Camera Parts
advertisement

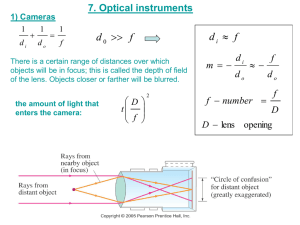
Camera Parts and Functions Camera Parts Lens Controls direction of light coming into the camera; focuses the photo Aperture Controls the amount of light admitted into the camera. How much light is allowed in. Shutter Controls length of exposure. How long the light is allowed in. Exposure (no not the dirty kind) Exposure is the total amount of light received by a photosensitive surface or an area of such a surface, expressed as the product of the degree of illumination and the period of illumination. Or simply put: taking a photo determined by the proper intensity of light and time, taking into account the films’ sensitivity. Or even more simply Intensity Megapixels Time Exposure When taking a photo consider these three steps for light: 1. know your ISO, choose the correct one 2. Adjust the aperture 3. Adjust the shutterspeed ISO (film’s sensitivity to light) Affects quality of picture = the slower (lower numbers) create more graininess (a sandlike appearance) and show less detail • ISO 50 / ISO 100: Bright Sun, Portrait Mode, Beach, Snow, Indoor Flash • ISO 200 / ISO400: Cloudy Day, Sports, Fast Shutter Speeds Bright Sun, Landscape • ISO 400 + : Low Light, Indoor Without a Flash, Night, Fast Shutter Speeds During Cloudy Day Megapixels (digital ISO) • Digital cameras capture images as pixel elements, known as pixels – 1 megapixel = one million pixels • The more pixels, the higher the image resolution – resolution = picture quality (how good it looks) Aperture • Measured in F/stops • affects the sharpness of your picture, but in a different way. • changes the depth of field, the depth in a scene from foreground to background that will be sharp in a photograph. – Smaller apertures increase depth of field while larger ones decrease it. Depth of Field • Where and how much of the scene a camera is focusing on Shutter Speed • controls exposure • control over how motion is captured in a photograph. – The longer the shutter is open, the more a moving subject will be blurred in the picture or that you will move and cause unintended blur to the whole photo Aperture Shutterspeed • They work in tandem or seesaw Meter • The meter measures the amount of light in the scene and calculates the best exposure value. • Most cameras have exposure meters built into them. Some in-camera meters set exposure automatically • All in-camera meters are reflective – measure the light reflected by the subject. Types of Camera Old School vs. New School Old School (film cameras) • • • • • • Simple Rangefinder Single Lens Reflex (SLR) Twin Lens Reflex (TLR) View Press Simple vs Rangefinder Simple • Fixed focus, aperture and shutterspeed. Rangefinder • Focusing device (rangefinder) • Variable aperture and shutterspeed SLR vs TLR Single Lens Reflex • Sames lens for viewing, focusing and exposure. • Variable shutterspeed, aperture and lens Twin Lens Reflex • One lens for focusing and viewing • One lens for exposure • Vairable shutterspeed, aperture and lens View vs Press View • Viewing and focusing done on ground glass plate. • Changeable lenses • Variable aperture and manual shutterspeed. Press • • • • Rangefinder for focus Ground glass for viewing Changeable lenses Variable aperture and shutterspeed. New School (Digital) • Simple • Rangefinder • Point and Shoot – Camera Phones • Fixed Lens • Single Lens Reflex Point and Shoot • • • • • Variable shutterspeed, aperture Mode settings!!! fewer controls than other digital cameras Small, bordering on tiny. Zoom lenses (optical and digital) • Camera Phones – Convienent and fastest growing purchases – image quality is improving very slowly and doesn't yet match that of dedicated cameras. Zoom Lenses • • Optical zoom true zoom- as the lens extends the object gets closer produces the best quality images • • • • Digital Zoom simulated zoom enlarges the central portion of an image. actual length of the lens does not change. pre-crops the center area of an image. resolution is reduced, giving the appearance of zooming in. Fixed Lens vs. SLR (digitally) Fixed Lens • Variable shutterspeed, aperture and focus • Non changeable lens • Same lens for viewing, focusing and exposure. Single Lens Reflex • Sames lens for viewing, focusing and exposure. • Variable shutterspeed, aperture and lens Film vs. Digital All cameras are basically black boxes with a lens to gather the light, a means to focus the image, an aperture that determines how bright the light is, and a shutter that determines how long the light enters. Film •Light enters through the lens •Light “burns” the silver halide emulsion on the film •Film is developed Digital •Light enters through the lens •Pixels collect light intensities •Converts into digital number and retranslates for the screen Settings and Modes Automatic Modes AUTO P AF • Auto- fully automatic, point-and-shoot mode; camera selects all settings. • Program AE - camera automatically sets the shutterspeed and aperture based on the brightness of the scene. User can adjust some settings such as exposure compensation, white balance, ISO, focusing and metering modes. • Auto Focus AF- camera selects