Erosion & Deposition
advertisement

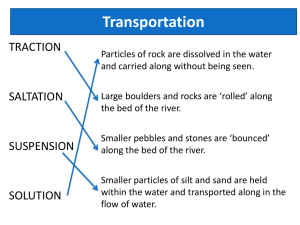
Erosion and Deposition Erosion is the process by which earth materials are moved by natural agents like water, wind, and ice. Running Water Running Water is the most effective agent of erosion. The sun is where running water gets its energy Rocks are weathered both Chemically and Physically by running water Physical Abrasion is the term given to the use of sand, pebbles, and even boulders as cutting tools to grind away at the stream bed. During this process the “tools” themselves wear down. Chemical The water dissolves soluble minerals Rivers carry rock material in three ways Solution – This is material that is dissolved from the bedrock. Most commonly found in solution are compounds of calcium and magnesium. Suspension – When small rock particles, such as clay silt and fine sand, are kept from sinking by the turbulence of the stream. This gives the water a muddy look. Bed Load – Sand, pebbles, and some boulders which move along the stream bed. Carrying Power Carrying Power is indicated by both the total amount of sediment in a stream and by the size of the particles being moved. **The stream discharge and speed will determine the carrying power of the stream. Discharge is the volume of water flowing past a given point at a given time. Speed is generally determined by the steepness, or gradient, of its bed. A stream moving at high speed with a high discharge can carry much larger sediments then a slow moving stream. Example: Spring time snow melting and excessive rain The River Valley **Rivers tend to have a V-shaped valley because the tend to flow at high speeds and dig into the stream bed. Base Level is the lowest level a river can cut into its bed. To form a permanent stream rain water must flow down a slope and dig deep enough to cut into the water table. This wearing away of the land to form a stream valley is called headward erosion. A Divide is an area of high land that separates one river valley from another. On either side of a divide a river system may form. Watershed is all of the land that drains into the river either directly or through its tributaries. Waterfalls Water flowing over a Steep cliff will result in a waterfall. Waterfalls are not permanent structures. Undermining is the erosional process occurring at the base of a waterfall. Here water carrying sediment plunges down and back into the the stream bed and cliff below. This causes the rocks at the top of the falls to overhang. Over time this overhang will collapse and the stream will move back towards its source River Deposition Deposition occurs when a stream either decreases in speed or discharge. Generally the speed decreases when its slope decreases or its bed widens. The greatest loss of speed occurs when a river empties into a quiet body of water. A decrease in discharge would occur if a river traveled through an area with low precipitation. As rivers begin to decrease their slope they move slower and will begin to move side to side. As the valley wall on either side is eroded the valley floor is widened. A Flood Plain is the widened valley floor area which will accumulate water during times of excess rain when the river floods Erosion and Deposition in a River Yukon River Basin Meanders are broad curves in the river (each bend or turn) Erosion is greatest on the outside of a meander where water is flowing the fastest. (cut bank) Deposition is greater on the inside of the meander where the water flows slower. (fill bank) Oxbow Lake - Meanders can only become so large before they break through into another meander. The river then deposits mud and silt along the end of the abandoned meander . The now separated meander becomes a lake. Running Water Deposits Well-Sorted Particles Vertical Sorting – When sediments are suddenly deposited into water. The particles separate by size with the largest on the bottom and smallest on top. Horizontal Sorting – When rivers empty their sediments into quiet bodies of water. Particles are sorted by size with larger particles being found closer to the shore and smaller particles being carried out into the body of water to be deposited. Delta – A fan-shaped deposit of sediment at the mouth of a river River Vocabulary (see attached) River Stages Young River Slope of the land – Steep Velocity – Fast Type of Erosion – Headward Erosion (deepens valley) Shape of the Valley - Straight Characteristic Features – Channel touches both valley walls **Valley is V-Shaped Examples – Upper Hudson and Niagara River Special Features – Waterfalls, rapids, islands, no tributaries Mature River Slope of the land – Less Steep Velocity - Slowing Down Type of Erosion –Lateral Erosion (widening the valley) Shape of the Valley - Meandering Characteristic Features – Channel touches both valley walls on the meanders Valley is wide and flat Examples – Ohio and Mississippi Rivers Special Features – Oxbow Lake, meanders, flood plain, tributaries Old River Slope of the land – Nearly Flat Velocity – Sluggish Type of Erosion – No Erosion (depositing sediments) Shape of the Valley – Very Meandering Characteristic Features – Channel does not touch the valley walls and valley is very wide and flat Examples – Lower Mississippi Special Features – Flood plain, oxbow lakes, yazoo streams, backswamps (bayous)