Paramyxoviruses 副黏液病毒 Objectives How many types of viruses
advertisement

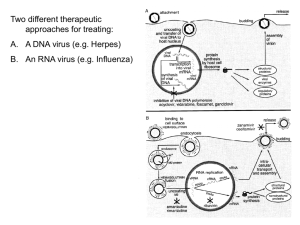
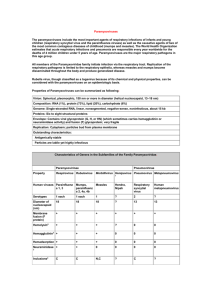
Paramyxoviruses 副黏液病毒 Objectives • How many types of viruses under paramyxovirus. • How many serotypes of each virus? • What is the status of Hemagglutinin and Neuraminidase in each virus? • Vaccine MMR is for what viruses? • The pathogenesis and clinical symptoms of each virus. • What drugs can be used to treat these viruses? I. Classification Family: Paramyxoviridae genera: Morbillivirus --> Measles V. Paramyxovirus--> Parainfluenza V. & Mumps V. Pneumovirus --> Respiratory Syncytial V. (RSV) Hemagglutinin and Neuraminidase RSV in MA104 cell RSV in Hep-2 cell Measles in kidney cell Measles in kidney cell Replication in cytoplasm Nucleus II. Measles virus * Cause maculopapular rash(班及丘疹) * Has hemagglutinin, no neuraminidase * One serotype Measles SSPE: Subacute Sclerosing Panencephalitis 亞急性硬化泛腦炎 * Systemic infection Epidemiology • * One of the most infectious diseases * Occurred in Winter and Spring in preschool children * 85% infected cause disease; 4 million death before 5-year old each year * 1-3 years/ cycle • * 1/1000 become encephalitis; 1/1 million become SSPE, (teenage and young adult) Pathogenesis Clinical Syndromes • Fever--> Koplik's spot (marker for clinical diagnosis) --> rash IV. Mumps viruses • Cause parotitis, similar to parainfluenza virus infection • With hemagglutinin and neuraminidase • One serotype Pathogenesis • Humans are the only natural hosts. • Mumps is a systemic viral disease. • Nasal or upper respiratory tract epithelial cells --> viremia --> salivary glands (parotid gland) • Difficult to control the transmission because of the various incubation periods ---> (7-25days). Mumps virus * Systemic infection Epidemiology • Worldwide infection, occurred endemically in Winter or Spring. • Incubation period is about one week • 90% infected before age of 15 • Aerosol or personal contact Clinical Syndromes • 1/3 subclinical; 95% of the patients with swelling of the salivary gland. • Malaise and anorexia --> enlargement of parotid glands Treatment, Prevention and Control • No-antiviral treatment III. Parainfluenza virus • With hemagglutinin and neuraminidase • 4 serotypes Pathogenesis Paramyxovirus Clinical Syndromes • Laryngitis, croup, tracheobronchitis and pneumonia • Cause common cold: sneezing, nasalobstruction or-discharge, sore throat, headache, mild cough, malaise, and chillness. Epidemiology • Newborn or children under 5 year old • Occurred in Fall • Hospital people may get infected Treatment, Prevention and Control • Hot steam, spread therapy (upper respiratory tract infection) • No effective vaccine Paramyxovirus in RhMK cells Hemadsorption Unfected cells V. Respiratory Syncytial Virus • Localized respiratory tract infection • First discovered in chimpanzee • without hemagglutinin, neuraminidase • With glycoprotein and fusion protein Pathogenesis Respiratory syncytial virus Clinical Syndromes • Running nose Epidemiology • Occurred in Winter • Spread through hands or aerosol Treatment, Prevention and Control • Treatment: drug--> ribavirin • Prevention:prevent cross contamination • Vaccine: NA