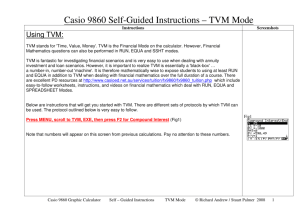
tvm and the use of the ti ba2+ financial calculator
advertisement

FIN. 3403--Corporate Finance INTRODUCTION © R. DIGGLE, CFA University of Central Florida 1999 COURSE OBJECTIVES: FIN 3403 • To learn to apply the 10 Axioms of Finance in Ch. 1 of your text. • To learn to APPLY time value of money and the financial calculator in every day problems. • To understand the basics of Capital Budgeting, Cost of Capital and Leverage. • To develop an understanding of applied financial performance and ratio analysis. FIN 3403 COURSE OBJECTIVES: CONTINUED • To understand the concepts of risk and return. • To gain a basic understanding of key financial instruments, markets and institutions. TOPICS • WEEK 1-5 – TVM – USING FINANCIAL CALCULATOR – USING TABLES IN BACK OF TEXT • WEEK 6-10 – COST OF CAPITAL – LEVERAGE – CAPITAL BUDGETING TOPICS CONTD. • WEEK 11-15 – FINANCIAL MARKETS, INSTRUMENTS AND RISK/RETURN – FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE (Financial ratio analysis --team project) – BOND AND STOCK VALUATION THEORY FIN 3403: SYLLABUS REVIEW • OFFICE / HOURS • GRADING – – – – Drop lowest exam Team project Homework Importance of taking notes in class • LECTURE NOTES • FINANCIAL CALC. • Do you need to brush up on accounting? • My job is to SIMPLIFY concepts in text and problems. • Ask questions if you are unclear on ANY concept, problem or definition. WARNING • This is a quantitative course. • Homework and class lectures are designed to help you understand the material. You are encouraged to work in a study group to master this material. • Grades in this course tend to be a bi-modal distribution. GETTING ORGANIZED • • • • • CLASS ROSTER ATTENDANCE POLICY TEAM GRADE ON PROJECT EXAMS AND MAKE UP POLICY WALL STREET JOURNAL SIGN UP -optional but HIGHLY recommended --you may share • QUESTIONS? STUDY TIPS TO HELP YOU GET AN “A” IN THIS COURSE • Get into a study group with your team or other classmates. • Begin NOW by studying the calculator manual. • DO THE HOMEWORK PRIOR TO EACH CLASS. Exam questions are taken from this material. • Write out definitions and terms. Do not just use a highlighter. Definitions given in class will be on exams. STUDY TIPS contd. • Use the Lecture Notes. They are on my Web Site and were written to help you on exams and to simplify note taking. • See me during office hours if you are confused or overwshelmed. • Ask questions until a topic is clear. • Pay close attention and participate in class. Move to front if you cannot see. DOWNLOAD LECTURE NOTES AND FILES FROM WEBSITE • WEB SITE ADDRESS IS IN SYLLABUS • DOWNLOAD LECTURE NOTES • DOWNLOAD EXCEL PROBLEMS • DOWNLOAD PPT LECTURES FOR REFERENCE • IF YOU DO NOT KNOW HOW TO DOWNLOAD, GET SOMEONE IN THE COMPUTER LAB TO HELP YOU. • PRINT LECTURE NOTES AND BRING TO CLASS My Qualifications R. Diggle, Jr. CFA • BBA, MBA UNIV. OF • CEO largest bank -MICHIGAN --finance investment sub in the and marketing Intermountain West • PhD coursework Ohio • Director of Research State University -and member of the honors --finance management committee --two • 30 years of senior regional brokers management • BEEN THERE-• Chartered Financial DONE THAT!! Analyst TEAM COMPANY REPORT • PLEASE SEE PAGES 5-7 OF LECTURE