Energy resolution
advertisement

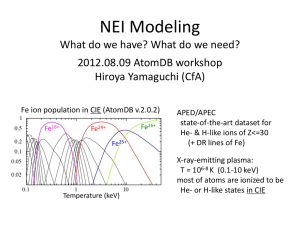
Brief Overview of China’s Future Space X-ray Astronomy Program Shuang-Nan Zhang Center for Particle Astrophysics Institute of High Energy Physics Chinese Academy of Sciences Outline • Approved missions: launch within the next 5 years – Hard X-ray Modulation Telescope (HXMT) – Space Variable Object Monitor (SVOM): China-France collaboration (Barret’s Talk) – Gamma-ray burst polarimeter (POLAR): China-Europe collaboration on China’s Spacelab • In mission definition and technology development phase: launch within next ~10 years – X-ray Timing and Polarization mission (XTP) • Proposed onboard China’s Space Station: launch around 2021-2022 – Optical/UV/X-ray All-Sky Monitor 2/37 Payload Cabin Platform Cabin HXMT is a collaboration between: Chinese Academy of Sciences, Tsinghua University Chinese Academy of Space Technology HE: NaI/CsI 5000 cm2 LE:SCD,384 cm2 ME:Si-PIN,952 cm2 Payloads onboard HXMT Size:1900×1600×1000 mm3 LE The Sun A sunshading board will be set so that the LE and ME instruments can work at low temperatures 5/37 High Energy X-ray Instrument HXMT/HE Components assembly • The 18 main collimated phoswich detectors • Charged-particle anticoincidence plates (6 pieces up side +12 lateral side) • Particle Monitor detectors • Calibration detectors (automatic gain control) 6/37 The Field of View configuration of HE 2 Modules of 5.7 °× 5.7 ° 1 Blind Module 15 Modules of 1.1 ° × 5.7 ° 7/37 Detector: Si-PIN Energy coverage: 5-30 keV Detecting area: ~950 cm2 (1728 pixels) Sensitivity: 0.5 mCrab Field of view: 1°×4°,4 °×4°, blind field Energy resolution: < 1.5 keV@17.8keV Work temperature: -20~-40℃ for Si-PIN Time resolution: 40 μs Mass: 105kg Power dissipation: 130 W 16 Si-PIN (0.56 cm2 each) pixels will be in one package and 2 packages read by a RENA-3 asic. 9/37 The low energy instrument (LE) 2×2 CCD236 16 cm2 FOVs of an LE module The Hard X-ray Modulation Telescope @ EAMA-7 11/37 Detector: SCD Energy coverage: 1-15 keV Charge flow Detecting area: ~384 cm2 (96 chips) Sensitivity: 0.5 mCrab Field of view: 1.5°×6°,4 °×6°, blind field 60 °×3°(48cm2), Energy resolution: <150 eV@6keV Work temperature: -40~-80℃ for SCD Real & dummy outputs in gap Time resolution: 1 ms Mass: 105 kg Power dissipation: 130 W Schematic map of a CCD236 (e2v) Characteristics of the HXMT Mission Detectors LE: SCD, 384 cm2;ME : Si-PIN, 952 cm2 HE : NaI/CsI, 5000 cm2 Energy Range LE: 1-15 keV;ME: 5-30 keV;HE: 20-250 keV Time Resolution HE: 25μs; ME: 20μs;LE: 1ms Energy Resolution LE: 2.5% @ 6 keV ME: 8% @ 17.8 keV HE: 19% @ 60 keV Field of View of one LE: 6°×1.5°; 6°×4°; 60°×3°; blind; module ME: 4°×1°; 4°×4°; blind; HE: 5.7°×1.1°; 5.7°×5.7°;blind Source Location <1' (20σ source) 13/37 Sensitivity (3σ, in 105s) LE: 4.4×10-5 cts cm-2s-1 keV–1 (@6keV) ME: 2.6×10-5 cts cm-2s-1 keV–1 (@20keV) HE: 3×10-7 cts cm-2s-1 keV–1 (@100keV) Orbit Altitude: ~550 km ; Inclination: ~43° Attitude Three-axis stabilized Control precision: ±0.1° Measurement accuracy: ±0.01° Data Rate LE: 3 Mbps; ME: 3 Mbps; HE: 300 kbps Payload Mass ~1000 kg Nominal Lifetime 4 years Working Mode Scan survey, pointed observation 14/37 Scientific objectives of pointed observations • X-ray Binaries – Broadband X-ray variability, especially the QPO properties of BH binaries at energy higher than 20 keV; – Broadband spectral characteristics and state transitions • Cyclotron Resonance Features (CRF) close to the neutron star surface; • Broadband spectrum of bright AGN: reflecting components and high energy cut off; Observation modes • Scanning Sky Survey mode • Deep scanning observations of selected sky regions (such as the Galactic center region) • Pointed observations Status of HXMT Full-funding decision: March 2011 • Phase-B (pre-flight module): 2011.6-2012.12 • Phase-C (flight module): 2013.1-2014.6 • Launch: ~2015 Outline • Approved missions: launch within the next 5 years – Hard X-ray Modulation Telescope (HXMT) – Space Variable Object Monitor (SVOM): China-France collaboration (Barret’s Talk) – Gamma-ray burst polarimeter (POLAR): China-Europe collaboration on China’s Spacelab • In mission definition and technology development phase: launch within next ~10 years – X-ray Timing and Polarization mission (XTP) • Proposed onboard China’s Space Station: launch around 2021-2022 – Optical/UV/X-ray All-Sky Monitor 18/37 Gamma-ray burst polarization experiment onboard China’s Spacelab: POLAR GRB prompt emission polarization: a last observables of GRBs •Different GRB models – E-M Model: well defined, moderate Plin ~ 50% – Fireball Model: high values excluded Plin ~ 10-20 % – Cannon ball Model: full range possible Plin = 0 - 100% •Probe quantum gravity (???): – Amelino-Camelia G., 2000, Nature, 408, 661 – Piran T, 2005, Lect. Notes Phys, 669, 351 From M. Lyutikov, 2003 – Fan, Y-Z; Wei, D-M; Xu, D. 2007, See papers discussing various GRB models: MNRAS, 376, 1857 T. Piran, A. Dar, M. Lyutikov, D. Eichler, G. Ghisellini, D. Lazzatti, M. Medvedev, E. Rossi etc. 19/37 Gamma-ray burst polarization experiment onboard China’s Spacelab: POLAR • Onboard China’s spacelab TG-2: launch time 2012-13 • A China-led international collaboration (Switzerland, France, Poland) • FOV of POLAR: ~½ sky Tian-Gong 天宫 Palace in Heaven Plastic scintillator stacks Instrument concept proposed by N. Produit, et al., NIM (2005) 20/37 POLAR capability summary One year observation of POLAR 180 TS2/DM2 FOV = 2π 160 Number of GRBs (N < MDP) 140 •10 GRBs per year down to 8%, or •60 GRBs per year down to 30%, or 100 GRBs per year down to 50% polarization, 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 Minimum Detectable Polarization with 3σ (%) 90 100 21/37 Outline • Approved missions: launch within the next 5 years – Hard X-ray Modulation Telescope (HXMT) – Space Variable Object Monitor (SVOM): China-France collaboration (Barret’s Talk) – Gamma-ray burst polarimeter (POLAR): China-Europe collaboration on China’s Spacelab • In mission definition and technology development phase: launch within next ~10 years – X-ray Timing and Polarization mission (XTP) • Proposed onboard China’s Space Station: launch around 2021-2022 – Optical/UV/X-ray All-Sky Monitor 22/37 X-ray Timing and Polarization (XTP) mission • Key Science: Matter under extreme conditions • Precise Light curve: Neutron Star equation of state, BH basic parameters, formation and growth … • Polarization of X-ray: Radiation mechanism… • Diffuse X-ray emission, hot gas distribution in