Female genital system
Dr. Amitabha Basu MD
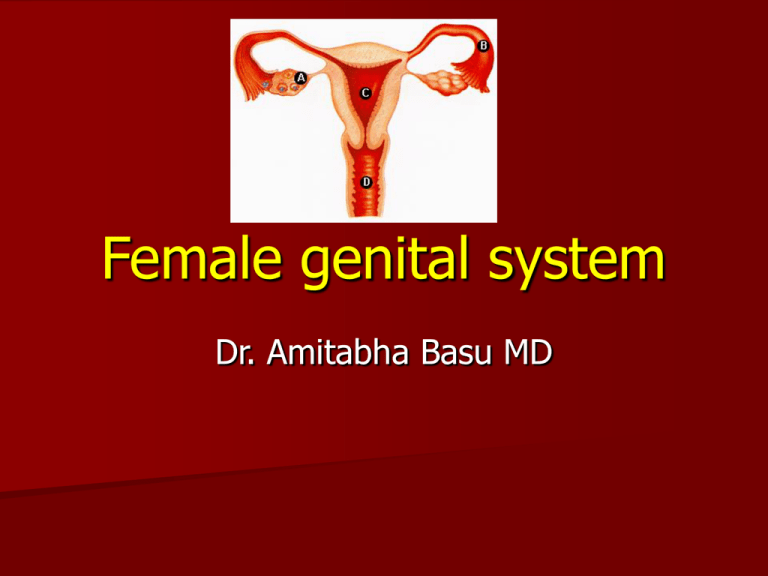
Topic of this Lecture
A. Disease of Cervix, Vagina, Vulva
B. Disease of endometrium
C. Disease of uterus
D. Disease of fallopian tube
Disease of Cervix
1. T-zone
2. Cervicitis
3. CIN
4. Malignancy of cervix
Normal cervix
Histology: T zone
T zone : Junction
between squamous and
columnar epithelium.
Most malignancy begin
here.
Cervicitis
Types:
Etiology
Morphology
Clinical
A.Acute
B.Chronic Cervicitis
Etiology
1. Mostly non specific Cervicitis
2. Specific form:
a. C. trachomatis.
b. Trichomonous and Candida infection.
Chronic Cervicitis;
Morphological features
1. Chronic inflammatory cells
2. Nabothian cyst.
3. Squamous metaplasia
C. Trachomatis Cervicitis
It produce follicular Cervicitis (
Plenty lymphocytes form FOLLICLES)
Clinical : Cervicitis
It can produce temporary Female
infertility.
It provide a fertile soil for malignancy.
Next topic CIN : Types
CIN = SIL
CIN = Cervical intraepithelial
neoplasia
Or,
SIN = Squamous intraepithelial
neoplasia
CIN [ cervical intraepithelial
neoplasia]
Etiology : Humane papilloma virus (
16,18), or inflammation.
CIN III = Carcinoma in situ = severe
dysplasia = irreversible : progress to
invasive squamous cell carcinoma
CIN I = Flat Condyloma; will show
koilocytic change
CIN I : lower 1/3 rd of the epithelium is Dysplastic
Koilocyte : Evidence of HPV
infections
HIGH POWER
CIN II : lower 2/3 rd is dysplastic
Carcinoma In Situ = CIN III : Entire
epithelium is involved.
Carcinoma in situ: intact basement
membrane
Screening of dysplasia : PAP smear of the exfoliated cell
from the cervix: Most important cause of reduced mortality
in west.
Time for carcinoma of cervix
Etiopathogenesis- CA cervix
Etiology : HPV type 16,18
Age : Peak incidence 45 years
High risk group:1. Multiple sex partner
2. Early age of 1st intercourse.
3. Persistent infection with HIGH RISK HPV
infection
4. A male partner with multiple previous sex
partner.
Cervical carcinoma and HPV
Squamous cell carcinoma MOST
COMMON by this infection.
Viral Oncogenes of HPV are
– E6 (bind to TP53) and E7 ( bind to RB)
– Cause inactivation of these two tumor
suppressor genes.
Cervical carcinoma
1. Squamous cell carcinoma [ HPV 16,
18]- MOST COMMON
2. Clear cell carcinoma [ exposure to
diethylstilbestrol (DES) ].