NOTES DEALING WITH PROJECT. • PRINT THE STEPS IN THIS PROJECT FROM THE EXCEL FILE I WILL GIVE YOU IN CLASS TODAY. • I WILL MEET WITH EACH TEAM. • YOUR IMMEDIATE JOB IS TO GET ORGANIZED AND PICK A COMPANY TO ANALYZE. • NOTE: SET A TIME FOR REGULAR TEAM MEETINGS. TEAM PRESENTATION USING EXCEL, COMPUSTAT AND POWERPOINT • Sign up for a team today. Get names and phone number of teammates • Pick a time when you ALL can meet to work on your project. See lecture notes for details. • Pick an INDUSTRIAL company. Write for original last annual report ASAP (do not use internet copies) • I will give each team an Excel disk to use to analyze your company TEAM REPORT CONTD. • GO TO MY WEB SITE • CHECK OUT POSSIBLE COMPANIES ON BIGCHARTS AND NASDAQ DATABASE. • CHECK EDGAR -SEC DATABASE • MUST HAVE AT LEAST 5 YEARS OF HISTORY (NO RECENT IPOs) AND SALES OF AT LEAST $500 MILLION. • MUST BE MAKING A PROFIT • I WILL HELP YOU. OBJECTIVES OF THIS TEAM REPORT (15% of grade) • To become more comfortable making a formal presentation before a group. • To learn how to use Powerpoint effectively • To function as a team. This is a skill you will need throughout your career. • Peer evaluations will be made. I know many of you work. Set team meeting times THIS IS MS POWERPOINT • It is EASY to learn • All you need to do is outline your talk • Pick your slide format and type slides from your outline. USE LARGE FONTS • You may add Clip art to jazz up your talk Be creative!!! It is fun • You can change the presentation designs. Just make sure text is easily visible in back of room • Be sure slide 1 lists the names of team members and your topic, class & date • USE Windows 95 or Windows NT version POWERPOINT IS POWERFUL • When you have some slides done you can select the SLIDE SORTER VIEW LIKE THIS……. • You can use the cut icon to move slides around • You can insert spreadsheets of photos • Use the “notes” icon 2nd from right at bottom to write your “script.” • Click on the “podium” icon at the lower right when you are ready to test a full page view for your talk. • Save on a floppy and put on C drive before TEAM MEETINGS --30 MIN • EXCHANGE NAMES, PHONE NUMBERS AND E MAIL ADDRESSES AND GIVE INSTRUCTOR A COPY • SET TIME FOR WEEKLY TEAM MEETING AND STUDY GROUP MEETING • SELECT CANDIDATES FOR COMPANY PRESENTATION I will spend 5 minutes with each team Axioms of Finance--TEXT CH 1 1 Balancing risk and reward is a key role of a manager. Some risk can be diversified away. Some cannot as we will see. 2 TVM -- our next lecture topic. Money received now is worth more than money received in future. 3 Cash is king!. 4 Think incrementally! 5 Competition is a great equalizer. Companies with consistently high margins are rare. 6 Capital markets are “Efficient.” Efficiency is created by free flow of information and capital. 7 Owners and management objectives may not coincide. 8 Taxes affect ALL business decisions. 