Morphology- Adults of

Introduction to the Helminths 蠕虫
Helminths means worms, multicellular organisms.
Phylum Class
Nemathelminthes Nematoda
(round worm) 线虫纲
线形动物门
Platyhelminthes Tremetoda
(flatworms) 吸虫纲
扁形动物门 Cestoda
绦虫纲
The Nematodes 线虫
There are many, many nematodes
2002 年诺贝尔奖:程序性细胞死亡
2006
诺贝尔奖
:
RNA干扰机制
C.Elegans
Morphology
Cylindrical, non-segmented, bilaterally symmetrical and sexes separate
Pseudocele 原体腔
( pseudocoelom)
The body wall: cuticle 角皮层 hypodermis 皮下层 longitudinal muscle 肌层
The arrangement of the somatic muscles
Polymyarian type
( Ascarids)
Meromyarian type
(Hookworm)
Holomyarian type
( Whipworm )
Digestive system
咽管 食管
Mouth pharynx esophagus intestine anus
肠管 肛门
Reproductive system male reproductive system
Testis seminal vesicle
睾丸 储精囊 vas deferens
输精管 ejaculatory duct
射精管
Most females usually have two ovaries , oviducts and uterus..
ovary — oviduct — uterus.
ovary — oviduct — uterus..
卵巢 输卵管 子宫 vulva -vagina
阴门 阴道
nervous system
Consist of : circumesophageal nerve ring
咽管神经环 and
2 or 4 longitudinal nerve trunks
神经干
Excretory system
Excretory pore is anterior.
排泄孔
No flame cells are present.
life cycle
M1 M2 M3 M4
Egg L1 L2 L3 L4 Adult larva (male & female)
Kinds of life cycle in nematodes
Direct life cycle:
Intermediate host is not necessary
Ascaris lumbricoides
Trichuris trichiura
Enterobius vermicularis
Hookworms
Indirect life cycle: intermediate host is necessary
土源性线虫
(肠道线虫)
Trichinella spiralis
Filaria
生物源性线虫
Pathogenesis
1)Larvae
:
( 1) dermatitis caused by cutaneous invasion and subcutaneous migration of larva;
( 2) injury to organs or tissues by migration of larvae in the body
2) Adults :
(1) injury to intestinal mucosa caused by the parasites living in gastro- intestinal system
(2) injury to lymphatic system, muscles or nervous system caused by the parasites living in tissues
What about Egg ?
INTESTINAL HELMINTHS
Ascaris lumbricoides (roundworm) 似蚓蛔线虫
Trichuris trichiura (whipworm) 毛首鞭形线虫
Enterobius vermicularis (pinworm) 蠕形住肠线虫
Ancylostoma duodenale and Necator americanus
(hookworms) 钩虫
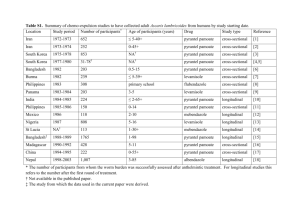
2004 年第二次寄调
Ascaris lumbricoides
(ascarids)
Adults live in intestine of human, cause Ascariasis ( 蛔虫病 ) ;
Human is the only definitive host of this parasite.
>
1 billion world wide the infective rate in China 12.72%
Hookworms
Five species of hookworms:
Ancylostma duodenale
十二指肠钩口线虫
Necator americanus
美洲板口线虫
Ancylostma ceylanicum
锡兰钩口线虫
Ancylostma caninum
犬钩口线虫
Ancylostma brazilience
巴西钩口线虫
Adult live in the intestine and take blood from the host, cause hookworm disease.
国内: 6.12%
Number of humans infected is estimated at 1.2 billion with
50,000 to 60,000 deaths each year .
Enterobius vermicularis
(Pinworm)
Almost anybody can become infected with this parasite , especially children.
国内: 10.28% The worldwide infection is about 210 million
Morphology
Morphology -
Adult of Ascaris lumbricoides the largest nematode parasites of humans
Creamy white or pinkish in color elongate and cylindrical
Morphology -
Adults of Ascaris lumbricoides
Female: measuring 35cm long, posterior end is straight
Male: measuring 25cm long , posterior end is curved .
Morphology -
Adults of Ascaris lumbricoides
Three lips around the mouth in
“ 品” type and possess small teeth
Morphology -
Adults of Trichuris trichiura
50 mm long with a slender anterior and a thicker posterior end
The male is smaller and has a coiled posterior end
Morphology -
Adults of Enterobius vermicularis
Adults: pin-like, white, small worm
咽管球 头翼
Female showing esophageal bulb & cephalic alae
Male with curved posterior end, Female has a long pointed end.
Morphology -
Adults of hookworms
Adult:
Slender, pinkish or creamy-gray in color, about 10mm in length.
Morphology -
Adults of hookworms
Females:
9-13 mm long with egg-filled uterus
Males:
7-11 mm long, Posterior end forms a Copulatory bursa ( 交合伞 )
Morphology of Ancylostoma duodenale
Buccal capsule contains 2 pairs of large ventral
(anterior) teeth
Copulatory bursa is at posterior end and contains 2 thin spicules that separate distally.
口囊
交合伞
Morphology
of Necator americanus
Buccal capsule contains a pair of ventral and dorsal cutting plates.
Copulatory bursa contains spicules that are fused distally.
