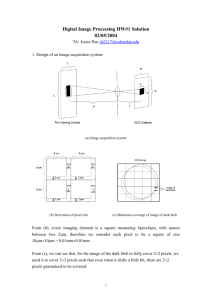
chap13_ColorProcessingV2
advertisement

Color Processing
• Introduction
• Color models
• Color image processing
1
Definition of Color
• Physical aspects
– color is a part of magnetic spectrum of visible
light.
• Perceptual aspects
– amount made up by varying R, G and B colors.
– cone cells in human eyes detecting color (one for
each R, G and B color)
– R, G, B = primary color
2
Primary and Secondary Colors
• Primary colors: the color consist of 1 primary
color
• Secondary colors: the color consist of 2
primary colors
3
Primary and Secondary Colors (2)
4
Color Model
• A.k.a. color space, color system
• Specify a color as a point in some standard
coordinate
• Popular color models:
–
–
–
–
RGB color models
HSV color models
YIQ color models (NTSC standard)
LUV and LAB color models
5
RGB Color Model
• Cartesian coordinate system
• Stand for RED, GREEN and BLUE color
6
Pixel Depth
• Pixel depth: #bit represented RGB image
– E.g. 24-bit RGB color image: 8-bit for each color.
Able to represent (28)3 color
• Full-color image = 24-bit RGB color image
7
R.C. Gonzalez and R.E. Woods, “Digital Image Processing”, 2nd Ed., Prentice Hall, 2002.
Safe RGB Colors
• A.k.a all-system-safe colors, safe Web colors,
safe browser color
• Set of the color that are likely to be reproduced
color independent of the hardware
• Set of 216 colors (the other 40 are reproduced
differently by various OS)
• Value for RGB: 0, 51, 102, 153, 204, 255
• Show in Hex format RRGGBB
8
Safe Color Diagram and Cube
Color only on the surface of the cube
9
R.C. Gonzalez and R.E. Woods, “Digital Image Processing”, 2nd Ed., Prentice Hall, 2002.
HSV Color Model
• Hue: true color attribute
• Saturation: amount that the color is diluted by
white
– pure red high saturation
– light red low saturation
• Value: degree of brightness
10
HSV Color Space
11
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:HSV_cone.png
HSV RGB
V max{R, G, B}
V min{R, G, B}
S
V
1 GB
IF R V T HEN H
6
1
BR
IF G V T HEN H 2
6
1
R G
IF B V T HEN H 4
6
H 6 H
F 6H H
P V (1 S )
Q V (1 SF )
T V (1 S (1 F ))
H’
R
G
0
V
T
1
Q
V
2
P
V
3
P
Q
4
T
P
5
V
P
B
P
P
T
V
V
Q
12
All values are normalized.
HSV: MATLAB Command
• RGB HSV
– MATLAB: rgb2hsv(Red, Green, Blue);
• HSVRGB
– MATLAB: hsv2rgb(Hue, Saturation, Value);
13
RGB Image VS HSV Image
RGB Image
Hue Image
Saturation Image
(white : low)
Value Image
14
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HSV_color_space
YIQ Color Space
• Y : luminance, brightness
• I, Q: chrominance (color information)
Y 0.299
I 0.596
Q 0.211
R 1.000
G 1.000
B 1.000
0.587
0.274
0.523
0.956
0.272
1.106
0.114 R
0.322 G
0.312 B
0.621 Y
0.647 I
1.703 Q
15
YIQ: MATLAB Command
• RGB YIQ
– MATLAB: rgb2ntsc(Red, Green, Blue);
• YIQRGB
– MATLAB: ntsc2rgb(Y, I, Q);
16
RGB Image VS YIQ Image
RGB Image
Y Image
I Image
Q Image
17
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/YIQ
MATLAB Structure
• 3-dimensional matrix:
– [row, column, color space]
• RGB(HSV, YIQ):
– red (hue, Y) components: [.., .., 1]
– green (saturation, I) components: [.., .., 2]
– blue (value, Q) components: [.., .., 3]
18
Contrast Enhancement
• Use histogram manipulation (E.g. histogram
equalization) on only intensity component.
• Processing on RGB matrix leads to color
distortion.
19
Histogram Equalization on RGB
BEFORE
AFTER
http://documents.wolfram.com/applications/digitalimage/UsersGuide/3.4.html
20
Spatial Filtering
• Blurring: any are fine
– average filter on RGB components
– average filter on intensity(Y) components
• High-pass filter (E.g. unsharp)
– process on intensity components
• General: work on intensity components
21
Smoothed Lena
Blame the reddish tone on the scanner!!!
22
R.C. Gonzalez and R.E. Woods, “Digital Image Processing”, 2nd Ed., Prentice Hall, 2002.
Noise Reduction
• Depended on where noise is generated.
– generated in RGB spaces: reduce noise in RGB
matrix
– generated in brightness space: reduce noise in
intensity (Y) components
23
Edge Detection
• Use edge detection on intensity component
only
• Use edge detection on R, G and B components
separately and join the result
24