depth of field and subject of focus. Auto Scene Modes • Portrait – photos of people during the day. Aperture is larger (less depth of field, blurry background), “ISO” is slower for less fine detail, shutterspeed is variable, but quicker to avoid capturing movement. Flash used when necessary. Focus is 3-10 ft in front of you. • Night Portrait - take photos of a subject against a night scene. Aperture, focus and “ISO” are same as portrait but shutterspeeds are low - Use of tripod recommended. The built-in flash and red-eye reduction are enabled. • Landscape - take photos of wide scenes. Aperture is small to pick up detail, shutterspeed is vairable, “ISO” is fast for detail. No flash. Focuses on a distant object 10 - ∞ ft. • Night Scene - photograph nightscapes. Same as Landscape but with slow shutterspeeds. Use of tripod recommended. Focus is 10 - ∞ • Macro - take close-up shots of small objects, flowers and insects. Aperture small for detail, shutterspeed is fast, and “ISO” is fast. Focus is 0-3 ft. Hold the camera steady or use a tripod. • Sports- take photos of a fast moving subject. Aperture is smaller (more depth of field), fast shutter speeds to “freeze” the action and fast “ISO” to capture more light. Best when taking photos bright light; pre-focusing recommended. Focus is 3-10 ft. • Slow Shutterspeed –intentionally blur moving objects. Aperture small for deetail, shutterspeed is slowed to blur movement and “ISO” is slowere for less detail. Focus is 3-10 ft. Auto Special Lighting Modes • Beach/Snow - photograph beach, snow and sunlit water scenes. Exposure and white balance are set to help prevent the scene from becoming washed out looking. • Fireworks - shutter speed and exposure are set for shooting fireworks; pre-focusing & use of tripod recommended. • Party - take photos in a dim lit room; aperture and shutter speed are automatically adjusted for room brightness. Captures indoor background lighting or candlelight. Hold the camera very steady when using this mode. • Sunset - take photos of sunsets and sunrises; helps keep the deep hues in the scene. • Aquarium (Underwater) - selects ISO, white balance and color balance to photograph fish and other items in an indoor aquarium. • Foliage - photographs autumn, garden and similar scenes in vivid colors. • Backlight - eliminates dark shadows when light is coming from behind a subject, or when the subject is in the shade. The built-in flash automatically fires to “fill in” the shadows. Semi-automatic/Manual Modes Tv • Shutter priority (Tv) - User selects shutter speed and the camera automatically selects the aperture. Av • Aperture priority (Av) - User selects aperture and the camera automatically selects shutter speed. M• Manual mode- User manually selects the shutter speed and aperture. An Exposure Display visible on the LCD or electronic viewfinder shows the amount a photo will be over- or underexposed. Long exposures are taken in manual mode. Drive Modes • Single Shot- Press on the shutter release button and takes one picture • Continuous or Burst- Press on the shutter release button and it takes continuous pictures until you release the button • Self Timer – used is to take photos of a group or scene, or when you want to take a self-portrait. – The camera must be set on a tripod or level surface – taking close-up shots. – taking photos in low light without a flash or shooting long exposures. Flash Modes A • Automatic mode — Flash triggers automatically when the camera determines more light is needed in a scene. Turn off this mode in places that forbid inside flash photography such as museums. • Red-eye reduction — Fires the flash several times just prior to exposing a photo. Reduces the reflection in a subject’s eyes that causes red-eye. The rapid flashes cause a subject’s pupils to contract and helps minimize the red-eye effect. Inform subjects before using this mode as the pre-flashes can cause people to look startled. • Forced (fill-in) flash — Keeps the flash on in situations where automatic mode would keep it off. Used when additional illumination is needed, such as when the main source of light is in the back of a subject or shadows prevent details from showing. Can be effectively used outside when subjects are within the flash range. • Suppressed flash — Turns the flash off. • Slow sync (also called night scene) — Use to capture a dimly lit background at night. The flash fires briefly to light the foreground subject. Tripod or other camera support recommended. SLOW REAR • Rear-curtain sync — Similar to slow synch but flash doesn’t fire until right before the shutter closes. Tripod or other camera support recommended. Sources http://afbgraphics.com/Client4/ART141%20Intro%20to%20B&W%20Ph otography/LECTURES/class_2_CAMERACONTROLS_EXPOSURE .ppt#340http://afbgraphics.com/Client4/ART141%20Intro%20to%20 B&W%20Photography/LECTURES/class_2_CAMERACONTROLS_ EXPOSURE.ppt#340,30,Bring http://www.digicamhelp.com/camera-features/camera-modes/flashmodes/ https://www.images.google/imgres?imgurl http://www.photo.net/equipment/digital/basics/digital_zoom_vs_optical_ zoom.jpg&imgrefurl http://www.shortcourses.com/guide/guide1-3.html