Difference between A.duodenale and N. americanus
A.duodenale shape
“ c
”
, 1cm ±
N. americanus
“ s
”
, 1cm ± buccal capsule flat and oval-shape oval-shape two pairs one pair cutting plates
Copulatory bursa round oblate spicule two, separated two, fused at their ends
Morphology - larva of hookworms rhabditiform Larva 杆状蚴 filariform larva : infective stage
Morphology -
Eggs of Ascaris lumbricoides
Eggs are unembryonated when passed in the feces.
Embryonation occurs in the soil. broadly oval yellowish to brown in color
Thick shell protein coat ovum
Unembryonated egg in feces fertilized
unfertilized and fertilized egg
Morphology -
Eggs of Ascaris lumbricoides
Embryonated egg in soil
Decorticated egg
(lost outer albuminous coating)
Morphology -
Eggs of Trichuris trichiura size: 5054 µm by 22-23 µm, smaller than Ascarids’
Shape : a typical barrel
Color : yellow-brown unstained two polar plugs
Shell : quite thick
Contains : unembryonated egg
Morphology -
Eggs of
Enterobius vermicularis size: smaller than Ascarids’
Shape : oval, flattened on one side
Color : colorless
Shell : quite thick
Contains : an undeveloped larva inside
Morphology -
Eggs of hookworms
Shape : oval-round
Shell : thin with smooth and colorless (transparent) eggshell
Size: 5776 µm by 35-
47 µm
Contains: clear space between the egg-shell and the ovum. feces
Usually 2 to 16 cells in
Morphology -
Eggs of hookworms
Life cycle
Life cycle of Ascaris lumbricoides
Life cycle
Ingested by man
Adult egg infective egg larva migration
Migration of larva in the host:
Vessels of intestine liver heart lungs trachea
(swallowed) pharynx intestine
Life cycle of hookworm
Life Cycle
Adult egg rhabditiform filariform larva larva
Swallowed pharynx trachea lung circulation
Penetrate skin
Life cycle of
Enterobius vermicularis
Life cycle
(in lumen of cecum)
Adult egg ingested infective egg
Pathogenesis
Pathogenesis of
Ascaris lumbricoides
1) larvae: Ascaris Pneumonitis
Asthma
Larva in section of lung
Pathogenesis
2) Adults :
(1) Malnutrition
(2) Disorder of digestive system: main complaint--- abdominal pain anorexia ( 食欲不振 ) nausea ( 恶心 ) vomiting ( 呕吐 ) diarrhea ( 腹泻 )
(3) Allergic responses
Complication
并发症 penetrate to bile ducts 胆道蛔虫症 penetrate to the pancreatic and the appendix
胰腺 阑尾
intestinal obstruction 肠梗阻
Ectopic parasitism 异位寄生
Pathogenesis of
Enterobius vermicularis
1. cause irritation( pruritus 搔痒 ) of the anal region
Secondary bacterial infection in areas scratched raw may occur.
2. vaginitis and rarely salpingitis in young girls.
阴道炎 输卵管炎
3. cause mental anguish
Pathogenesis of hookworm
1. Local dermatitis (ground itch) 钩蚴性皮炎
2.Pulmonary (pneumonia-like) symptoms
(symptoms are not as severe as Ascaris migration)
3. Anemia a. The worm sucks blood and the wound oozes blood
A. duodenale takes 0.26 ml/day;
N. americanus 0.03 ml/day
b. The worm usually changes its sucking site c. Disfunction of intestine to absorb iron gradually produce an iron-deficiency anemia
4. gastroenteric symptoms 胃肠道症状
Slight, intermittent abdominal pain
5. Aberration of appetite(geophagy 异嗜症 ) .
loss of normal appetite and desire to eat soil or un-normal materials
6. Hookworm diseases of infant
7. eosinophilia
Laboratory Diagnosis
Laboratory Diagnosis
1. By identifying the eggs
1. direct fecal smear
2. brine-floatation method
(饱和盐水浮聚法)
3. Scotch tape technique
(cellophane tape impression)
透明胶纸黏贴法
4. Larval cultivation
(钩蚴培养法)
2. By identifying the adults
3. therapeutic test
Epidemiology distribution
Basic conditions in parasitic epidemiology
Souce of infection
Patients and infected persons
Mode of transmission (Factors of prevalence)
For round worm
Via mouth
For hookworm
Via skin
Others:
Oral ( A. doudenale)
Placenta
Mother’s milk
Paratenic hosts
Warmer and poor sanitation
Inadequate disposal of feces
Using nightsoil as fertilizer
Bare-foot walking
For pinworm
“Hand-to-Mouth”Transmission retroinfection through anus inhalation of ova
Susceptible population
Epidemiology the reason for wide distribution of Ascaris l
1. simple life cycle
2. high reproductive capacity (240,000 eggs per day)
3. resistance of egg (due to presence of ascarosidal )
4. social customs and habits
Treatment Prevention and control
Treatment of patients and carriers,
Blockade of the route of transmission
Protection of the susceptible population
(personal prophylaxis)
Chemoprophylaxis, vaccines, other preventive measures
Treatment Prevention and control
Treatment:
Mebendazole(甲苯哒唑)
Albendazole(阿苯哒唑,肠虫清)
To prevent re-infection of E.v, treat the whole family.
Others for hookworm diseases?
透热疗法
纠正贫血
Prevention and control:
Good hygiene is the best preventive measure hygienic control of food, feces avoidance of contact with infected fecal material
Wash all bed clothes and bedding in hot water to kill infective eggs of E.v.
Others?
Dog and Cat Hookworms
HUMANS may serve as accidental hosts of these hookworms when the filariform larvae penetrate human skin
Creeping
Eruption
匍形疹