Vitiligo
advertisement

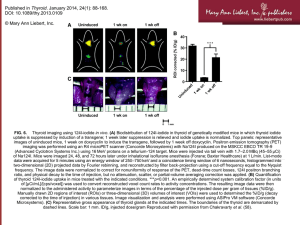
THYROID GLAND History Taking Endocrine and Metabolism System 2011-2012 The basic concept of the function of thyroid hormones Up-regulate the function of other hormones e.g. growth hormone & catecholamines They heat up the other endocrinal functions Thyroid Disorders affect Peoples’ Health and Quality of Life Hypothyroidism Hyperthyroidism The Thyroid Gland is - as important as your heart decreased Thyroid hormones increased Thyroid hormones Hypothyroidism Hyperthyroidism Hypothyroidism is much more common than Hyperthyroidism Effects of Thyroid Hormones Fetal brain and skeletal maturation Cardiovascular system (Inotropic and chronotropic effects on heart) Muscle function Brain, nervous system Increase sensitivity to catecholamines Stimulate gut motility The thyroid: the “heart” of metabolism Involvement of thyroid function: Growth and development, fertility Energy metabolism Protein and carbohydrate metabolism Fat metabolism Bone metabolism Cardiovascular system Muscle function Brain, nervous system, psyche larynx trachea thyroid gland Effects Of Thyroid Hormones On The Cardiovascular System Increase heart rate Increase force of cardiac contractions Increase stroke volume Increase Cardiac output Up-regulate catecholamine receptors The Respiratory System Increase resting respiratory rate Increase minute ventilation Increase ventilatory response to hypercapnia and hypoxia On The Renal System Increase blood flow Increase glomerular filtration rate On Oxygen Carrying Capacity *Increase RBC mass *Increase oxygen dissociation from hemoglobin On Intermediary Metabolism Increase glucose absorption from the GI tract Increase carbohydrate,lipid and protein turnover Down-regulate insulin receptors Increase substrate availability On Growth And Tissue Development Increase growth and maturation of bone Increase tooth development and eruption Increase growth and maturation of epidermis,hair follicles and nails Increase rate and force of skeletal muscle contraction Inhibits synthesis and increases degradation of mucopolysaccharides in subcutaneous tissue On The Nervous System Critical for normal CNS neuronal development Enhances wakefulness and alertness Enhances memory and learning capacity Required for normal emotional tone Increase speed and amplitude of peripheral nerve reflexes On The Reproductive System Required for normal follicular development and ovulation in the female Required for the normal maintenance of pregnancy Required for normal spermatogenesis in the male Two young women with goiter History Taking INTRODUCTION HISTORY TAKING Greet the patient and introduce the examiner’s name Ask the patient’s identity : - The patient’s name, age, occupation, and patient’s residence CHIEF COMPLAINT - - Ask the patient why she/he come to clinic Ask the date of onset (The onset was sudden or insidious) - Ask the symptoms Thyroid Hypo function - coldness weight gain constipation menstrual irregularities muscle cramps. malaise fatigue Hypothyroidism before and after treatment Thyroid Hyper function: - palpitations - heat intolerance - nervousness - easy fatigability - restlessness - diarrhea. - excessive sweating. - preference to cold. - weight loss without loss appetite. - emotional instability Past History Exposure to ionizing radiation in childhood Surgery Thyroiditis Drugs: - Amiodarone - IV Contrast agent - Lithium Family history of Thyroid disease History of other autoimmune diseases like: - Diabetes - Rheumatoid arthritis - Vitiligo - Pernicious anaemia Prevalence of thyroid abnormalities in general population: Total study population (n=25862) Subjects taking thyroid medication (n=1525) Euthyroid 88.3 % 60.1 % Hypothyroid * 0.4 % 0.7 % Subclinical hypothyroid 9.0 % 17.6 % Hyperthyroid 0.1 % 0.9 % Subclinical hyperthyroid 2.1% 20.7 % * probably underestimated (assessed by TT4) Canaris GJ et al. (2000) Prevalence of thyroid dysfunction in elderly population (age > 35 yrs.) Condition Hypothyroidism Reported prevalences in adult population, % 2 Mild (subclinical) hypothyroidism Hyperthyroidism 5- 17 Mild (subclinical) hyperthyroidism 0.1- 6.0 (TSH<0.1, normal T4,T3) (Adapted from Vanderpump and Tunbridge, 2000) 0.2 THANK YOU