9 Some risk can be diversified away and some can’t 10 Ethics are important. GOAL OF THE CORPORATION • In this course we will focus on PUBLIC CORPORATIONS • Other forms of organization are discussed on pp 4-6 of your text • A Public Corporation is responsible to its owners • The Board of Directors are chosen by the shareowners to oversee management. • In the U.S. there is no National Corporation Act. Corporations are incorporated in a state. What is the MOST IMPORTANT goal of the Modern Public Corporation? • See TEXT P. 2: IT IS NOT profit maximization. • The goal is “maximization of shareholder wealth” by increasing the price of the common stock over the long term. There are many ways to accomplish this goal. Let us list a few: Wealth Maximization is the key!! • Profit maximization is very important but is only one way to increase shareholder value. – Increasing profits should be an important goal however. – Wall Street focuses on Earnings per Share (not net income) in measuring profits. • Wealth maximization reflects ALL factors that contribute to a higher stock price. HOW DO WE MEASURE WEALTH MAXIMIZATION? • Return on Equity (ROE) – Net income / SH equity OR ROA divided by Total debt/ total assets THIS IS CALLED THE DUPONT MODEL SEE TEXT P. 107 • Increasing ROE – – – – > sales > net income > net margin Make an acquisition where margins are improved – Make a divestiture where profits > – Buy back stock Ways to Maximize S/H Value • Increasing sales – Internal growth – Acquisition • Increasing profit margins – Decreasing costs – Emphasizing profitable lines or products • Buying back stock • Using “Financial Leverage” (Debt) to magnify return to shareowners • Reducing taxes • Can you think of other ways? Maximizing Shareholder Value By buying back stock • RECAP ROE = NET INCOME / TOTAL COMMON EQUITY • COMMON EQUITY = VALUE OF COMMON STOCK ON BALANCE SHEET • USING CASH TO BUY BACK COMMON STOCK REDUCES COMMON EQUITY ACCOUNTING REVIEW FIN 3403 Has it been more than 2 years since you had basic accounting? SUGGESTION Please STUDY ch 3 p. 81-111 NOW While this chapter is assigned later to study ratios, it is important for you to review this material since accounting knowledge is assumed in this course. Ask questions if you are unclear on any concept in this chapter. I am here to help. Income statement review: ACCOUNTING PROFIT SALES (units x price) less Cost Goods sold = GROSS INCOME less SG&A less depreciation = OPERATING INCOME plus other income less interest expense= EBIT (Earnings before interest and taxes) EBIT less interest exp. = PRETAX INCOME less FIT paid = Net Income less Dividends paid to Common shareholders= Contribution to Retained Earnings (PLOWBACK) E.P.S. = Net income / common shs outstanding Why does Wall Street Focus on E.P.S.? • EPS measures the return to the shareowner. Stock prices are usually measured in terms of the PRICE / EARNINGS RATIO which relates S/H value to earnings. • Many things impact E.P.S. Some are outside control of management such as tax rate or mandated depreciation rules. E.P.S. is impacted by many of the same things as S/H Wealth • Sales growth – internal growth – acquisitions • Margins – Raw material costs – Product line emphasis • Use of leverage (debt) • Depreciation • Taxes • New product development (R&D) – Our system rewards innovation with 14 year patent protection – New products and services tend to have higher margins • Share repurchase • Other ideas????? Income statement review contd: CASH FLOW Simple definition= net income + depreciation and other non cash charges SEE Axiom 3 & 4 in text p. 16--cash