Curved Mirrors: Concave
advertisement

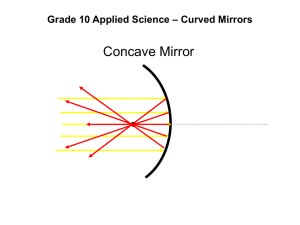
Curved Mirrors: Concave Applied Physics and Chemistry Reflection Lecture 2 Curved mirrors • What if the mirror isn’t flat? – light still follows the same rules, with local surface normal • Parabolic mirrors have exact focus – spherical mirrors may experience distortion – used in telescopes, backyard satellite dishes, etc. – also forms virtual image education.jlab.org/powerpoint/0708_optics_mirrors_and_lenses.ppt 0 82a425d7 Concave Mirrors • Curve inward • May be real or virtual image education.jlab.org/powerpoint/0708_optics_mirrors_and_lenses.ppt Concave Mirror • The center C of a concave mirror is outside the mirror. • Focal point F is also outside the mirror, half way between the center and the surface of the mirror. • The focal length f is half of the radius of curvature. www.physics.umd.edu/courses/Phys106/FL11.ppt Image from a concave mirror: case 1 Step 1 Step 3 Step 2 Step 4 www.physics.umd.edu/courses/Phys106/FL11.ppt Image from a concave mirror: case 1 www.physics.umd.edu/courses/Phys106/FL11.ppt Properties of the Image • If we put an object outside of the center of a concave mirror, we find the image is – Real, in the sense that all light rays pass through the image. – Inverted, in the sense that the direction of the arrow has been changed. – The image is smaller! www.physics.umd.edu/courses/Phys106/FL11.ppt Animation for case 1 www.physics.umd.edu/courses/Phys106/FL11.ppt Image for a concave mirror: case 2 www.physics.umd.edu/courses/Phys106/FL11.ppt • If the object is in between the center and the focal point, the image is – Real – Inverted – Magnified in the sense that the image is bigger than the real object. www.physics.umd.edu/courses/Phys106/FL11.ppt Animation for case 2 www.physics.umd.edu/courses/Phys106/FL11.ppt Image from a concave mirror: case 3 www.physics.umd.edu/courses/Phys106/FL11.ppt Image from a concave mirror: case 3 www.physics.umd.edu/courses/Phys106/FL11.ppt Animation for case 3 www.physics.umd.edu/courses/Phys106/FL11.ppt Properties of the image • If the object is closer to the mirror than the focal point F, the image is – Virtual, it is behind the mirror – Upright, not inverted – Magnified www.physics.umd.edu/courses/Phys106/FL11.ppt Java Applet • http://www.microscopy.fsu.edu/primer/java/ mirrors/concave.html