Ch 6 Angiosperm Evolution
advertisement

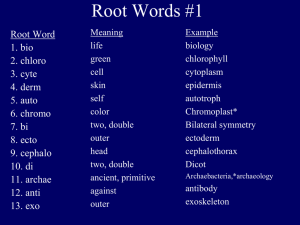
Angiosperm Evolution Chapter 6 Simpson, 2nd Edition Major Evolutionary Advances Life - 3,800 mya Prokaryotic cell/autotrophic Eukaryotic cell - 1,400 mya Multicellar plants - 1,000 mya Vascular tissue - 430 mya Needed on land - why? 1. Earth 2. Prokaryotes 3. Eukaryotes 4. Multicellular life 5. Vascular tissue 6. Seeds 7. Flowers Seeds - 350 mya Flowers – 130 mya Earth Forms 5,000 mya Prokaryotic Cells 4,000 mya Eukaryotic Cells 3,000 mya 2,000 mya Multicellular Plants 1,000 mya Vascular tissue Seeds Flowers Timeline Devonian Period • 400mya – 1st vasc plts • Psilotum – like Devonian-Carboniferous • ferns, lycophytes, sphenophytes & progymnosperms Mesozoic • gymnosperm-dominant seed plants Cretaceous Period • 130 mya 1st fossil flowers • 90 mya - worldwide angiosperm dominance Relationships of Angiosperms Bennettitales and Genetophytes – 225 mya Relationships of Angiosperms Systematics • phylogeny represented by cladogram (phylogenetic tree • branching diagram that conceptually represent the evolutionary pattern of descent • lines represent lineages, with implied time scale • branch = divergence • ancestral = preexisting • apomorphy = derived (evolutionary novelty) Systematics • Phylogenetic Systematics (cladistics) • methodology to infer evolutionary history using apomorphies • recognizes monophyletic groups (= clade) • Phylogenetic Classification Scheme can result • avoids: • paraphyletic groups • • com anc but not all descendants polyphyletic groups • two or more sep groups with sep anc Angiosperm Systematics What conclusions can be drawn from this cladogram? Angiosperm Apomorphies 1. flower, usually with perianth Angiosperm Apomorphies 2. stamens with 2 lateral thecae, each composed of 2 microsporangia 3. reduced, 3-nucleate male gametophyte Angiosperm Apomorphies 4. carpels and fruit formation • • conduplicate (inwardly folded longitudinally & along the central margin) megasporophyll bearing 2 adaxial rows of ovules carpel body encloses seed (angiosperm name origin) Angiosperm Apomorphies 5. ovules with 2 integuments • bitegmic with micropyle at distal end Angiosperm Apomorphies 6. reduced, 8-nucleate female gametophyte Angiosperm Apomorphies 6. reduced, 8-nucleate female gametophyte: • evolution of female gametophyte Angiosperm Apomorphies 7. endosperm formation • product of double fertilization • zygote = 1 sperm + egg • endosperm = 1 sperm + polar nuclei Angiosperm Apomorphies 8. sieve tube members • sieve plates – contain pores at end walls larger than lateral pores • sieve cells are primitive sugar-conducting cells vessels found in all but primitive angiosperms Origin of Angiosperms Archaefructus 130 mya northern China reconstruction of Archaefructus sinensis fossil imprint of Archaefructus lianogensis Four evolutionary trends among flowers 1. floral parts many -> few 2. floral whorls from 4, long floral axis, separate parts -> reduced whorls, short floral axis, fused parts 3. superior -> inferior ovary 4. symmetry radial -> bilateral Lonicera (honeysuckle) Vanilla (vanilla bean orchid) Nelumbo (Lotus) 1. 2. 3. 4. floral parts few reduced whorls, short floral axis, fused parts inferior ovary bilateral symmetry Helianthus disk floret Anemone Order Asterales Asteraceae (=Compositae) Sunflower Family 1620 genera 23,600 species 1) 2) 3) 4) most diverse dicot family 98% herbaceous, but shrubs, trees or vines also inflorescence a head, subtended by involucre of phyllaries K 0-∞ C (5) [4] or (3) A (5) [(4)] G (2) inferior p. 429 Fig. 8.131 Order Asterales Asteraceae (=Compositae) Sunflower Family 1620 genera 23,600 species p. 430 Fig. 8.132 Order Asterales Asteraceae (=Compositae) Sunflower Family 1620 genera 23,600 species p. 431 Fig. 8.133 Order Asterales Asteraceae (=Compositae) Sunflower Family 1620 genera 23,600 species p. 432 Fig. 8.132 Order Asterales Asteraceae (=Compositae) Sunflower Family 1620 genera 23,600 species