flow is the measure we use not accounting profits The Efficient Markets Hypothesis (axiom 6) External or macroeconomic factors impacting stock prices: 1. Interest rates & inflation 2. Economic growth, currency & tariffs 3. Competitive pressure 4. Investor confidence Balance Sheet Review ASSETS • Cash + AR + Inv = Current Assets Current = less than 1 year ___________________ • Long term assets – Plant & equipment – “Goodwill” • TOTAL ASSETS LIABILITIES AND S/H EQUITY • Current Liabilities ______________________________________________________ • Long term liabilities – LT debt + Pfd stock • COMMON EQUITY= CS + SURPLUS + RE “Net worth” or equity capital = TA - TL TOTAL LIAB + S/H EQ. The Historical cost concept • Why do we use historical cost? – LIMITATIONS – ADVANTAGES • The Weyerhaeuser Example – ASSETS AT COST LESS LIABILITIES = S/H EQUITY – BVPS = S/H EQUITY / COMMON SHS OUT • What about a company that grew by acquisition? – What is “Goodwill?” – When you buy a company do you pay book value or market? – Companies are often measured in terms of stock price / BVPS or Price/book. What is wrong with this? ASSIGNMENT • SEE SYLLABUS FOR ASSIGNMENTS • MEET WITH YOUR TEAM OUTSIDE CLASS. • CHECK OUT WEB SITE • DOWNLOAD LECTURE NOTES AND OTHER FILES • READ CH. 1 • STUDY CALCULATOR MANUAL AND GET FAMILIAR WITH KEYS TVM AND THE USE OF THE TI BA2+ FINANCIAL CALCULATOR FIN 3403 UCF School of Business R. DIGGLE, CFA RECAP OF LAST LECTURE • We learned about Powerpoint and how you will be using it. • We examined the concept of Wealth Maximization • We compared an income statement and a cash flow statement • We reviewed the 10 axioms of finance summarized on p. 26 of your text. • If you are rusty on accounting --STUDY chapter 3 ASAP • Are there questions from last time??? TEAM ORGANIZATION • ARE YOU SIGNED UP WITH A TEAM? • HAVE YOU PICKED A COMPANY? • DO YOU HAVE A REGULAR TIME SET FOR TEAM MEETINGS THAT IS OK WITH ALL? All teams will meet with • HAVE YOU CHECKED OUT MY WEB SITE? • DO YOU ALL HAVE A TIBA2 + CALCULATOR? • HAVE YOU STUDIED CALC.MANUAL? me at end of this class Company Ratio Analysis Project • Read instructions in Lecture Notes. • Copy ALL Excel spreadsheets on disk onto blank disks for each team member. Return original disk to instructor. Do NOT write on my disk. • Print instructions for each team member. Work on assigning tasks for everyone. • Make a list of questions for instructor. TVM • IN ALL TOPICS WE WILL PROCEED AS FOLLOWS: – – – – – THEORY APPLICATIONS TEXT PROBLEMS ADDITIONAL PRACTICAL PROBLEMS QUESTIONS AND REVIEW • WE WILL REFER TO LECTURE NOTES FIRST AND THEN TO TEXT. TIME VALUE OF MONEY see lecture notes p. 8-10 CONCEPT I: The “PRESENT VALUE” of one dollar received in the FUTURE is worth less than a dollar received today. CONCEPT 2: The further out in the future money is received the less is its “NET PRESENT VALUE” CONCEPT 3: When we compound money (as in a savings account) the FUTURE VALUE is increased in direct proportion to the rate of interest and the number of compounding periods. THE FINANCIAL CALCULATOR AND TVM TABLES HELP YOU MEASURE PV AND FV PRACTICAL THINGS YOU WILL LEARN IN THIS PART OF THE COURSE • Determining how much money you must save for retirement. • Computing a mortgage