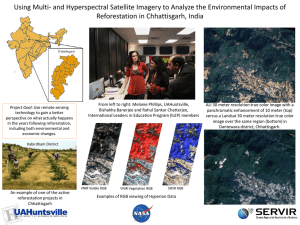
Color Image Processing
advertisement

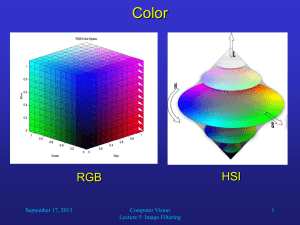
بسمهتعالي Digital Image Processing Color Image Processing (Chapter 6) H.R. Pourreza H.R. Pourreza Preview Motive - Color is a powerful descriptor that often simplifies object identification and extraction from a scene. - Human can discern thousands of color shades and intensities, compared to about only two dozen shades of gray. H.R. Pourreza Preview H.R. Pourreza Preview H.R. Pourreza Preview Color image processing is divide into two major area: Full-Color Processing Pseudo-Color Processing H.R. Pourreza Color Fundamentals The experiment of Sir Isaac Newton, in 1666. H.R. Pourreza Color Fundamentals (con’t)c H.R. Pourreza Color Fundamentals (con’t)c Basic quantities to describe the quality of light source: Radiance: Total amount of energy that flows from the light source (in W). Luminance: A measure of the amount of energy an observer perceives from the light source (in lm) Brightness: A subjective descriptor that embodies the achromatic notion of intensity and is practical impossible to measure. H.R. Pourreza Color Fundamentals (con’t) Standard wavelength values for the primary colors H.R. Pourreza Color Fundamentals (con’t) H.R. Pourreza Color Fundamentals (con’t) The characteristics generally used to distinguish one color from another are Brightness, Hue, and Saturation. Hue: Represents dominant color as perceive by an observer. Saturation: Relative purity or the amount of white light mixed with a hue Hue and saturation taken together are called Chromaticity, and therefore, a color may be characterized by its Brightness and Chromaticity. H.R. Pourreza Color Fundamentals (con’t) Tri-stimulus values: The amount of Red, Green and Blue needed to form any particular color Denoted by: X, Y and Z Tri-chromatic coefficient: X x X Y Z Y y X Y Z x y z 1 H.R. Pourreza Z z X Y Z Color Fundamentals (con’t) Chromaticity Diagram Green Point = 62% green, 25% red, 13% blue. H.R. Pourreza Color Fundamentals (con’t) Color Gamut produced by RGB monitors Color Gamut produced by high quality color printing device H.R. Pourreza Color Models The purpose of a color model (also called color space or color system) is to facilitate the specification of colors in some standard, generally accept way. RGB (red,green,blue) : monitor, video camera. CMY(cyan,magenta,yellow),CMYK (CMY, black) model for color printing. and HSI model,which corresponds closely with the way humans describe and interpret color. H.R. Pourreza The RGB Color Models H.R. Pourreza The RGB Color Models (con’t) 2 8 3 16,777,216 Colors H.R. Pourreza The RGB Color Models (con’t) H.R. Pourreza The RGB Color Models (con’t) Safe RGB Colors (Safe Web colors) H.R. Pourreza The RGB Color Models (con’t) H.R. Pourreza The CMY and CMYK Color Models Cyan, Magenta and Yellow are the secondary colors of light Most devices that deposit colored pigments on paper, such as color printers and copiers, require CMY data input. C 1 R M 1 G Y 1 B H.R. Pourreza The HSI Color Models H.R. Pourreza The HSI Color Models H.R. Pourreza The HSI Color Models H.R. Pourreza The HSI Color Models Converting colors from RGB to HSI H 360 if B G if B G 1 [( R G ) ( R B )] 1 2 cos 2 1/ 2 [( R G ) ( R B )( G B )] 3 S 1 [min(R, G, B)] ( R G B) 1 I ( R G B) 3 H.R. Pourreza The HSI Color Models Converting colors from HIS to RGB RG sector : 0 H 120 B I (1 S ) S cos H R I 1 cos( 60 H ) G 3I ( R B) H.R. Pourreza The HSI Color Models Converting colors from HIS to RGB GB sector : 120 H 240 H H 120 R I (1 S ) S cos H G I 1 cos( 60 H ) B 3I ( R G) H.R. Pourreza The HSI Color Models Converting colors from HIS to RGB BR sector : 240 H 360 H H 240 G I (1 S ) S cos H B I 1 cos( 60 H ) R 3I (G B) H.R. Pourreza The HSI Color Models H.R. Pourreza The HSI Color Models RGB H H S S I I RGB H.R. Pourreza Pseudocolor Image Processing Pseudocolor (also called false color) image processing consists of assigning colors to gray values based on a specified criterion. The principal use of pseudocolor is for human visualization and interpretation of gray-scale events in an image or sequence of images. H.R. Pourreza Intensity Slicing H.R. Pourreza Intensity Slicing (con’t) H.R. Pourreza Intensity Slicing (con’t) H.R. Pourreza Intensity Slicing (con’t) H.R. Pourreza Gray Level to Color Transformations H.R. Pourreza Gray Level to Color Transformations H.R. Pourreza Gray Level to Color Transformations H.R. Pourreza Gray Level to Color Transformations H.R. Pourreza Gray Level to Color Transformations H.R. Pourreza Gray Level to Color Transformations H.R. Pourreza Basic of Full Color Image Processing Let c represent an arbitrary vector in RGB color space cR R c cG G cB B For an image of size M*N, c R ( x, y ) R ( x, y ) c( x, y ) cG ( x, y ) G ( x, y ) cB ( x, y ) B ( x, y ) H.R. Pourreza Basic of Full Color Image Processing H.R. Pourreza Basic of Full-Color Image Processing Major categories of full-color Image processing: Per-color-component processing Vector-based processing H.R. Pourreza Basic of Full-Color Image