Final Jeopardy
advertisement
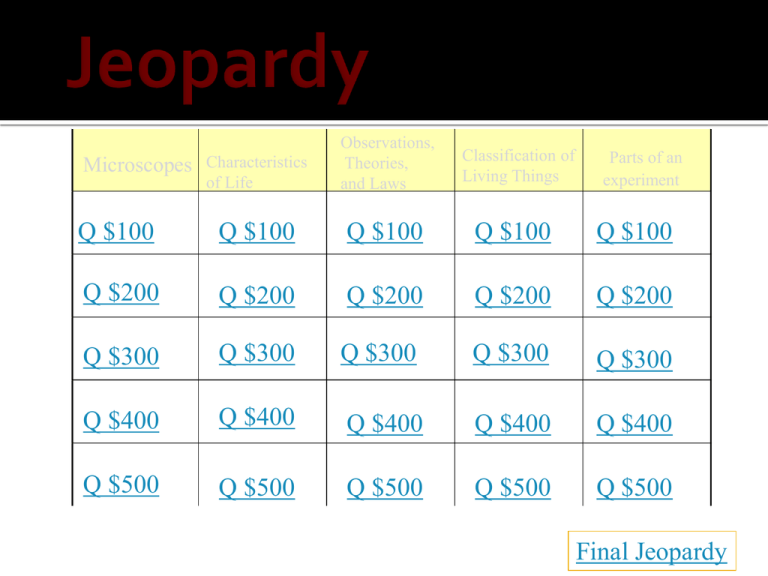
Characteristics of Life Observations, Theories, and Laws Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400 Q $500 Q $500 Q $500 Q $500 Q $500 Microscopes Classification of Living Things Parts of an experiment Final Jeopardy The lense in a compound light microscope where light enters and is first concentrated What is the Objective Lense The part of the light microscope that allows the researcher to put the lenses into focus What are the Adjustment knobs The part of the light microscope that controls the amount of light that is passed through the sample What is the diaphragm The term for half of the microscope where light passes through from the objective to the eyepiece What is the Body The part that changes the intensity of light What is the condenser How all living things are organized. They contain a phospholipid bilayer What is cells Beginning, Growth, Maturity, Decline, Death What is the five stages of Development The way that genetic information is passed from one generation to the next What is DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) The idea that all living things maintain an constant internal enviornment What is Homeostasis The two characteristics of Life that involve interacting with the outside world What is 1. Responding to stimulus 2. Adapting to the environment What is the Difference? A description of relationships among observable phenomenon What is a Scientific Law A hypothesis that has been confirmed by evidence and has endured all attempts to disprove it What is a Scientific Theory The facts that allow scientists to create a theory Data and observations An observation that includes a measurement or numbers What is a quantitative observation An observation based on the scientists senses What is a Qualitative Observation The whole Earth What is the biosphere The simplest living structure What is a cell A group of the same organisms living in the same place What is a population All the living and non-living parts of a defined area What is a community All of the deserts of the entire planet What is the desert biome The part of the experiment that the researcher changes between groups What is the Independent Variable The part of the experiment that the researcher measures to collect data What is the dependent variable The statement made by the researcher with regards to the experimental question What is the hypothesis The parts of the experiment that are the same for all repetitions (cohorts) The constants (constant variables) The part of the experiment that is unaffected by the independent variable What is the control identify the following components of an experiment. 1. Independent variable 2. Dependent variable 3. Control Group 4. Repeated trials 5. Constants (at least 3) Norm wanted to know if adding peat moss to sand would affect its ability to hold water. He put 200mL of pure sand into container A. He put a mixture of 80% sand and 20% peat moss into container B. He put a mixture of 60% sand and 40% peat moss into container C. He put a mixture or 40% sand and 60% peat moss into container D. He added water to each container and measured the amount of water the contents would absorb. He dried the sand and peat moss and repeated the experiment 5 times. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What is the ratio of sand to peat moss (IV) What is the amount of water the contents would absorb (DV) What the sample with pure sand (control) 5 repetitions Containers, Amount of Dirt, Water (and many more)