GERD - City Tech OpenLab
advertisement

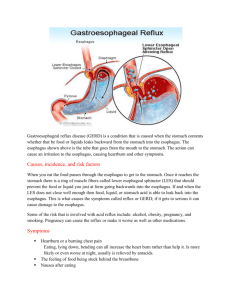
GERD Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease By: Ruth Fernandez Faviola Calixto Vanessa Oyola What is GERD ? GERD is the return of the stomach’s acidic contents back up to the esophagus nchmedicalgroup.com Question #1 How long is the esophagus? Answer: The esophagus is an 18 to 26 cm hollow muscular tube that acts as a conduit for the transport of food from the oral cavity to the stomach. http://www.redorbit.com/news/health/274845/understanding_acid_reflux_and_its_dental_manifestations/ What causes GERD ? • GERD is caused by a weak or relaxed lower esophageal sphincter, the junction between the esophagus and the stomach Dallasreflux.com Question #2 About how many Americans are affected with GERD? Answer: Approximately 19 million Americans are affected with GERD. http://heartburn.about.com/od/gerdacidrefluxdisease/a/gerd_facts.htm Question #3 Does GERD affect infants? Answer: Yes, About 1 in 300 infants will present signs and symptoms of GERD. http://www.coliccalm.com/baby_infant_newborn_articles/acid-reflux.htm Symptoms of GERD • • • • Heartburn Chest pain Coughing or choking while lying down Increased asthma symptoms while sleeping Question #4 What is the percentage of Americans suffering from heartburn? Answer: Evidence indicates that up to 36% (60 million Americans) of the Americans suffer heartburn once a month and 7% (25 million Americans) suffer heartburn every day. http://heartburn.about.com/od/understandingheartburn/a/heartburn_facts.htm Treatment for GERD Lifestyle Changes • For severe GERD, it is recommended elevating the head of the bed on 6-inch blocks or sleeping on a specially designed wedge to reduce heartburn by allowing gravity to minimize reflux of stomach contents into esophagus Dietary Changes • Avoid foods and beverages that can weaken the lower esophageal sphincter such as chocolate, peppermint, fatty foods, coffee and alcoholic beverages • Eating meals 2-3 hours before bedtime may lessen reflux by allowing the acid in the stomach to empty partially Treatment for GERD • Along with lifestyle and diet changes, physician may recommend over-thecounter or prescription medications such as: Over The Counter Drugs • There are 3 Pharmacologic categories: 1. Antacids 2. Histamine-2 (H2) blockers 3. Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs) Antacids •Maalox •Mylanta •Rolaids Drugline.org Drugline.org •Tums MOA: neutralize stomach acid Drug3k.com Soap.com Adverse effects: chalky taste, stomach cramps, constipation, headache. Histamine-2 Blockers MOA: works by decreasing the amount of acid the stomach produces • Axid AR (nizatidine) • Pepcid AC (famotidine) • Zantac 75 (ranitidine) • Tagamet HB (cimetidine) Drugshoponline.com Planterx.com Vitacost.com Adverse effects: headache, dizziness, diarrhea, constipation, abdominal pain, rash, fever. Proton Pump Inhibitors MOA: blocks acid production and heal the esophagus. •Prevacid 24HR (Lansoprazole) •Prilosec OTC (Omeprazole) •Zegerid OTC (Omeprazole and Sodium Bicarbonate) Walmart.com Amazon.com Drugcounter.com Adverse effect: headache, dizziness, rash, abdominal pain, constipation, diarrhea, nausea. Prescription Medications • There are 3 Pharmacologic Categories: 1. Histamine-2 (H2) Blockers 2. Proton Pump Inhibitors 3. Promotility Agents Histamine-2 (H2) Blockers • Tagamet • Zantac • Pepcid Drug3k.com Drug3k.com Everydayhealth.com MOA- works by decreasing the amount of acid the stomach produces. Adverse Affects- headache, abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, gas, sore throat, runny nose, and dizziness. Proton Pump Inhibitors • Nexium • Protonix • Aciphex • Prevacid Prescriptionpictures.com Rubell.com Drugs.com Totalhealth4life.net MOA- blocks acid production and heals the esophagus. Adverse Affects- headache, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and nausea. Promotility Agents • Reglan Pubrecord.org MOA- help speed digestion, reducing the amount of time that acidic contents stay in the stomach. These may be used when therapy with H2 Blockers or PPI’s do not work. Adverse Affects- drowsiness, fatigue, diarrhea, restlessness, and movement disorders (dyskinesia) Another treatment for GERD When medications are not enough to treat and relieve the symptoms of GERD, surgery is another option. •The most common surgery for GERD is called Fundoplication surgery. •In this surgery the upper curve of the stomach (the fundus) is wrapped around the esophagus and sewn into place so that the lower portion of the esophagus passes through a small tunnel of stomach muscle. This surgery strengthens the valve between the esophagus and stomach (lower esophageal sphincter), which stops acid from backing up into the esophagus as easily. This allows the esophagus to heal. •This surgery helps 60-90% of the people with GERD. Dallasreflux.com Oral manifestations of GERD: • Enamel erosion • Bruxism (tooth grinding or clenching) • Oral mucosal lesions may result by direct acid or acidic vapor contact in the oral cavity such as: oral ulcers, erythema of the palatal mucosa and uvula • Xerostomia Role of Dental Hygienists • Recommendations: • • • • • • • Smoking cessation. Smoking weakens the lower esophageal sphincter and increases reflux Do not brush immediately after reflux: Patients should be advised to rinse their mouths either with water, milk sodium bicarbonate solutions or sodium fluoride mouth rinses Brushing teeth, chewing hard foods and sugar- free gums should be avoided for approximately 2 hours after a regurgitation episode to allow for the re-establishment of salivary pellicle and subsequent tooth surface remineralization Nutritional counseling Use of specific oral products to keep oral cavity and dentition protected Discussing with health care provider the intake of certain medications such as over-the-counter pain relievers, including aspirin, ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), or medicines for osteoporosis. These can aggravate reflux in some people