Vet Med Introduction - Agricultural Education
Introduction to Veterinary Medicine
Submitted by Callie Parr and used in cooperation with the University of Illinois at
Urbana-Champaign.
The materials that appear in this document may be freely reproduced for educational/training activities. There is no requirement to obtain special permission for such uses. We do, however, ask that the following statement appear on all reproductions:
INTRODUCTION TO VETERINARY MEDICINE, by CALLIE PARR
Materials produced for classroom use in conjunction with permission from the
University of Illinois Agricultural Education Program.
This permission statement is limited to the reproduction of material for educational/training events. Systematic or large-scale reproduction or distribution
(more than one hundred copies per year) —or inclusion of items in publications for sale —may be done only with prior written permission. Also, reproduction on computer disk or by any other electronic means requires prior written permission.
Contact the University of Illinois Agricultural Education Program to obtain special permission.
The University of Illinois and its affiliated entities, in addition to the individual submitting the materials, assumes no liability to original work or activities therein.
Introduction to
Veterinary Medicine
What is it?
Veterinary Medicine is the medical treatment of animals.
How is it different from a
Doctor?
Must know many different species.
Must know many areas such as internal medicine, pediatrics, obstetrics, surgery, etc.
Can’t talk to the patient
What animals does a Vet treat?
Pets, livestock, lab animals, zoo animals, wildlife
What is the History of Vet
Med?
Veterinary Medicine developed alongside human medical advancements.
Recorded references as early as 9000 bc in the
Middle Eastern sheparding cultures.
Hieroglyphs in Egypt refer to placing stones in a female camel’s uterus to prevent pregnancy.
In American West a veterinarian would find themselves treating animals and people alike because of their skills in many areas.
What are the Career options in Vet Med?
Veterinarian
Small Animal
Large Animal
Exotic
Zoological
Veterinary Technologist
Veterinary Assistant
Clinical Pathologist
Academia
What education is needed for Veterinary Medicine?
A DVM needs 8 years of post secondary education.
There are 28 schools of veterinary medicine in the country .
A Vet Tech needs 4 years of post secondary education.
A Vet assistant can have 2-4 years of post secondary education.
A pathologist will need 4-6 years of post secondary education
Duties in Veterinary
Medicine
Breed selection Treat illness/injury
Nutrition
Grooming
Training
General husbandry
Health screening
Treat parasites
Provide referrals
Humane euthanasia
Vaccination
Spay/neuter
Allay concerns of owner
How does someone in Vet
Med contribute to society?
By Promoting animal health and welfare.
By Combating zoonotic diseases.
By inspecting livestock and food-processing procedures to ensure safety of food supply.
By preserving and conserving wildlife.
By conducting scientific research that impacts the food we eat, the medicine we take, etc.
Veterinary Medical
Terminology
On the body:
Dorsal - toward the ceiling or back
Ventral - toward the floor or belly
Cranial/anterior - toward the head
Caudal/posterior - toward the butt rear
Lateral - toward the side
Medial - toward the midline
On the limbs:
Proximal - toward the body
Distal - away from the body
Palmar - the front foot pads
Plantar - the rear foot pads
On the head:
Rostral – toward the nose
Caudal – toward the tail/rear
Movement:
Flexion decreasing a joint’s angle
Extension increasing a joint’s angle
Suffixes
…ectomy – to remove ______
…itis – inflammation of ______
…ose – sugar
…ase – enzyme
…gen – producing
…tomy – incision
…emia – blood
…oid - resemble
Suffixes cont.
… oma – tumor/swelling
…osis/iasis – abnormal
…sclerosis – hardening
…plegia – paralysis
…rrhea – discharge
…rrhage – burst forth
…ptosis – prolapse/falling out
…spasm - contraction
Prefixes
Hema/o… - having to do with the blood
Hyper… - increased levels/activity of ______
Hypo… - decreased levels/activity of _______
Hetero… - different
Homo… - the same
Psuedo… - false
Anti… - against
Peri… - around
Prefixes cont.
Tachy… - fast
Mega/macro… - large
Micro… - small
Poly… - many
Pan… - all
Hap/mono… - one
Di… - two
A… - none/not
Prim… - first
Iso… - equal
Ambi… - both
Laevo… - left
Dextro… - right
Trans… - through
Ex/o… - out
End/o… - in
Prefixes cont.
Brachy… - short
Steno… - narrow
Ortho… - straight
Leuk/o… - white
Cirrh/o… - yellow
Chlor/o… - green
Melan… - black
Glauc/o… - grey
Misc terms
Malignant – cancerous
Benign – non-cancerous
Local – in one specific location
General – all over or in many locations
Acute – rapid onset
Palpate – to feel by hand
Feces/fecal – excrement
Triage – to collect information and assess the situation
Misc Terms
Infectious – can be spread
Diagnosis – to determine a cause for symptoms
Prognosis – how it will turn out
Congenital – with/upon/before birth
Appendages – arms or legs
Digits – fingers or toes
Vestigial – non-functional
Phalanges – fingers/toes
Clinical Experience
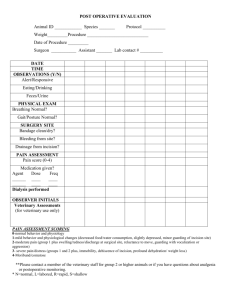
You will be required to complete and document 10 clinical hours.
Clinical hours include working with animals in any structured environment.
Examples are:
working at a vets office cleaning cages, feeding, etc.
Working at a local animal shelter cleaning cages, feeding, socializing, etc.
Working at a barn/stable
Documentation comes in the form of detailed records listing days & hours worked, tasks completed, and skills learned. Signed by the owner/ operator/ manager.