Document
advertisement

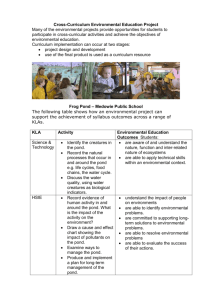
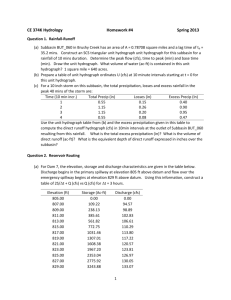
Agricultural Pond Private Engineering Resources & Costs Agricultural Water Resource Development Workshops Presented by: Cavanaugh & Associates P.A. 530 N. Trade Street, Suite 302 Winston-Salem, NC 336.759.9001 Why Hire An Engineer? • Is the pond in the best location? • How much water do I need? • How much water will it yield? • Will it hold water? • Which will work - Excavated or embankment? Does it matter? • Are there wetlands? • What about all these permits? This looks like a good spot! How much water will it yield? Inflow Hydrograph for Small Watersheds • Need: – Peak Discharge, Qp – Time to Peak Discharge, Tp – Shape of the Hydrograph The Rational Method Q = CIA (Calculating peak flood discharge at a given point) • Q = estimated design discharge (cfs) • C = Composite Runoff Coefficient for the drainage area • I = Rainfall intensity for the design storm (inches/hour) • A = Drainage Area (acres) Delineating Drainage Area, A • The first step in determining if your pond is in the “right spot” • Orange Pond A = 25 acres • Blue Pond A = 125 acres • Purple Pond A = 350 acres Determine Time of Concentration, tc • Depends on – Hydraulic Length of the drainage area – Height of the most remote point on the watershed above the outlet point • Orange Pond tc = 5 min • Blue Pond tc = 7 min • Purple Pond tc = 8.3 min Determine Rainfall Intensity, I • Depends on – Statistical rainfall for the design location – Designated return period for the design Determine Composite Runoff Coefficient, C • Depends on land use in the drainage area – Building types – Ground coverings – Soil types – Building densities Wooded, Sparse Ground Litter, C = 0.20 Wooded, Deep Ground Litter, C = 0.10 Commercial, C = 0.85 Apartments, C = 0.60 Residences, 2 dwellings per acre, C = 0.35 Time to Peak, Tp • Based on Qp & Volume of Water Under the Hydrograph – Qp is estimated by Rational Method – Volume is estimated based on •duration of the design storm •Soil types •Cover conditions Shape of the Hydrograph • Accepted practice is to assume a step function unit hydrograph to estimate the shape Use the Inflow Hydrograph to determine if the pond is sufficient for your needs. Excavation Ponds • Is there adequate drainage to fill? • What is the level of the water table? • What is the impact of the water table? • Will the soil types sustain water storage? Source: Dwane Jones/NCSU Co-op Extension Embankment Ponds • Is there adequate drainage to fill? • Will the soil types sustain water storage? • Is an earthen dam adequate? • What type of outlets are needed? • What is the downstream impact? Source: Dwane Jones/NCSU Co-op Extension Embankment Earthen Dams • • • • • Built in natural topographic draw Low flow outlet device Riser/Barrel Outlet Emergency spillway Outlet size calculated using Stage-Storage Function to control pond level and downstream needs • Dam Construction must meet Dam Safety Requirements General Steps in Pond Design • Base Topography – Existing Conditions – Height of Dam Required – Earthwork Required • Geotechnical Investigation – Dam Core Design – Seepage Control – Compaction & Materials Testing General Steps in Pond Design • Hydrologic Design – Rainfall Event Investigation – Peak Discharge – Watershed Yield/Water Supply • Hydraulic Design – – – – Primary Spillway Design Riser/Barrel Design Emergency Spillway Design Overtopping Control Construction Considerations • Preparation of Construction Documents – Plans & specifications to be sealed by Professional Engineer – Permits required from NC Division of Land Quality/Dam Safety • Bid Acquisition – Qualifying construction contractors – Hold bid opening – Ensuring contractor has proper bonds • Construction Administration – On-site observation of construction to protect investment and safety – Engineer certification of construction and asbuilts What’s the Engineering Cost? • Site dependant • Two phases: – Preliminary Site Evaluation – Design: Engineering Design, Permitting & Construction Document Preparation • Rough estimate of design cost is 15-20% of construction cost • Preliminary engineering evaluation – – – – Preliminary hydraulic & hydrologic calculations Cost estimate of geotechnical & wetland investigations Preliminary design concept Preliminary cost estimate of engineering costs, permitting fees and construction costs Why Hire An Engineer? • Professional recommendation on construction alternatives • Familiar with Dam Safety Rules and other permitting needs • Protect your interest during construction • Reduce your liability and risk • In long run will save money and time