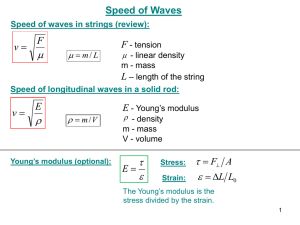
Document
Today Ch.36 (Diffraction)
Next week, Dec.6, Review
This week off. hours:
Th: 2:00-3:15pm; F: 1:00-3:00pm
Next week off. hours:
Tu:2-3:15pm,W:1-3pm,Th:1-3pm
Webct homework is due by Dec.12.
Check your Midterm Exams Grades on elearning!
Final Exam: (Ch.21-25, 27-29, 32,33,35,36)
Secs.511-515: December 9, Friday: 12:30-2:30 pm
Secs.521-525, 528: December 12, Monday, 8-10 am
Lecture 24 (Ch. 36)
Diffraction
1. Huygen’s principle, bending of the rays
2. Fraunhofer’s diffraction
3. Single slit
4.Two slits with a finite width
5. Resolution of the lens
6. Diffraction grating
7.Spectroscopy
8. x-ray diffraction
9. e diffraction
Huygen’s principle and bending of the rays
Augustin-Jean Fresnel
1788 – 1827
Joseph von Fraunhofer
(1787 – 1826)
Single slit diffraction
How to describe the real picture?
r
r
a sin
Single slit diffraction a
2 sin min :
a
sin
2
( 1 st m
min)
( m
a sin
1 ,
2 ,...)
NB : m
( m
0
0 all rays
0 !
parallel to axis
max!
) for small
; sin
tan
y x
, min : y m
x
m a
Intensity distribution
R=
1 st max
0
E
k
r
2
a sin
E
2
R sin
2
,
E
0 ,
R
E
E
0
sin
2 min max
:
:
2
m
a sin
( 2 m
1 )
m
( m
2
0 )
, I
I
0
{
sin
2
}
2
2
E
1 st min:
2
1 st max:
3
I
I
0
{
sin
2
}
2
; min :
2
m
a sin
m
( m
0 )
2
Narrowing of the first fringe with increase of the slit width
1
a
Circular hole diffraction
The photographs of four very small sources of light taken made with a circular aperture in front of the lens
Rayleigh’s criterion for resolution of two point objects : Two objects are barely resolved if the center of one diffraction pattern coincides with the first minimum if the other.
S
L sin
1 .
22
D
L
For a microscop
John William Strutt, 3rd Baron Rayleigh
1842 – 1919
CD :
780 nm
DVD :
( 0 .
7 gigabytes )
650 nm ( 4 .
7 gigabytes )
Hubble vs Arecibo
Hubble: D=2.4m,
Arecibo: D=300m,
500 nm
75 cm
S
L
L sin
1 .
22
D
3 .
8
10
8 m ( to the moon )
S
H
L
77
4 ly ( m , S
A
nearest
1000 km ( crater star ,
size
Centaury )
)
1 ly
S
H
c
1 year
10
7 km ,
3
10
8
D
Jupiter m
10
7 s s
10
5 km
10
13 km
Giant Magellan Telescope (2016)
D
1
=8.5m, D eq
=24m
500 nm
Interferometry:
Arrays of telescopes
Two slits with a finite width
Interefere nce
Difraction factor : factor :
E
E
0
(
)
2 E
0
(
)
cos
2 sin
E
0
2
,
,
kd sin ka sin
2
I
4 I
0
{
sin
2
}
2 cos
2
2
2
Diffraction grating max :
2
m
d sin
m
E
0 t
E ot
NE
0
I ot
N 2 I
0
!
N-1 minima
With increase of N principal maxima becomes narrower and their amplitude grows as N
2
Grating spectroscopy
Spectrum of sunlight produced by a diffraction grating has dark absorption lines due to absorption of the corresponding wavelength by the solar atmosphere. It allows to find out a chemical composition of the solar atmosphere.
x-ray diffraction
~ 0 .
1
10 nm
Wilhelm Röntgen (1845 – 1923)
The 1 st Nobel Prize,1901
Bragg condition
2 d sin
n
An x-ray scattering pattern of DNA recorded by
Rosalind Franklin led Watson and Crick to discovery of the DNA double helix structure
Louis de Broglie (1892 – 1987)
Electromagnetically induced transparency (EIT)
Two undistinguishable absorption passes for light result in cancellation of absorption (transparency ).
An electron has the wave property. It may be in a superposition of states 1 and 1’.
Monohromatic light with a frequency resonant either to one or another atomic transition is absorbed.
Bichromatic light containing two resonant frequencies goes through.
1
2
1’
1
O.K., Y.I.Khanin, JETP, 1986; O.K., P. Mandel, Phys. Rev. A. 1990. theory
S.E. Harris, PRL, 1991. experiment
Electromagnetically induced transparency (EIT)
2
1
1’
Two undistinguishable absorption passes for light result in cancellation of absorption (transparency).
An electron has the wave property. It may be in a superposition of states 1 and 1’.
A circular polarized light interacts only with 1-
2 (or 1’-2) state and absorbed. A linear polarized light interacts with both 1-2 and 12’ states and goes through the medium without absorption.
To make medium transparent for light with given circular polarization send through the medium simultaneously light with another circular polarization.
1
2
The same is true for two beams of different frequencies
1’
When the frequency difference coincides with the frequency of the atomic transition 1-
1’.
1
O.K., Y.I.Khanin, JETP, 1986; O.K., P. Mandel, Phys. Rev. A. 1990. theory
S.E. Harris, PRL, 1991. experiment