Optics_lenses
advertisement

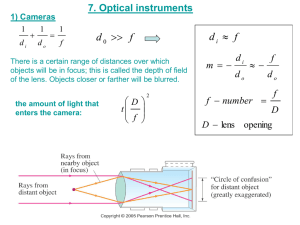
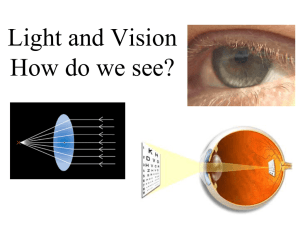
... MAKES YOUR NETWORK SMARTER Lenses & Filters Lens and optical filter in a camera Flash memory Camera functions Compression CPU DRAM Lens Optical filter Image sensor Ethernet Interface Filters - IR filter 100 Wavelength Y Rays Radio Waves X Rays UV IR Radar TV 80 Sound Radio 60 Visible light I/R 40 20 300 400 500 600 700 800 Wavelength in nanonmetres Filters 900 0 300 400 500 600 700 800 Transmission curve (Example) the Infrared light invisible for the human eye but visible for cameras 900 1000 1100 Filters - Optical low pass filter Splits the incoming light Improves color representation Filters – Example: Without optical low pass filter Filters – Example: With optical low pass filter The Lens Focal length Wid ng a e ew i v of le ( ) f view) o le g n a o t Tele(pho Mount Iris Lens element Angle of view Horizontal Angle of View (HOV) Same as “Field of view” What the camera with a given lens can “see” Horizontal, vertical or diagonal Vertical Angle of View (VOV) Lenses - Focal length Focal point Focal length A small focal length gives wide angle view. A large focal length gives tele view. Lenses – Calculating the focal length W I D f Calculating the focal length (f): f = D*I/ W Which focal length is needed for the application? Lenses – Depth of field Focus point Dep The th o f fie ld regions in front of and behind the focus point where the image remains in focus 0 0 5' 1.5m 10' 3m 15' 4.5m 20' 6m 8 8 Lenses - Aperture 25' 7.5m F2 F5.6 F16 F number f1.0 f1.2 f1.4 f1.7 f2.8 f4.0 f5.6 % of light passed 20% 14.14% 10% 7.07 2.5% 1.25% 0.625% Lenses – Lens Iris A wire between the camera and the lens is needed with an automatic iris lens. Opening in the lens that controls the amount of incoming light that reaches the image sensor Lenses - Lens elements Spherical lens element Image plane A lens contains several lens elements Aspherical elements reduces distortion Aspherical lens element Image plane Lenses- Mount standards 17.526 mm 12.5 mm 5 mm spacer C-mount Lens CS-mount ¬ 12.5mm from camera edge to sensor C-mount ¬ 17.5mm from camera edge to sensor ¬ Conversion C to CS is possible CS-mount Lens Lenses – Sensor dependency Image Size Image Circle Image Size Vertical Horizontal The lens must make an image circle large enough to cover the sensor Larger sensor = more expensive lens The size (e.g. 1/3”) can not be measured anywhere. corresponds to old TV camera tubes Low end lenses produces unsharp corners Lenses - Resolution 1/4" 1/3" 4.5 6 8 11 1/2" 2/3" 1/4" 2/3" 1/2" 1/3" A typical CCTV lens has a resolution of 100 lines/mm. 1" 16 1" Lenses – Types: Wide angle Focal point Short focal length Large angle of view Good in low light Good depth of field “Barrel” distortion Not for long distances Lenses – Types: Wide angle image example Example of barrel distortion & missing optical low pass filter Lenses – Types: Telephoto Focal point Long focal length Good on long distance No barrel distortion Shallow (small ) depth of field Bad in low light Lenses – Types: Vari-focal The focal length can be adjusted Needs refocusing after focal length adjustment Less precision needed in focal length calculation Lenses – Types: Zoom – the focal length can be adjusted with maintained focus Often motorised. Zoom Special Lenses – Fish eye Extremely wide angle (~180 deg) lenses are called “Fish eye lenses” Lenses – Example: Fisheye image A fish eye lens on a high resolution camera can work as a pan/tilt/zoom camera Special Lenses – Pin hole Exit pupil is 1-3mm. Can be either low end $1 lenses or high end >$500 lenses. Questions & Answers 2 3 YZ XYZ 395 X Y ZK D HU P PO 15 PQ 10.000 PQ O YZ KH D O