Processing Color Transformation Processing the components of a color image within the context of a single color model. g ( x, y) T f ( x, y) si Ti r1 , r2 ,, rn , Color components of g i 1,2,...,n Color components of f Color mapping functions H.R. Pourreza Full-Color Image Processing Color Transformation CMYK RGB Some difficulty in interpreting the HUE: Discontinuity where 0 and 360º meet. HSI H.R. Pourreza Hue is undefined for a saturation 0 Full-Color Image Processing Color Transformation: Modify the Intensity g ( x, y) kf ( x, y) si kri s1 r1 i 1,2,3 si kri (1 k ) i 1,2,3 H.R. Pourreza s2 r2 s3 kr3 Full-Color Image Processing Color Transformation: Color Complement H.R. Pourreza Full-Color Image Processing Color Transformation: Color Complement H.R. Pourreza Full-Color Image Processing Color Transformation: Color Slicing Motive: Highlighting a specific range of colors in an image Basic Idea: Display the color of interest so that they stand out from background Use the region defined by the colors as a mask for further processing 0.5 si r i W if rj a j 2 any1 j n , otherwise H.R. Pourreza i 1,2,...,n Full-Color Image Processing Color Transformation: Color Slicing 1. Colors of interest are enclosed by cube (or hypercube for n>3) 0.5 si r i W if rj a j 2 any1 j n , otherwise i 1,2,...,n 2. Colors of interest are enclosed by Sphere n 2 2 0.5 if (rj a j ) R0 si , j 1 otherwise ri H.R. Pourreza i 1,2,...,n Full-Color Image Processing Color Transformation: Color Slicing Cube Sphere H.R. Pourreza Full-Color Image Processing Color Transformation: Tone and Color Correction The tonal rang of an image, also called its key-type, refers to its general distribution of color intensities. High-key images: Most of the information is concentrated at high intensities. Low-key images: Most of the information is concentrated at low intensities. H.R. Pourreza Full-Color Image Processing Color Transformation: Tonal Correction Middle-key Image H.R. Pourreza Full-Color Image Processing Color Transformation: Tonal Correction High-key Image H.R. Pourreza Full-Color Image Processing Color Transformation: Tonal Correction Low-key Image H.R. Pourreza Full-Color Image Processing Color Transformation: Color Correction The proportion of any color can be increased by decreasing the amount of the opposite (or complementary) color in the image or by raising the proportion of the two immediately adjacent colors or decreasing the percentage of the two colors adjacent to the complement. Magenta Removing Red and Blue H.R. Pourreza Adding Green Full-Color Image Processing Color Transformation: Color Correction H.R. Pourreza Full-Color Image Processing Color Transformation: Histogram Processing Histogram Equalizing the Intensity Saturation Adjustment H.R. Pourreza Full-Color Image Processing Color Image Smoothing Averaging: 1 c ( x, y ) K c( x, y ) ( x , y )S xy 1 R ( x, y ) K ( x , y )S xy 1 c ( x, y ) G ( x, y ) K ( x , y )S xy 1 K B ( x, y ) ( x , y )S xy H.R. Pourreza Full-Color Image Processing Color Image Smoothing Red Blue Green H.R. Pourreza Full-Color Image Processing Color Image Smoothing Hue Saturation H.R. Pourreza Intensity Full-Color Image Processing Color Image Smoothing Averaging R,G and B Averaging Intensity H.R. Pourreza Difference Full-Color Image Processing Color Image Sharpening The Laplacian of Vector c : 2 R ( x, y ) 2 2 c( x, y ) G ( x, y ) 2 B ( x, y ) H.R. Pourreza Full-Color Image Processing Color Image Sharpening Sharpening R,G and B Sharpening Intensity H.R. Pourreza Difference Full-Color Image Processing Color Segmentation Segmentation is a process that partitions an image into regions Segmentation in HIS Color Space Segmentation in RGB Vector Space Color Edge Detection H.R. Pourreza Full-Color Image Processing Color Segmentation: in HIS Color Space H.R. Pourreza Full-Color Image Processing Color Segmentation: in RGB Vector Space z is similar to a if the distance between them is less than a specified threshold. Euclidian Distance: D(z, a) z a ( z (z a)T (z a) Generalized form: 1/ 2 aR ) ( zG aG ) ( z B aB ) 2 R D(z, a) (z a)T C1 (z a) H.R. Pourreza 2 1/ 2 2 1/ 2 Full-Color Image Processing Color Segmentation: in RGB Vector Space H.R. Pourreza Full-Color Image Processing Color Segmentation: Color Edge Detection H.R. Pourreza Full-Color Image Processing Color Segmentation: Color Edge Detection R G B r g b x x x R G B v r g b y y y u R G B g xx u u x x x 2 2 2 2 2 2 T R G B g yy v v y y y T R R G G B B g xy u v x y x y x y T H.R. Pourreza Full-Color Image Processing Color Segmentation: Color Edge Detection 2 g xy 1 1 tan 2 g xx g yy 1/ 2 1 F ( ) g xx g yy g xx g yy cos 2 2 g xy sin 2 2 H.R. Pourreza Full-Color Image Processing Color Segmentation: Color Edge Detection H.R. Pourreza Full-Color Image Processing Color Segmentation: Color Edge Detection H.R. Pourreza Full-Color Image Processing Noise in Color Images H.R. Pourreza Full-Color Image Processing Noise in Color Images H.R. Pourreza Full-Color Image Processing Noise in Color Images H.R. Pourreza Full-Color Image Processing Color Image Compression H.R. Pourreza