T4 - Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland
advertisement

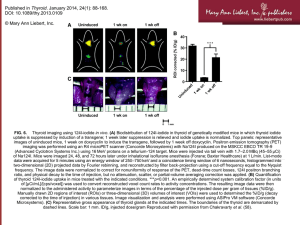
Thyroid Disease Dr John McDermott Consultant Endocrinologist Connolly Hospital Blanchardstown Hermitage Medical Clinic Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland Thyroid Hormones • Thyroid gland manufactures and releases thyroid hormones • Thyroid hormones are iodine containing amino acids • 3, 5, 3’ triiodothyronine = T3 • 3, 5, 3’,5’ tetraiodothyronine = T4 Thyroid Hormones • ‘Maintain the level of metabolism in the tissues that is optimal for their normal function’ • Small amounts secreted continuously Thyroid Hormones • Deficiency or excess of thyroid hormones: wide and varied symptoms and physical signs involving any organ system Thyroid Case • 33 year old woman • Gaining weight • Tired – busy job and 2 young children • Rows over thermostat Thyroid Case • T4: 6 (normal 9 – 22) • TSH: 36 (normal 0.4 – 4) • Diagnosis: Hypothyroidism Other symptoms of hypothyroidism • Constipation • Heavy periods • Cold dry skin, dry hair, hair loss • Muscle pains/stiffness Hypothyroidism • Joseph Fourier, a French mathematician • ‘began to suffer from a strange disease, whose main effect was to render him extremely sensitive to cold….caused him to wrap up in many layers of heavy clothing, and live in a highly heated room from which he seldom ventured forth, even in summer heatwaves’. Paul Strathern, Napoleon in Egypt Treatment of Hypothyroidism • Thyroid hormone, T4 (Eltroxin) • Aim to abolish symptoms • Aim to achieve a high normal T4 and lownormal TSH • NB Pregnancy issues Thyroid Case [2] • 26 year old woman • Noticed prominence of right eye x 3 weeks • Increased appetite – but weight decreasing • Difficulty getting out of the bath On Examination • Pulse 120 regular • Tremulous, sweaty hands • Enlarged, rubbery thyroid Thyroid Case [2] • T4: 37 (normal 8 – 22) • TSH < 0.01 (normal 0.4 – 4) • Anti-TSH receptor antibodies ++ • Diagnosis: Graves Disease causing hyperthyroidism, ophthalmopathy Graves Disease • Autoimmune condition • Antibodies against TSH receptor – stimulate excess thyroid hormone • Antibodies attack back of eye - proptosis Treatment of Hyperthyroidism • Antithyroid drugs: Carbimazole (Neomercazole) Propylthiouracil (PTU) • Radioactive Iodine • Surgery - thyroidectomy Radioactive Iodine • Commonly prescribed treatment for hyperthyroidism • Orally-administered I131 • Concentrated in thyroid gland, radiation destroys thyroid tissue Radioactive Iodine • Precautions after dose • Long-term hypothyroidism Surgery • ‘Subtotal’ thyroidectomy • Hypothyroidism • Potential other complications Diseases of the Thyroid Disorders of function: • Hyperthyroidism • Hypothyroidism Disorders of structure: • Goitre • Thyroid nodules/cancer Goitre • Enlarged thyroid • Symptoms: Cosmetic concerns, obstructive symptoms • Toxic Multinodular Goitre: hyperthyroidism Thyroid nodules • 5% of population have palpable thyroid nodules • 30-40% of popn have non-palpable nodules detectable on ultrasound • Thyroid cancer in 8% of palpable thyroid nodules • Differentiated cancers: slow growing, good prognosis Thyroid nodules • Risk stratify: risk factors, u/s characteristics, hot or cold • Fine needle aspiration • Observation, surgery Summary • Thyroid disease common but treatable, wide and varied complaints • Disorders of function: Hypo/Hyper, diagnosis TFTs • Disorders of structure: Goitre, nodules