3. Adenocarcinoma ( RARE)
Rare thing : Think rarely
Squamous cells carcinoma : gross
Exophytic growth
Squamous cells carcinoma of cervix
Clear cell carcinoma microscopy:
Recall etiology
Exposure to diethylstilbestrol (DES)
Clinical features of squamous cell
carcinoma cervix
1. Dyspareunia.
2. Post coital bleeding.
3. Leucorrhoea.
Diagnosis:
Papanicolaou smear
Biopsy (cone)
Colposcopy.
Staging of carcinoma cervix with prognosis
Stage 0.
Stage I.
Carcinoma
confined to the
cervix
Carcinoma in situ (CIN III)
1A. Micro invasive
carcinoma (Stromal
invasion no greater than 3
mm)
1B. Histologically invasive
carcinoma > 3 mm
invasion.
Micro invasive carcinoma
Stage II. Carcinoma involves the vagina (upper
2/3rd).
Stage
III.
Stage
IV.
Carcinoma has extended onto pelvic
wall and beyond it.
The tumor involves entire vagina.
Involve the mucosa of the bladder or
rectum.
Present with metastatic dissemination.
Prognosis [ 5 year survival]
1. Stage 0 ( ca-in situ) = 100%
2. Stage 1( tumor confined to cervix)=
90%
3. Stage 2 = 82%
4. Stage 3 = 35%
5. Stage 4 ( tumor with distant
metastasis)=10%
Disease of vagina
A.
B.
Sarcoma botroid
Effect of diethylstilbestrol (DES)
during pregnancy.
A. Vaginal adenosis
B. Clear cell carcinoma of vagina
Sarcoma botroid
Age : 0-5 years
Type of malignancy : Embryonal
rhabdomyosarcoma
“Rare form” of Primary vaginal
malignancy
Clear cell carcinoma of vagina
Common in the young girls whose
mother took diethylstilbestrol (DES)
during pregnancy.
Now vulval diseases
Vulval disease
1.
Extra mammary pagets disease
– Gross: crushed rash
–
2.
Micro: intraepithelial malignant cells
and intraepithelial spread.
Condyloma acuminatum
– Wart like, HPV 6, 11
– Micro: koilocytic change,
hyperkeratois.
Vulval disease
Lichen atrophicus
Thinning of the
epidermis , dermal
fibrosis, scant
lymphocytes.
Pre-cancerous
lesion.
Disease of the uterus: Relax for a
few minutes
Disease of uterus
1.
2.
3.
4.
Endometritis
Adenomyosis
Endometriosis
Endometrial
Hyperplasia.
Endometritis
Acute
Bacterial infection after
delivery (parturition).
Miscarriage.
Chronic
Etiology: Tuberculosis,
Neutrophils cells in
the endometrial
biopsy
Caseating granuloma
and or plasma cells
With IUD, PID.
Clinical Feature: infertility and
dysmenorrhea
Adenomyosis
Endometrial tissue deep in
the myometrium of uterus.
Gross : enlargement of
uterus
Clinical :
– irregular profuse menstruation
– Dysmenorrhea , menorrhagia
Adenomyosis
Normal Endomyometrium
reaction
Adenomyosis:
Uterus enlarged
Adenomyosis : Enlarged Uterus
Clinical d/d :
Fibroid
C/F : irregular
profuse
menstruation
(Dysmenorrhea ,
menorrhagia )
Endometriosis
A. Location
B. Pathogenesis
C. Pathophysiology
D. Chocolate cyst (
endometriosis of Ovary)
E. Clinical Features
Endometriosis
Endometrial tissue ( BOTH GLAND
AND STROMA ) in any place out side
the uterus.
Ovary or other tissue
Endometriosis: location
And : Laparoscopic Scar ( during
caesarian section).
Endometriosis: pathogenesis
1. Metapalstic
Differentiation of
Celomic Epithelium.
2.Lymphatic
dissemination.
3. Regurgitation of
endometrial fluid to
ovary.
4. Dissemination through
pelvic vein.
Endometriosis: Pathophysiology
In this case Endometrial
glands respond to the
cyclical change of
Hormone.
So, it bleeds along with
menstruation.
And produce
hemorrhage at the site
of endometriosis.