payment. • Determining a lease payment on a car. • Figuring how much you need to save to put a child through college. • Measuring return on investment QUESTION 1: • ALBERT EINSTEIN WAS ASKED WHAT THE MOST IMPORTANT INVENTION OF MANKIND WAS? WHAT WAS HIS REPLY? • HINT: HE DID NOT SAY E = MC2 HOW MANY OF YOU BELIEVE YOU WILL BE A MILLIONAIRE? • RAISE YOUR HANDS IF YOU FIRMLY BELIEVE YOU CAN DO THIS. • WHAT IS YOUR ACTION PLAN? CAN YOU SAVE $300 PER MONTH? • ASSUME YOU ARE OUT OF UCF AND WORKING. • UCF FINANCE/ACCTG. MAJORS SHOULD START AT $35K • RAISE YOU HAND IF YOU THINK YOU CAN SAVE $300 PER MONTH You can be a Millionaire. I will show you how! Can you Save $300 per month YEAR N=P/Y FV I/Y = 10% X YEARS P/Y =12 PMT = -300 FV I/Y = 15% P/Y =12 PMT = -300 1 $ 3,801 $ 3,906 5 $ 23,425 $ 26,904 10 $ 61,966 $ 83,597 20 $ 229,709 $ 454,786 30 $ 683,798 $ 2,102,946 ANNUALLY AT 10% AND 15% RULE OF 72 = 72 / I/Y NUMBER OF YRS FOR A SUM TO DOUBLE 72/10= 7.2 yrs 72/15=4.8 YRS SEE LECTURE NOTES PP. 8-14 • Turn to page 9 NOW • You may wish to either take notes on Lecture notes or incorporate class notes in with lecture notes. • All material in the next slides is also discussed in lecture notes. • THIS MATERIAL IS THE MOST IMPORTANT MATERIAL IN THE FV CONCEPTS • An INCREASE in I/Y > FV • AS N increases FV > • The more frequent the compounding (P/Y) the more FV >. • FVn= PV (1+r)n Learn this formula. See lecture notes. Formulas will be provided in exam NPV CONCEPTS • As the interest rate I/Y > the < PV • The longer the time period N, the more PV <. • The more frequent the compounding P/Y the more PV <. • PV = FV n lump sum (1+r)n Annuity • PVA = FV + FV + FV (1+R) (1+R)2 (1+R)n (See lec notes p 9) ? HISTORICAL INVESTMENT RETURNS Ibbotson Data 1928 to present NOMINAL COMMON STOCKS 13% LONG TERM BONDS 8% SAVINGS ACCOUNTS AND T BILLS 3% REAL COMMON STOCKS 10% LONG TERM BONDS 5% SAVINGS ACCOUNTS AND T-BILLS 0% Value of $5000 INVESTED ONCE at different rates of return SET BGN, P/Y =1, PV = -5000 RATE: YRS =N 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 $ $ $ $ $ $ $ 3% FV 5,796 $ 6,720 $ 7,790 $ 9,031 $ 10,469 $ 12,136 $ 14,069 $ 5% FV 6,381 $ 8,144 $ 10,395 $ 13,266 $ 16,932 $ 21,610 $ 27,580 $ 8% 12% FV FV 7,347 $ 8,812 10,795 $ 15,529 15,861 $ 27,368 23,305 $ 48,231 34,242 $ 85,000 50,313 $ 149,800 73,927 $ 263,998 Value of $300 PER MONTH at different rates of return SET BGN , P/Y =12 PMT = -300 RATE (I/Y): YEARS N 5 60 10 120 15 180 20 240 25 300 30 360 35 420 $ $ $ $ $ $ $ 5% FV 20,402 46,585 80,187 123,310 178,653 249,678 340,828 $ $ $ $ $ $ $ 8% FV 22,043 54,884 103,811 176,706 285,308 447,108 688,165 12% FV $ 24,501 $ 69,012 $ 149,874 $ 296,777 $ 563,654 $ 1,048,489 $ 1,929,288 USING THE TVM TABLES IN THE BACK OF YOUR TEXT • BACK FLYLEAF • TEXT PP. 883 TO 890 --more detail – B = FV of A Lump sum. A lump sum is • B = pp. 883 to884 one payment or receipt. • C = pp. 885 to 886 – D = FV of an “annuity” • D = pp. 887 to 888 An annuity is a repetitive payment or • E = pp. 889 to 890 income. NOTE: TABLES ARE – C = PV of a lump sum – E = PV of an annuity FOR ANNUAL PERIODS ONLY TABLES APPLICATION • NOTE: Tables will be provided in Exam 1 • STEPS: Must determine WHICH TABLE you must use – COLUMN = interest rate ROW = years – TABLES ARE ANNUAL ONLY • What is the value of $10,000 compounded at 5% for 15 years? – TABLE B p. 883 value = 2.079 – Multiply table value times PV of $10000 – Answer is $20,790 TABLES VS. FINANCIAL CALCULATOR • We will begin using the tables in the back of your text. The tables are ANNUAL. This will help you understand basic concepts. • You will have problems using tables in EXAM 1. • We will move from the tables to your Financial Calculator. Bring the calculator to each class and exam. The new calculators are easy to use and prompt you for an answer. Data can be monthly, daily or any other time frame. Using your Financial Calculator to solve TVM problems • The calculator provides more accurate answers than tables • 5 TVM VARIABLES (excluding P/Y) THE THIRD ROW OF KEYS ON YOUR CALCULATOR P/Y = Compounding periods per year I/Y = Annual interest rate N = (p/y x # of years) PMT FV PV • You can enter data in any order. • YOU CAN SOLVE FOR ANY OF THE VARIABLES CALCULATOR SET UP • Set 4 decimal point accuracy as follows: – 2nd format – DEC = 4 • Set BGN or END as follows: – 2nd BGN (above PMT key) – To toggle press 2nd ENTER to change from BGN to END If BGN is set it appears in upper right of display • Clear REGISTERS – 2nd CLR TVM, 2nd CLR WORK, 2nd QUIT ACCURACY • In Finance we DO NOT ROUND TO WHOLE NUMBERS • Because we are dealing with large numbers, use calculator to 4 decimal points. Show 2 decimals in answer asking for dollars or pct. • If you purchase 750 shares of stock at 33 and 5/8 what is your cost? – 750 x 33.625 = $25,218.75 – IN AN EXAM DOUBLE UNDERLINE YOUR ANSWER. Do not circle it or draw arrows to it. SHOW $ OR % CLEARLY THE 6 TVM KEYS -3rd row • P/Y (2nd P/Y = number of compounding periods per year) • N = number of time periods = P/Y times number of years • I/Y = annual interest rate (8.5% entered 8.5) • PV = Present value (outflows are entered by entering number and pressing MINUS key in lower right) • PMT = annuity payment (inflow or outflow) • FV = Future value USING YOUR TI BA II + FINANCIAL CALCULATOR TO DO TVM PROBLEMS • See lecture notes p.11 • FOLLOW THESE STEPS – READ QUESTION – Clear all registers – Set BGN or End – Set P/Y--2nd P/Y-enter number --press ENTER – Determine what you are solving for – WRITE INPUTS NEATLY • STEPS CONTD – Enter 4 TVM inputs on calculator. I suggest you do it in same order each time. – Enter data with outflows negative – enter CPT and TVM key for solution – Check inputs – Is solution logical? What do the KEYS mean? • P/Y must be reset for each problem. P/Y = number of compounding periods per year • N = years times P/Y. In a 20 year mortgage with monthly payments N = 240. • I/Y is the stated rate. • PMT = Regular repetitive payments such as a mortgage or car payment. Enter outflows as a negative number. • PV = Present value • FV = Future value Enter data in any order Calculator keys contd. • BGN vs END – Set BGN unless otherwise specified in problem. – BGN means interest accrues from day 1. – END means interest accrues at end of period. – ALL EXAM QUESTIONS WILL SPECIFY BGN OR END • If BGN is set, the letters BGN appear in upper right of your calculator window. • CLEARING REGISTERS. There are multiple memory registers in the TI BA II +. Clear them ALL. SELF