Physical Layer
advertisement
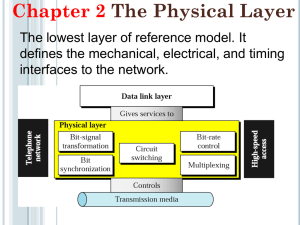
Physical Layer B. Konkoth The physical layer is responsible for movements of individual bits from one node to the next. Physical layer Physical Links How to make computers talk across a wire How to share the wire 4 From Signals to Packets Analog Signal “Digital” Signal Bit Stream Packets 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 0100010101011100101010101011101110000001111010101110101010101101011010111001 Header/Body Packet Transmission 5 Sender Header/Body Header/Body Receiver Analog An Analog signal is any continuous signal for which the time varying feature is a representation of some other time varying quantity. For example, in sound recording, fluctuations in air pressure (sound) strike the diaphragm of a microphone which induces corresponding fluctuations in the current produced by a coil in an electromagnetic microphone, or the voltage produced by a condenser microphone. The voltage or the current is said to be an "analog" of the sound. Digital A data technology that uses discrete (discontinuous) values The word digital is most commonly used in computing and electronics, especially where real-world information is converted to binary numeric form as in digital audio and digital photography. Transmission Media Transmission medium: the physical path between transmitter and receiver. Communication of electromagnetic waves is guided or unguided. Guided media: waves are guided along a physical path (eg, twisted pair, coaxial cable and optical fiber). Unguided media: means for transmitting but not guiding electromagnetic waves (eg, the atmosphere and outer space). 8 Repeaters or amplifiers may be used to extend the length of the medium. Transmission Media Choices Twisted pair Coaxial cable Optical fiber Wireless communications 9 Cables Coaxial Twisted pair Fiber optics Twisted Pair Two insulated wires arranged in a spiral pattern Copper or steel coated with copper The signal is transmitted through one wire and a ground reference is transmitted in the other wire. Typically twisted pair is installed in building telephone wiring. 11 Unshielded Twisted-Pair (UTP) Typically wrapped inside a plastic cover (for mechanical protection) A sample UTP cable with 5 unshielded twisted pairs of wires Insulator 12 Metal Categories of UTP Cables UTP cables are classified according to the quality: Category 1 ― the lowest quality, only good for voice, mainly found in very old buildings, not recommended now Category 2 ― good for voice and low data rates (up to 4Mbps for low-speed token ring networks) Category 3 ― at least 3 twists per foot, for up to 10 Mbps (common in phone networks in residential buildings) Category 4 ― up to 16 Mbps (mainly for token rings) Category 5 (or 5e) ― up to 100 Mbps (common for networks targeted for high-speed data communications) Category 6 ― more twists than Cat 5, up to 1 Gbps 13 Shielded Twisted-Pair (STP) 14 STP cables are similar to UTP cables, except there is a metal foil or braided-metal-mesh cover that encases each pair of insulated wires Twisted Pair Limited in distance, bandwidth and data rate due to problems with attenuation, interference and noise 15 Issue: cross-talk due to interference from other signals “shielding” wire (shielded twisted pair (STP)) with metallic braid or sheathing reduces interference. “twisting” reduces low-frequency interference and crosstalk. Coaxial Cable Center conductor Dielectric material 16 Braided outer conductor Outer cover Coaxial Cable Divided into two basic categories for coax used in LANs: 17 50-ohm cable [baseband] 75-ohm cable [broadband or single channel baseband] In general, coax has better noise immunity for higher frequencies than twisted pair. Coaxial cable provides much higher bandwidth than twisted pair. However, cable is ‘bulky’. Communication channel Baseband – sends 1 signal or 1 channel at any given time Broadband - enables a single wire to carry multiple signals at the same time Optical Fiber Optical fiber: a thin flexible medium capable of conducting optical rays. Optical fiber consists of a very fine cylinder of glass surrounded by concentric layers of glass. Attenuation in the fiber can be kept low by controlling the impurities in the glass. 19 Optical Fiber (a) Geometry of optical fiber light cladding core (b) Reflection in optical fiber c 20 jacket Wireless Infrared - Infrared radiation (IR) is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength between 0.7 and 300 micrometers Microwave - Microwaves are electromagnetic waves with wavelengths ranging from as long as one meter to as short as one millimeter Radio - Radio waves transmit music, conversations, pictures and data invisibly through the air, often over millions of miles - wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum longer than microwave Electromagnetic spectrum