Uterus
Ovary
Gross
Red – blue nodule at the site
of implant.
Ovary:
– Produce chocolate cyst
(hemosiderin)
– In ovary it occurs due to
regurgitation of
endometrial fluid in
fallopian tube.
Chocolate cyst of the ovary = endometriosis
of ovary: Regurgitation of endometrial
fluid to ovary.
Why it is called chocolate cysts ?
It is the color of altered blood in the
cyst.
This color is due to Hemosiderin
pigments.
Clinical Features: Endometriosis
Generalized pelvic pain
Dysmenorrhea
Dyspareunia
Infertility
Endometrial Hyperplasia
Endometrial Hyperplasia
1. Etiology
2. Types
3. Clinical Features
Endometrial Hyperplasia
Etiology: Prolonged , elevated level
of Estrogen.
Clinical Examples :
1. Polycystic Ovary ( stein –Leventhal
syndrome).
2. Functional Granulosa Theca cell Tumor
Types
1. Simple cystic Hyperplasia
2. Complex Hyperplasia
3. Atypical Hyperplasia
Simple cystic Hyperplasia: cystically dilated
glands and adequate compact stroma
Complex Hyperplasia; more glands
less stroma
Atypical Hyperplasia – Atypical glands: 20 25% risk of progression to adenocarcinoma.
Clinical features
Irregular Bleeding
Menometrorrhagia
Tumor of the Uterus
Tumors of the Uterus
1. Leiomyoma (fibroids)
2. Malignant mixed möllerian tumor
3. Endometrial adenocarcinoma
We shall discuss about1. Leiomyoma
2. Endometrial carcinoma
1. Etiology
2. Types
3. Complications
Leiomyoma( Fibroid)
Estrogen , OCP stimulate their
growth.
Increases in size as the pregnancy
progress ( if present in a pregnant
lady).
Leiomyoma- types
•Sub Mucosal
•Intra mural
•Sub serosal
Leiomyoma ;
A benign
tumor of the
smooth
muscles
Leiomyoma complication
1. Bleeding
2. Infertility
3. Abortion ( in a pregnant
lady).
4. Pain : due to red
degeneration( Ischemic
necrosis) within a large
Leiomyoma.
Leiomyosarcoma
Malignant tumor of the smooth muscle.
often have very large bizarre giant cells
along with the spindle cells.
Prognosis = Bad
Recurrence after
removal is common.
Metastasize widely.
Endometrial carcinoma
Etiology :
1. Atypical endometrial
Hyperplasia.
2. Prolonged estrogenic
stimulation.
1. Tumor of ovary
2. ERT
Risk factors
1. Obesity
2. Diabetes
3. Hypertension
4. Infertility
5. Lynch syndrome: colon,
endometrial and ovarian
cancer
C/F : Abnormal excessive
Bleeding
Age : 55-65 years
Morphology and Clinical
Morphology:
– Gross: early case : no significant change
in size of uterus.
– Later: invasion occur and produce a
polypoid mass.
– Micro: Endometroid adenocarcinoma
Clinical : Post menopausal women with
irregular Bleeding.
Red Flag sign
Fallopian tube
A. Inflammation of the Tube ( may be
associated with pelvic inflammatory
disease).
a)
b)
c)
d)
Chlamydia
Neisseria gonorrheae
Streptococci ( postpartum period)
Tuberculosis
B. Ectopic Pregnancy
Gross: Bilateral tuboovarian abscess .
(asymmetric Involvement)
Micro: Acute salpingitis by Neisseria
gonorrheae.
Salpingitis : clinical Features
1. Fever
2. Lower abdominal pain
3. Pelvic masses ( if tube contain
exudates, and inflammatory debris,
even fibrosis)
Tubal Ectopic Pregnancy : 1 in
500 pregnancies
Tubal pregnancy
Risk factors
Pelvic
inflammatory
disease (PID
Progesteronebearing IUD's.
Micro: Tubal Pregnancy
Villi
Clinical
Vaginal spotting
Mild Lower abdominal pain
Complication of Tubal pregnancy
Rupture and hemoperitoneum
Hemorrhagic shock.
It is an absolute emergency
requiring immediate surgical
correction
Thank you!









