Lab 5 Part 2
advertisement

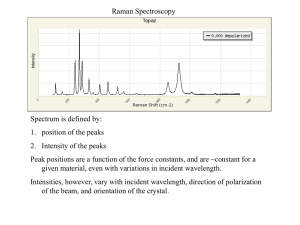
Modern Optics Lab Lab 5 Part 2: Experiments involving Light Polarization Topics Use birefringence to generate and quantify elliptically polarized light. Understand, measure and characterize the optical activity of syrup. Modern Optics Lab Lab 5 Part 2: Experiments involving Light Polarization Birefringence 270 0 Fast axis: n2 180 90 c v1 n1 Slow axis : n1 c v2 n2 The birefringent retarder in your box causes a phase delay of 140nm (approximately 0.22*llaser). Phase delay depends on the thickness of the birefringent material. Modern Optics Lab Lab 5 Part 2: Experiments involving Light Polarization Retardation in a ”l/4-waveplate” for light polarized linearly at 45 with respect to main axes (=superposition of two orthogonal in-phase linearly polarized waves) Fast axis Slow axis y x F E A y D C y B y x D C B A y E x x x y F x Has fallen behind by l/4 y x Polarization before the l/4-waveplate: When looking against the direction of light propagation: A, B, C, … pass you by successively. Modern Optics Lab Lab 5 Part 2: Experiments involving Light Polarization Polarization after the ”l/4-waveplate” Fast axis Slow axis C D y x F B E y y y A C B x D x x A y E x y F x y x This light is “left-circularly” polarized (What does electric field do at one point in space when looking against propagation direction – Physics definition; careful: EE is opposite!). Modern Optics Lab Lab 5 Part 2: Experiments involving Light Polarization V.D Measure transmitted intensity I as a function of Retarder orientation Q Polarizer ( to laser polarization) Retarder To photometer Laser Vary the orientation Q of retarder. Measure I(Q) and plot I versus Q . Discuss the result in terms of the retardation properties of the retarder. Modern Optics Lab Lab 5 Part 2: Experiments involving Light Polarization V.D Measure intensity I as a function of polarizer orientation Q Retarder at 45 angle to laser polarization. Polarizer/Analyzer To photometer Laser Set retarder so that either the slow or the fast axis is at a 45 angle with respect to the laser polarization. Vary the orientation Q of polarizer(used as an analyzer). Measure I(Q) and plot I versus Q on polar graph paper. Write down exactly how the retarder was oriented with respect to the laser polarization and figure out whether the light got left- or right-polarized in your setup. Modern Optics Lab Lab 5 Part 2: Experiments involving Light Polarization Optical Activity Left circularly polarized light n Right circularly polarized light n Modern Optics Lab Lab 5 Part 2: Experiments involving Light Polarization Linearly Polarized Light = Superposition of Circularly Polarized Light (left and right) + = Modern Optics Lab Lab 5 Part 2: Experiments involving Light Polarization …and if one circular polarization is phase shifted… + = Modern Optics Lab Lab 5 Part 2: Experiments involving Light Polarization Rotation Due to Optical Activity b n and n d Linearly polarized light Linearly polarized light – different orientation Polarization rotated by angle b Rotation angle : b d nleft nright l Modern Optics Lab Lab 5 Part 2: Experiments involving Light Polarization Dextrorotary versus Levorotary (“Looking” against the direction of light propagation.) Dextrorotary Levorotary b b before after Optical activity causes a rotation of polarization to the right. after before Optical activity causes a rotation of polarization to the left.