TEST PROBLEMS • ANSWERS TO ALL ST PROBLEMS ARE AT END OF CHAPTER. • PROBLEMS ARE ON P. 193. ANSWERS ARE ON PP. 204-5. • I recommend you do ST problems FIRST in each chapter to learn how to approach problems. ST problems are NOT in homework assignments. ST PROBLEMS CH 5 P. 193 • ST1 This is the FV of a lump sum--Table A • This is a 2 step problem: – A. 8% column, 3 year line. FACTOR = 1.2597= $31500 – B. 10% column, 3 year line. FACTOR = 1.3310 – answer = $41926 • ST1 on financial calculator: • Set BGN P/Y = 1 • n=3 • i/y = 8 • pv = -25000 (OUTFLOW) • FV (PART A) = $31492--Note that this differs slightly from table amount SIMPLE TVM PROBLEMS 1. LUMP SUM FV You inherit $50,000 now. You invest this money at 8% interest. What is this worth in 5 years? 2. ANNUITY FV You save $500 per month at 10% return. What is this worth in 20 years? 3. LUMP SUM PV You inherit $50000 in 10 years. Assuming an 8% return, what is this worth today? 4. ANNUITY PV You win the lottery. You are paid $1000 per month over 30 years. At an 8% return, what is this worth today? SIMPLE TVM PROBLEMS CALCULATOR SOLUTIONS • PROBLEM 1 – – – – – – – SET BGN P/Y = 1 SET ENTER CLEAR REGISTERS N=5 I/Y = 8 PV = - 50000 SOLVE FOR FV – FV =$73466 • PROBLEM 2 – – – – – – – SET BGN P/Y = 12 SET ENTER CLEAR REGISTERS N = 20 X 12 = 240 I/Y = 10 PMT = -500 SOLVE FOR FV – FV = $382848 SIMPLE TVM PROBLEMS CALCULATOR SOLUTIONS • • • • • • • • PROBLEM 3 SET BGN P/Y = 1 SET ENTER CLEAR REGISTERS N = 10 I/y = 8 FV = 50000 SOLVE FOR PV • PV = -$23160 • • • • • • • • PROBLEM 4 SET BGN P/Y = 12 SET ENTER CLEAR REGISTERS N = 360 (30 X 12) I/Y = 8 PMT = 1000 SOLVE FOR PV • PV = -$137192 ASSIGNMENT • COMPLETE SIMPLE TVM PROBLEMS AT END OF CH. 5. DO THIS WITH YOUR STUDY GROUP. Print your name, date, course and section and problem ch 1 on page one of your assignment. STAPLE. • I am providing solutions. They are also on web site • Begin work on PROBLEM HANDOUT IN YOUR STUDY GROUP. • LIST ANY QUESTIONS YOU MAY ENCOUNTER IN USING YOUR CALCULATOR OR TABLES. TEAM MEETINGS • Is there anyone not signed up on a team? • Do you have a meeting time set? • Pick a company for team analysis project ONE EXCEL DISK GIVEN TO EACH TEAM FOR NEXT TIME COPY DISK FOR EACH TEAM MEMBER AND RETURN ORIGINAL TO INSTRUCTOR Do homework problems assigned. Homework must be STAPLED and have name, assignment Fin 3403, section and date on p. 1 LEC 3 FIN 3403: TVM PROBLEMS AND QUESTIONS • IN THIS CLASS WE WILL: – REVIEW USE OF YOUR TIBA2+ CALCULATOR – REVIEW THE STEPS IN SOLVING ALL TVM PROBLEMS – DO THE HOMEWORK IN CH. 5 – EXAMINE TIBA2+ OTHER APPLICATIONS – TIME PERMITTING--START ON PROBLEM HANDOUT REVIEW: STEPS IN SOLVING TVM PROBLEMS ON AN EXAM • See lecture notes p.11 • FOLLOW THESE STEPS – READ QUESTION – Clear all registers – Set BGN or End – Set P/Y--2nd P/Y-enter number --press ENTER – Determine what you are solving for – List inputs on TIBA2+ • STEPS CONTD – Enter 4 TVM inputs on calculator. I suggest you do it in same order each time. – Enter data with outflows negative – enter CPT and TVM key for solution – Check inputs – Is solution logical? COMMON EXAM MISTAKES • Failure to clear registers between EACH problem • Failure to reset P/Y – Default value is 12 since things like a mortgage or