ppt
advertisement

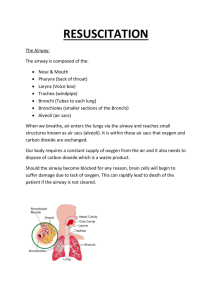
An Overview of Paediatric Anaesthesia Dr Anna Englin Paediatric Anaesthetist, MMC Overview Equipment/room set up Crises we see in kids Equipment Airway Breathing Circulation Drugs Environment/ exposure Anaesthesia checklist Airway Breathing Circulation Drugs Environment/ exposure Airway Infants and neonates have anatomical differences cf adults Different sized equipment Face masks Airways Lift tongue and epiglottis away from upper airway Different sizes: measure from centre of incisors to angle of jaw Nasopharyngeal airways LMA’s Don’t forget in a difficult intubation! Less reliable than in adults Intubation laryngoscopes ETT size ETT size = 4 +age/4 Cuffed vs uncuffed Equipment Airway Breathing Circulation Drugs Environment/ exposure Breathing T piece vs closed circuit Paediatric breathing circuit Equipment Airway Breathing Circulation Drugs Environment/ exposure Circulation ECG sometimes not used, mainly useful to detect bradycardia Blood pressure lower Arterial line setup is different Equipment Airway Breathing Circulation Drugs Environment/ exposure Exposure Neonates especially prone to hypothermia Prevention of hypothermia – Operating theatre – Patient covering esp head – Warming blankets/ overhead heaters – Fluid warmers – Monitoring Paediatric crises Laryngospasm •Common and can be scary! •Risk factors •Active or recent URTI •Reactive airways •Airway surgery •Stimulation during light anaesthesia Features Treatment of laryngospasm CPAP with 100%O2 Propofol Lignocaine: topical or IV 2mg/kg Sux: 2mg/kg IV or 4mg/kg IM Bradycardia Risk factors – – – – – Cardiac disease Hypoxia Drugs esp sux CVP insertion Reflex eg oculo-cardiac reflex Treatment – Treat cause – Atropine: 20mcg/kg IV or IM Chest compressions if persistent The end NB: no children were harmed in the making of this talk