Galaxy • … • Main Requirement: large effective area & high counting rate • The most accurate light curve and polarization observation at 1-30 keV 23/37 HERO concept: High Energy Replicated Optics – Small Aperture, Short Focal Length and Shallow Grazing Incidence Using small mirror array to achieve large collection area at hard X-ray (>10 keV): technically more feasible than single large mirror. Ramsey et al, SPIE 2000 24/37 Bepicolombo soft X-ray (<10 keV) MPO telescope: short focal length & lightweight 2009-11-19 25 25/37 XTP Mission Concept 26/37 XTP (Possible) Instruments SDD/CZT High-energy Collimated Array (1-100 keV) High-energy Focused Array (1-100 keV) All Sky Monitor (5-300 keV) SDD/CZT CZT GEM CCD SCD 4m focal length Polarization Observation Telescope (2-10 keV) Low-energy Focused (0.5-10 keV) Low-energy Collimated Array (0.5-15 keV) 27/37 LFA: Low energy有效载荷初步方案 X-ray Focusing telescope Array 0.5-10 keV Micro-pore Optics (MPO) mirrors, mDEPFET detectors MPO光学原理 矩形微通道排列 环形微通道排列 28/37 High energy X-ray Focusing telescope Array (HFA): 1-100 keV Double conical nested mirrors SDD+CZT composite detector 29/37 Low energy x-ray Collimated detector Array (LCA): 0.5-15 keV SCD: e2V 一个LCA模块示意图 LIGA made collimator: 30μm thickness each layer 30/37 HCA: High energy X-ray Collimated detector Array 1-100 keV HCA composite detector 31/37 POT: Polarization Observation Telescopes 2-10 keV 掠射望远镜可通过国际合 作由意大利INAF研制,图示 为意大利原为HXMT设计的多 层掠射镜的装配图。 GEM-TPC: 0.25-30 keV 32/37 ASM: All-Sky Monitor FOV~2Sr, 4-300 keV, 1000cm2, 6400 × 4mm×4mm CdZnTe 33/37 XTP Basic Parameters HFA:1-100 keV, 480 kg, 1°×1°, 1’ LFA:0.5-10 keV, 170 kg, 1°×1°, 1’ Energy Range, HCA:1-100 keV, 500 kg, 2°×2° Weight, FOV & LCA:0.5-15 keV, 400 kg, 2°×2° Angular Resolution ASM:4-300 keV, 100 kg, 2 Sr POT:2-10 keV, 110 kg, 22’ ×22’ Total satellite mass: 3210 kg Geometrical Area Energy Resolution Timing Resolution HFA: 5000 cm2 (1-6 keV), 2800 cm2@30 keV LFA:7400 cm2@1 keV HCA: 15000 cm2 (6-30 keV) LCA: 15000 cm2 (1-6 keV) 150 eV@5.9 keV 4 keV@30 keV 10 μs May choose near-earth orbit or L2 orbit, depending on available launcher (money) 34/37 Outline • Approved missions: launch within the next 5 years – Hard X-ray Modulation Telescope (HXMT) – Space Variable Object Monitor (SVOM): China-France collaboration (Barret’s Talk) – Gamma-ray burst polarimeter (POLAR): China-Europe collaboration on China’s Spacelab • In mission definition and technology development phase: launch within next ~10 years – X-ray Timing and Polarization mission (XTP) • Proposed onboard China’s Space Station: launch around 2021-2022 – Optical/UV/X-ray All-Sky Monitor 35/37 OUVX-ASM Mission Concept One X-ray ASM Module zenith FOV of OUV-ASM Motion of spacecraft FOV of X-ASM 36/37 Summary on China’s Future Space X-ray Astronomy Program • Approved missions – Hard X-ray Modulation Telescope (HXMT): 2014-2015 – Space Variable Object Monitor (SVOM): China-France collaboration (Barret’s Talk) ~2015 – Gamma-ray burst polarimeter (POLAR): China-Europe collaboration on China’s Spacelab 2012-2013 • In mission definition and technology development phase – X-ray Timing and Polarization mission (XTP) ~2020 • Proposed onboard China’s Space Station – Optical/UV/X-ray All-Sky Monitor ~2021-2022 37/37