car payment are made monthly • Failure to set BGN or END--given for each problem • setting N = yrs x P/Y – YRS 2nd N – Press N again • MOST IMPORTANT: – FAILURE TO NEATLY LIST INPUTS: – I WILL GIVE PARTIAL CREDIT IF YOU DO THIS • Failure to check inputs twice. Is answer logical? HOW TO GET AN “A’ ON EXAM 1 • EXAM 1 WILL FOCUS ON TVM. • WORK PROBLEMS Be sure you understand each step. Work with classmates. • ASK QUESTIONS!!! This is confusing at first but you will get the hang of it. • Read the problem over carefully before starting! • Always follow the steps I just outlined and draw a time line. • Write down inputs. • Go through handouts. Solve them on your calculator. CH 5 HOMEWORK • SET A: 5-1 TO 5-15, 5-19 TO 5-21 – SOLUTIONS PROVIDED THROUGH 5-6 A – PARTIAL SOLUTIONS PROVIDED FOR OTHER PROBLEMS – TABLE SOLUTIONS PROVIDED TO ANNUAL PROBLEMS ONLY 5-1A TO 5-7A – TIBA2+ SOLUTIONS PROVIDED --answers in italics THE TI BA II + FINANCIAL CALCULATOR: ADVANCED FUNCTIONS • SPREADSHEET REGISTERS – During the term we will use several built in worksheets. Become familiar with them and read how to use them in the TI manual • Use the right spreadsheet to check work on TVM keys • Days between dates – 2nd 1 solve for DBD – DAYS BETWEEN DATES • Delta % (CHANGE) – 2nd 5 • Cash Flow worksheet – 2nd CF – use in 2nd part of course • Bond worksheet – 2nd and 9 – use in last 3rd. of course OTHER TVM PROBLEMS • You want to buy a home. You decide on a 30 year mortgage with an interest rate of 6.75%. The home costs $100,000 and you put 20% down. How much is your monthly payment for P&I (principal & interest)? SET END. • LIST INPUTS – – – – – – – SET END P/Y = 12 N = 360 I/Y = 6.75 PV = - 80000 (MTG) FV = 0 SOLVE FOR PMT – PMT = 518.87 OTHER TVM PROBLEMS • You want to retire at age 60. You are 25. • You figure you need $1 million to retire comfortably. • You can save $300 per month. • What return do you need to achieve your goal? • SET END --THIS WILL ALWAYS BE GIVEN • • • • • • P/Y = 12 n = 420 (35*12) PV = 0 PMT = -300 FV 1000000 SOLVE FOR I/Y • I/Y = 9.49% OTHER TVM PROBLEMS • You LEASE a car. • The cost is $20,000 + 6% tax and $300 dealer prep. • The dealer is offering 0.99% financing. • The term is 3 years. • The residual is $10000 • What is the payment? • • • • • • • Set BGN. P/Y = 12 n = 36 I/Y = 0.99 PV = - 21500 FV = 10000 SOLVE FOR PMT • PMT = 332.31 TVM PROBLEMS: HANDOUT TVM will be 70-80% of Exam 1 Practice using your calculator to solve problems in text, workbook and handouts Let us go through a series of real world applications of TVM that you will use in your own personal finance. PLEASE INTERRUPT AT ANY TIME WITH QUESTIONS. DON’T BE SHY! RULE OF 72 • WHAT IS IT? NUMBER OF YEARS FOR A SUM TO DOUBLE • 72 / STATED INTEREST RATE = YRS TO DOUBLE • At 10% money doubles in 7.2 years: – 72/ 10 = 7.2 • At 15% money doubles in 4.8 years: – 72/15 = 4.8 • At 5% money takes 14.4 years to double. CH 1 HOMEWORK TVM • 5-1A AND 5-2A P. 193 • 5-3A - 5-9A P. 194 • 5-10A -5-15A P. 195 • 5-19A - 5-21A P. 196 • SOLUTION ON DISK + handout (1 per team please) • DO PROBLEMS IN YOUR TEAM • Which table? • Determine table value. • List calculator inputs • Solutions page shows answer in bold italics. • If unclear, write down questions for class.