3.3_Induction Pack_3_Presentation_May10
advertisement
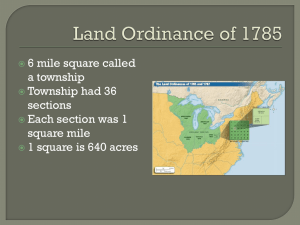
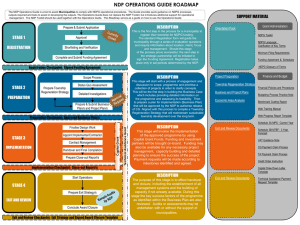
INDUCTION PACK 3 NDPG Overview Strategic Objectives • Mandate – “To support neighbourhood development projects that provide community infrastructure & create the platform for other public & private sector development, towards improving the quality of life of residents in targeted underserved neighbourhoods (townships generally)” • Purpose: – “A Technical Assistance [TA] Grant aimed at supporting the development of township development plans – A Capital Grant aimed at supporting nodal investment into the construction or upgrading of community facilities, which may attract private sector investment” DoRA 2 NDP Programme Objectives – Promote private sector investment & other public spending in townships – Provide institutional support & technical capacity to municipalities – Direct capital investment into township, nodal & linkage projects – Promote knowledge, best practice & innovation in township development 3 Focus on Townships • Challenges – Exclusion by design – Absence of township & township nodal development capacity (forward-oriented versus backlogs-driven) – Limited funding for capital works for public facilities & places – Limited municipal capacity to assemble & align multiple funding sources in single large-scale multi-faceted property development project – Mismatch between capital investment & maintenance & operational budgets • Features – Large concentrations of poor households – High levels of unemployment – Slower household income growth – Poor-performing residential property markets – Considerable fiscal burden • Opportunities – Limited income retention – Undiversified & marginal local economies – Untapped markets - limited private sector investment 4 Programme SACN SCI (DBSA) SHRP MPCCs (TSCs) Top 20 Townships URP NDP ISRDP NSDP 5 Research Policy & Strategy Township Linkages Nodal development Investment (capex) Whole township investment (capex) Scope Poverty Relief Spatial Restructuring Economic development Housing Infrastructure Informal Settlement Township Type of Intervention Rural Urban Training Subsidies Operational/transitional funding Incentives Loans Capital Grant Central Technical Assistance Technical Assistance Grant NDPG & Other Initiatives Focus MIG vs. NDPG Capital Investment MIG NDP For services infrastructure For social & economic infrastructure Deals with backlog re basic service delivery, especially for poor Provides forward-looking development support to community & commercial development Targets all areas Targets township environments in specific precincts Partnerships not required Partnerships desired with the private sector Penalties & rewards apply - Emphasis on capacity building of LG - 6 Thohoyando u Gauteng Kimberley Durban East London Cape Town PE 7 Grant Make-Up • Technical assistance (Schedule 7 mainly, also Schedule 6) – Strategic planning → Township regeneration strategy, business case & business plan) – Capacity → development coordination, construction management – Detailed planning → for capital investment from NDPG → feasibilities, design work • Capital Grant (Schedule 6 only) – For any capital cost, as usually spent by councils – To make projects happen • Nodal & precinct projects • Linkages • General improvements • Used in conjunction with other grants that have a local government focus → ‘synthesis’ 8 What does Leverage mean? • Includes – – – – Other government funding streams Mobilisation any non-governmental support & resources Private sector Investor groupings • • • • • • • • Formal developers Project financiers Equity investment funds Community investment funds Stokvels NGOs, CBOs & other community organisations Cooperatives Any non-government organisation or individual • Not purely financial → “sweat equity”, land, in-kind 9 Status Quo: NDPG Portfolio Applications Round 3 All 1 2 Rec’d 243 151 109 226 729 Awards 33 20 19 Other Investment (inc Private Sector) 58% 4 14 86 Other Levels of Government 7% Baseline NDPG 30% Municipality 5% Muni Other Government NDPG Other (inc private sector Total R1.34bn R1.9bn R8.75bn R17bn R29.3bn • 86 awards to 51 municipalities for +135 townships • Leverage of Other Funds → NDPG → R8.7bn of total +R29bn project value • NDPG is catalyst but perception is that it can ‘do it all’ → changing mindset is challenge 10 Status Quo: NDPG Portfolio R 30,000,000,000 R 25,000,000,000 R 20,000,000,000 Ratio Muni Other Govern -ment NDPG Other (inc private sector Promised 1 1 7 13 Actual 3 1 205 13 Desired 1 1 1 1 R 15,000,000,000 R 10,000,000,000 R 5,000,000,000 RPromised Actual 11 NDPG Municipality Other Levels of Government Other Investment (inc Private Sector) Township Regeneration Strategy A WELL-FUNCTIONING RESIDENTIAL AREA WITH BUSINESS NODES ATTRACTING PRIVATE SECTOR INVESTMENT Soweto Development Initiative: Administrative (JDA) & political co-ordination (new Committees) Planning, Social Land Use DevelopManagement & ment & Education Land & Release Childcare Economic Sector Support & Business Node Development Infrastructure & Services Safety & Security Natural Environment EDU DPTE DPTE SOCIAL DEVELOPMENT JMPD Environmental Management Accountability EDU, M&T, JDA, DPTE, MTC, JPC DPTE, Big 5 UACs, EDU DPTE, JPC, EDU SD, EDU, Province & National JMPD, Regions DPTE, Regions, Citiparks & other UACs Key involvement, responsibility & action Pillar/Key Component Cross-cutting involvement & action: Regions, Core, committees, etc. Guiding Principles •‘Sense of Place’ •City Future vs. City Past •Sustainability of SDI, projects & programmes 12 Township Nodes & Catchments • • • • Concentration of activity in township Typically economic also social, civic, transport – Intensity of land uses – Strong relationship to transport & other movement Nodes are dynamic Nodal hierarchies in urban & rural areas 13 Township Development Scenarios • Nodes as a structuring element • As starting pint for township regeneration • Place where public & private sector interests can be combined 14 Nodes as a Structuring Element 15 Conceptual Nodal Development 1. Layout of roads & rail – basic public transport 2. Public space – paving, planting & street furniture 3. Initial public buildings (eg: clinic, library), public transport structures & trading structures 4. School, recreational park, extension of landscaping 5. Public buildings, commercial, mixed use & high density residential 6. Mixed use, high density residential & medium density residential → Demand-driven 7. High density residential & medium density 16 residential