egg osmosis lab
advertisement

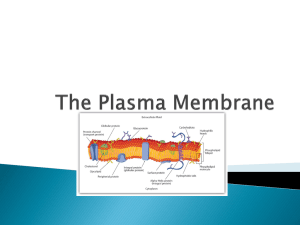
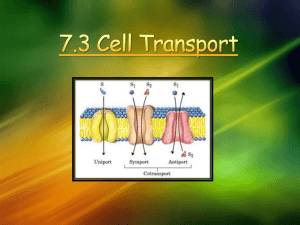
EGG OSMOSIS LAB 10-10-1985 Warm-up ◦List 1 positive thing that happened to you this week ◦List 1 positive thing you look forward to this weekend! (woohoo!) Homework Reminders 1. MasteringBiology: due Monday, October 13 at 10:45 am ◦ Chapter 5 tutorial ◦ Chapter 6 tutorial ◦ Chapter 6 questions Chapter 6 material may take up to 50 minutes….so do this ahead of time! 2. The chapter 7 worksheet is yours to work on...bring it 100% completed on Monday, and 10 extra points will be banked towards the Unit 3 Exam 3. Lab Write-up: due Tuesday, October 14 in beginning of class Unit 3 Exam Projected to be Thursday, October 16 Topics covered yesterday ◦Cell membrane ◦Diffusion ◦Osmosis Today’s objectives ◦SWBAT qualitatively investigate osmosis in cells and explain that external environments can be hypotonic, hypertonic, or isotonic to internal environments of cells. ◦Science Practice #6: SWBAT perform data analysis and evaluation of evidence Getting through cell membrane ◦ Passive transport ◦ Facilitated transport ◦ Active transport Cell (plasma) membrane Cells need an inside & an outside… separate cell from its environment cell membrane is the boundary Can it be an impenetrable boundary? NO! OUT IN food carbohydrates sugars, proteins amino acids lipids salts, O2, H2O AP Biology OUT IN waste ammonia salts CO2 H2O products cell needs materials in & products or waste out 2005-2006 Building a membrane How do you build a barrier that keeps the watery contents of the cell separate from the watery environment? Your choices carbohydrates? proteins? nucleic acids? lipids? AP Biology LIPIDS oil & water don’t mix!! Lipids of cell membrane Membrane is made of phospholipids phospholipid bilayer inside cell phosphate hydrophilic lipid hydrophobic outside cell AP Biology Phospholipids AP Biology It’s like this demented Rudolph looking thing It’s amphipathic! has a split personality Semi-permeable membrane Need to allow passage through the membrane But need to control what gets in or out membrane needs to be semi-permeable sugar aa lipid H 2O salt NH3 So how do you build a semi-permeable membrane? AP Biology Phospholipid bilayer What molecules can get through directly? inside cell NH3 outside cell AP Biology lipid salt sugar aa H 2O fats & other lipids can slip directly through the phospholipid cell membrane, but… what about other stuff? Simple diffusion across membrane Which way will lipid move? lipid inside cell low lipid lipid lipid lipid lipid high outside cell lipid lipid lipid lipid AP Biology lipid lipid lipid lipid Permeable cell membrane Need to allow more material through membrane needs to be permeable to… all materials a cell needs to bring in all waste a cell needs excrete out all products a cell needs to export out inside cell Haa sugar 2O “holes”, or channels, in cell membrane allow material in & out AP Biology outside cell NH salt3 lipid Diffusion through a channel Movement from high to low sugar low inside cell sugar sugar sugar sugar Which way will sugar move? high outside cell sugar sugar sugar AP Biology sugar sugar sugar sugar Semi-permeable cell membrane But the cell still needs control membrane needs to be semi-permeable specific channels allow specific material in & out inside cell salt outside NH3 cell AP Biology H 2O aa sugar How do you build a semi-permeable cell membrane? What molecule will sit “comfortably” in a phospholipid bilayer forming channels bi-lipid membrane protein channels in bi-lipid membrane what properties does it need? AP Biology Why proteins? Proteins are mixed molecules hydrophobic amino acids stick in the lipid membrane anchors the protein in membrane hydrophilic amino acids stick out in the watery fluid in & around cell specialized “receptor” for specific molecules AP Biology 2005-2006 Facilitated Diffusion Globular proteins act as doors in membrane channels to move specific molecules through cell membrane open channel = fast transport high low AP Biology “The Bouncer” Active Transport Globular proteins act as ferry for specific molecules shape change transports solute from one side of membrane to other protein “pump” “costs” energy low high AP Biology conformational change “The Doorman” Getting through cell membrane Passive transport diffusion of hydrophobic (lipids) molecules high low concentration gradient Facilitated transport diffusion of hydrophilic molecules through a protein channel high low concentration gradient Active transport diffusion against concentration gradient low high AP Biology uses a protein pump requires ATP Facilitated diffusion Move from HIGH to LOW concentration through a protein channel passive transport no energy needed facilitated = with help AP Biology 2005-2006 Active transport Cells may need molecules to move against concentration situation need to pump against concentration protein pump requires energy ATP Na+/K+ pump in nerve cell membranes AP Biology 2005-2006 Active transport Many models & mechanisms using ATP AP Biology using ATP Osmosis is diffusion of water Water is very important, so we talk about water separately Diffusion of water from high concentration of water to low concentration of water AP Biology across a semi-permeable membrane 2005-2006 Concentration of water Direction of osmosis is determined by comparing total solute concentrations Hypertonic - more solute, less water Hypotonic - less solute, more water Isotonic - equal solute, equal water water hypotonic hypertonic net movement of water AP Biology Managing water balance Cell survival depends on balancing water uptake & loss AP Biology freshwater balanced saltwater Managing water balance Isotonic AP Biology animal cell immersed in isotonic solution blood cells in blood no net movement of water across plasma membrane water flows across membrane, at same rate in both directions volume of cell is stable Egg Osmosis Lab An unfertilized egg is a very big cell Purpose of lab Given two different solutions and an egg as a cell, you will determine whether the solutions are hypotonic or hypertonic Methods Corn syrup Distilled water 2 replicates 2 replicates Why is having replicates important in scientific research? Methods Corn syrup Distilled water 2 replicates 2 replicates What are our hypotheses & predictions? Hypothesis and predictions ◦ Hypothesis: The tonicity of a solution will affect the mass of the egg. ◦ Null Hypothesis: The tonicity of a solution will not affect the mass of the egg ◦ Predictions: If a solution is hypertonic, then the eggs will ____________mass over time If a solution is hypotonic, then the eggs will ________________ mass over time If a solution is isotonic, then the eggs will ______________________ mass over time. Procedures 1. Each group will go back one at a time to record the final egg mass. When your group is done, please throw away the egg and thoroughly rinse the beakers and place them in the spots as directed by Dr. Cao. 2. Please work efficiently so that we can get all the data collected in a timely manner. 3. Everyone in a group has a role 4. While your group waits to record data, work on your Chapter 7 (cell membrane) worksheet. It will be checked for completion on Monday, and an extra 5 points will be banked to the Unit 3 exam…so it is both a study guide and extra credit. 5. We will pool our data as a class and analyze them together. 6. Lab write ups are due Monday, October 13 in the beginning of class. Group roles: Person 1: Water 1 Egg Person 2: Water 2 Egg Person 3: Syrup 1 Egg Person 4: Syrup 2 Egg Person 5: Cleans beakers Everyone: records data on data sheet Chrome books ◦Log in name: first initial of first name + last name+ last four digits of student ID@cms.gaggle.net ◦Ex: ncao1234@cms.gaggle.net ◦Password: usual for computer login (yy/mm/dd) ◦Once logged in, go to the address below: ◦ to wiki and click on the last hyperlink Go http://drcaobiology.cmswiki.wikispaces.net/# Class data https://docs.google.com/a/cms.k12.nc.us/sp readsheets/d/1OzawI2hsiCfxxlIfpl09u329R9iZp1jhVsT_pA94sQ/edit#gid=0 Data analysis -In science, it is important to quantify the trends that we see in our data -Statistics allows us to test our hypotheses and determine whether our data show a significant relationship in the variables in which we are studying -P-values tell us whether a result is significant or not. -A small p-value (typically ≤ 0.05) indicates strong evidence against the null hypothesis, so you reject the null hypothesis and accept the other hypothesis. Hypothesis and predictions ◦ Hypothesis: The tonicity of a solution will affect the mass of the egg. ◦ Null Hypothesis: The tonicity of a solution will not affect the mass of the egg ◦ Predictions: If a solution is hypertonic, then the eggs will ____________mass over time If a solution is hypotonic, then the eggs will ________________ mass over time If a solution is isotonic, then the eggs will ______________________ mass over time. If P > 0.05, then we can reject the null hypothesis. Simple Linear Regression ◦ Quantifies the linear relationship between the independent and dependent variables ANOVA df SS Regression MS 1 5356.965659 5356.965659 Residual 29 1766.201438 60.90349785 Total 30 7123.167097 Coefficients Intercept 0 Standard Error t Stat Significanc eF F 87.95825934 P-value 2.77E-10 Lower 95% Upper 95% Lower 95.0% Upper 95.0% 72.12116476 1.776126889 40.6058628 4.13467E-27 68.48858 75.75375 68.48858 75.75375 -0.010743771 0.001145562 -9.378606471 2.77133E-10 -0.01309 -0.0084 -0.01309 -0.0084 Things to consider in conclusion… ◦ Which solutions were hypertonic and hypotonic? What evidence do you have in your data that supports this? ◦ Someone observed in class that the water solutions had ‘stuff ’ in it…what do you think it could be and why is it in the water? ◦ Why is it important to consider the solution tonicity when it comes to cellular shape?