Root cause analysis
Slides adapted from:
•
the proceedings of the first workshop of Leadership mentorship for Maternal,
Newborn and Child health: a programme for DCSTs in KwaZulu-Natal , 13 to 17
August 2012.KZN DOH/UNICEF/UKZN.
•
A presentation given by Dr MG Schoon, Department of Health, Free State
Provence
Definition
Purpose
Identify causative factors and develop
corrective strategies
Any event in the chain of causes that, when
acted upon by a solution, prevents the
problem from recurring.
To prevent adverse events/outcomes
Prevent harm
Improve quality care and patient safety
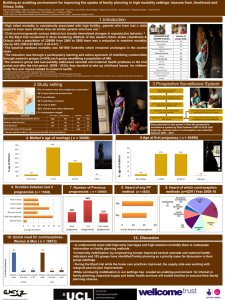
Age distribution per age and sex
North Cape
Namakwa
Access to piped water
N Cape maternal, infant and mortality rates
Mortality
2010/2011
2011/2012
Maternal mortality
ratio
239/100 000 live births
167/100 000 live births
Facility infant mortality
rate
6.5/1000 live births
8.4/1000 live births
Under 5 mortality rate
5.3/1000 live births
5.5/1000 live births
Top causes of maternal death in
Gauteng
NCCEMD 2012
Non Pregnancy Related Infections
53.4%
Hypertension
22.7%
Haemorrhage
22.4%
Pre-existing medical conditions
12.7%
Pregnancy related sepsis
10.6%
Acute collapse
6.3%
Anaesthetic related
2.4%
Abortion
4.9%
Causes of under-5 mortality in SA
Diarrhoeal Disease
22%
Neonatal causes
15%
Acute respiratory infection
14%
HIV contributes to at least half of child deaths in SA
60% of deaths in the Child PIP are associated with malnutrition
10% of children 1-9 yrs underweight*
20% of children aged 1-9yrs stunted*
CoMMiC Report 2011
*National Food consumption survey in CoMMiC Report 2011
Root course analysis
An effective tool for
systematically identifying
problems and analysing critical
incidents to generate
systems improvements
WHY! WHY? Why……………
Knowing what adverse events occur is
only the first step. Most adverse events
result from a complex series of
behaviours and failures in systems of
care. Investigation of the patterns of
adverse events requires unearthing the
latent conditions and systemic flaws
as well as the specific actions that
contributed to these outcomes.
Dr. G. Ross Baker & Dr. Peter Norton
RCA
1.It is inter-disciplinary, involving experts from the
frontline services;
2. Involves those who are the most familiar with the
situation;
3. Continually digs deeper by asking why, why, why at
each level of cause and effect;
4. Identifies changes that need to be made to systems;
and
5. Is as impartial as possible in order to make clear the
need to be aware of and sensitive to potential
conflicts of interest
Check for eligibility for RCA
Deliberate harm test
whether the actions were as intended, not whether the
outcome was as intended
Incapacity test
Was a staff member ill or intoxicated
Foresight test
Did the individual depart from agreed protocols or safe
procedures?
Substitution test
Would another individual coming from the same professional
group, possessing comparable qualifications and
experience, behave in the same way in similar
circumstances?
Cases that should not be
subjected to RCA
Events thought to be the result of a
criminal act
Purposefully unsafe acts (intended to
cause harm)
Acts related to substance abuse
Events involving suspected patient
abuse of any kind
RCA (+as part of clinical audits):
Success depends on
involvement of the attending
physician, consulting specialist
and other providers
RCA steps
Collect information
Causal factor charting
Root cause identification
Recommendations
Process
Gather information already
documented
Review health records
Flow chart/ timeline
Get additional information
Site visit
Interviews
Swiss cheese model
most accidents can be
traced to one or more of four
levels of failure
Organizational influences,
unsafe supervision,
preconditions for unsafe
acts, and
the unsafe acts
themselves.
Ishikawa diagrams
Measurements
Environment
Materials
Personnel
Methods
Equipment
Ishikawa diagrams
Measurements
Training
Lubricants
Microscopes
Inspections
Humidity
Temperature
Shifts
Alloys
Callibration
Environment
Personnel
Materials
Suppliers
Operators
Angle
Wear
Callibration
Callibration
Methods
Speed
Callibration
Equipment
But why?
Why are there so many maternal and child deaths associated with
HIV?
But why?
Assign the role of ‘devil’s advocate’ to someone in your tribe …
“Devil's advocate role seeks to engage others in an argumentative
discussion process. The purpose of such process is typically to test the
quality of the original argument.”
The responsibility of the Devil’s Advocate is to ask the question: ‘But …
So why?'
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Devil's_advocate
Identify themes/categories that the factors you have identified
can fit into
How do these themes/categories relate to each other?
Draw a large picture to show your thinking
Root cause summary
Causal factor # 1
Paths Through Root
Cause Map
Recommendations
Mary leaves the frying
chicken unattended.
• Personnel difficulty.
• Administrative/
management systems.
• Standards, policies or
administrative controls
(SPACs) less than
adequate (LTA).
• No SPACs.
• Implement a policy that hot oil
is never left unattended on the
stove.
• Determine whether policies
should be developed for other
types of hazards in the facility to
ensure they are not left
unattended.
• Modify the risk assessment
process or procedure
development process to address
requirements for personnel
attendance during process
operations.
Root cause summary
Causal factor # 2
Paths Through Root
Cause Map
Recommendations
Description:
Electric burner
element fails (shorts
out).
• Equipment difficulty.
• Equipment reliability
program problem.
• Equipment reliability
program design LTA.
• No program.
• Replace all burners on stove.
• Develop a preventive
maintenance strategy
to periodically replace the burner
elements.
• Consider alternative methods
for preparing chicken that may
involve fewer hazards, such as
baking the chicken or purchasing
the finished product from a
supplier.
Recommendations
List the recommendations
Write a report regarding the findings
Suggest some implementation strategies