Sickle Cell Disease
advertisement

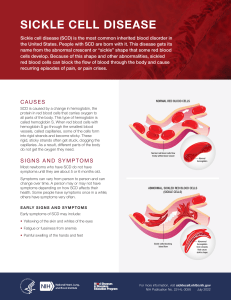
Sickle Cell Disease Sickle Cell Disease Group of genetic disorders characterized by: Hemolytic anemia - not enough red blood cells in the blood Vasculopathy - disorder of blood vessels In US, predominantly with African-Americans (i.e., 1 in 400) Also occurs in descendents of Mediterranean, Indian, Asian, and Caribbean cultures Sickle Cell Syndromes Sickle Cell Trait (HbS gene) Sickle Cell Anemia (HbS/HbS) Hgb SC Disease Sickle Beta-Thalassemia SCA: Impact on Red Blood Cells With low oxygen levels, the shape of red cells becomes distorted They appear elongated and sickle shaped Red blood cells become very fragile, short lived, and can clog blood vessels SCA: Complications Clinical manifestations do NOT appear until after ~ 6 months Vaso-occlusive pain crises CSA: Complications CNS complications Cardio-pulmonary complications Acute Chest Syndrome Chronic lung disease SCA: Complications Hepatobiliary Spleen atrophies Gallstones Liver failure Genitourinary Priapism Delayed puberty Amenorrhea Infertility SCA: Complications Musculoskeletal Acute painful crisis Avascular necrosis Immunological Susceptible to infection SCD: Transfusion Therapy Used to treat certain complications: Splenic sequestration Aplastic crisis Priapism Stroke Used to prevent complications Repeated strokes Surgery-related problems SCD: Medical Pain Management Vigorous hydration Warmth Rest Analgesic medications Demerol Morphine Nubain SCD: Psychological Issues Consequences of repeated pain crises Compromises daily routines Repeated hospitalizations Side effects of narcotic analgesics Development of “dependent” behaviors Apprehension, anxiety, depression SCD: Pain Management Biofeedback Relaxation training PMR Deep breathing Autogenics Imagery-based techniques SCD: Pain Management Pain behavior contracts Hydration Deep breathing Out of bed activities Dosage/frequency of pain medications Patient controlled anesthesia (PCA pump) SCD: Psychological Issues Emotional and behavioral competence of children Self-concept Externalizing behavior problems Internalizing behavior problems *links between depression/anxiety and pain perception SCD: Psychological Issues Social Competence Peer relationships Family relationships SCD: Coping Strategies Related to: Adjustment (e.g., anxiety) Activity level Health care services Distress in episode SCD: Now and the Future Longevity and Quality of Life Has improved over past 20 years Prophylactic penicillin Newer antibiotics Judicious use of blood transfusions Bone marrow transplant as “cure” New drugs to decrease pain episodes Genetic manipulation