter a guess value for the solution (modify as necessary): x 3 soln root( f ( x) x) Note: For a complex solution , input a complex guess value. Solution: soln 0.773 Convenient features • Use the worksheet as handouts. • Specify the unit of the results. • Change the input data and the results will be updated automatically. Note: Data must be placed above formulas. • • • • Many built-in functions (root, …) Comments can be entered after the “ key. You can save the worksheet. Resource center: Tutorials, quick sheets, … Advanced features • Symbolic process: The symbolic menu bar – Examples: type x^2”space”-1”space” and then select “Factor” from the symbolic menu bar. • Graphs: see attached Bode Plot example. • Array and range variables: Use the “;” key. See attached example. • Programming: The programming menu bar has the basic programming commands. • Calculus, differential equations, matrices, optimization, statistics, … Bode Plot Example 4 T 80 70 60 50 dB_T ( ) 40 30 20 10 0 20log j 5 10 1 j 1 j 3 4 10 10 d B_T 2 0 l og T _ T arg T 1 80 0 45 _T ( ) 90 135 1 1 10 1 3 4 5 6 10 1001 10 1 10 1 10 1 10 180 0 5 10 15 20 10 1001 10 1 10 1 10 1 10 3 1 0 arg 1 180 22.5 4 5 6 Range Variables E 0V 3V 9V E 0 V I ( E) 0 A 3 0.3 6 0.6 9 0.9 f 1Hz 5Hz f 1 R 10 E I ( E) R L 10H Hz XL( f ) 2f L XL( f ) 62.832 2 125.664 3 188.496 4 251.327 5 314.159 Examples: RLC circuit impedance R1 R2 C1 C2 L R3 f 1KHz R1 1k R2 2k R3 3k C1 1F C2 2F L 1mH 1 XC1 XC2 2 f C1 XC1 159.155 ZTotal Z4 R1 XL 6.283 3 1 Z2 0.013 6.283i 3 Z3 Z2 R2 ( jXC1) 2 f C2 Z1 3 10 79.577i 1 1 Z2 Z1 ( jXL) Z4 Z3 XL 2 f L XC2 79.577 Z1 R3 j XC2 1 1 Z3 2 10 6.283i 1 1 Z4 12.579 158.114i 3 ZTotal 1.013 10 158.114i Conclusion MathCAD is a versatile teaching tool: • Calculation steps (formulas) • Demonstrate specific effects • Graphics • Exam/Homework problems • Partial credit • Course note